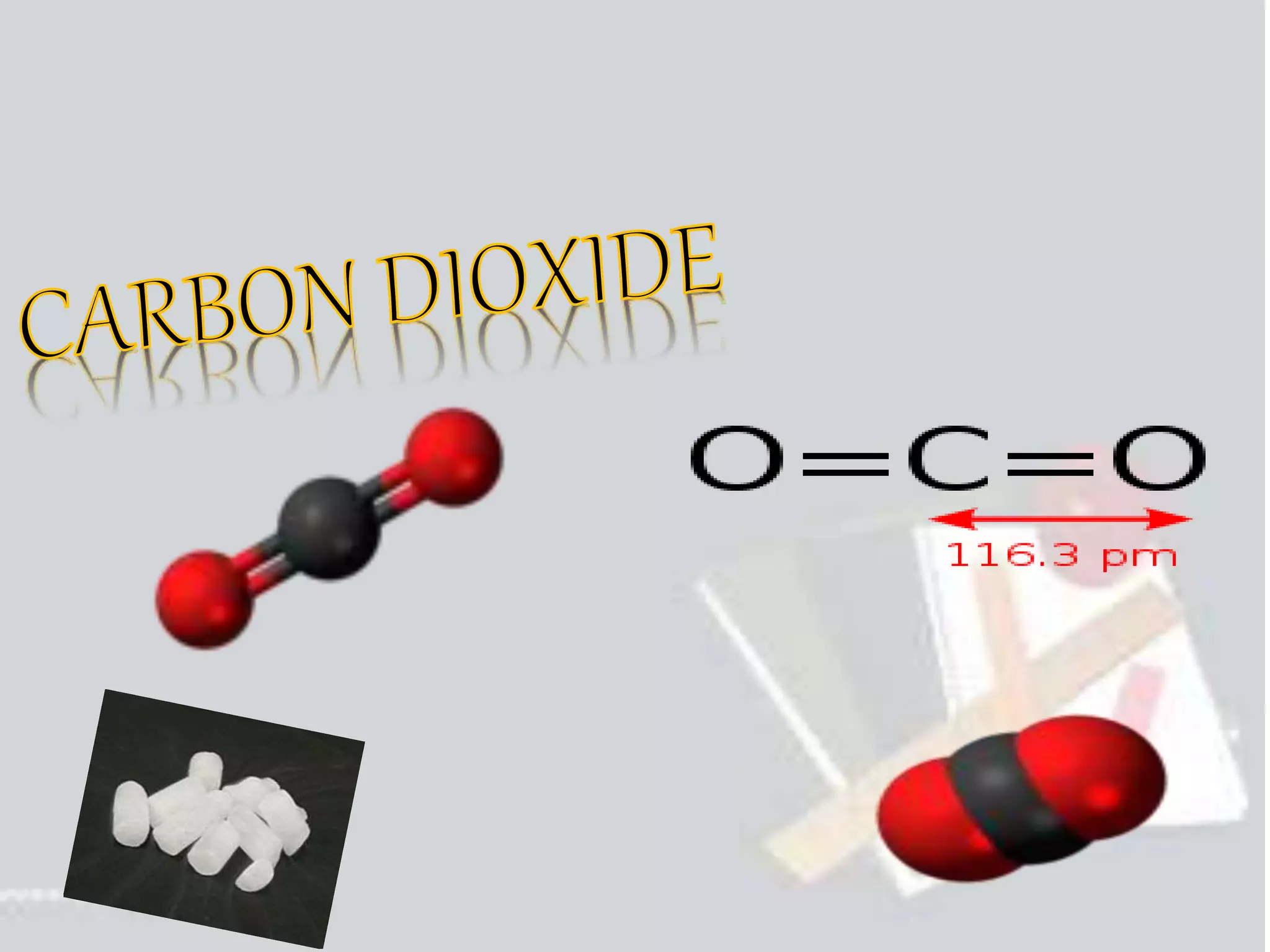
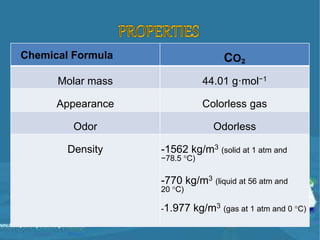
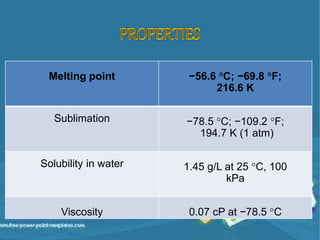
Carbon dioxide is a colorless, odorless gas that is vital for plant life. It comprises 0.039% of the atmosphere and is produced by combustion of fossil fuels and plant matter. Carbon dioxide has various industrial uses including in food production as a leavening agent and additive, in beverages as a carbonation agent, in welding as a shielding gas, and as a refrigerant and fire extinguishing agent. It is also used in oil recovery operations by increasing oil flow from wells.