The document discusses Drupal's approach to maintaining site security and addressing common web vulnerabilities. It explains how Drupal prevents issues like cross-site scripting, SQL injection, file execution, insecure direct object references, cross-site request forgery, information leakage, broken authentication, insecure data storage, unencrypted communications, and unauthorized URL access through features like input filtering, access control validation, encryption, and its database abstraction layer. It also provides tips for writing secure Drupal code.





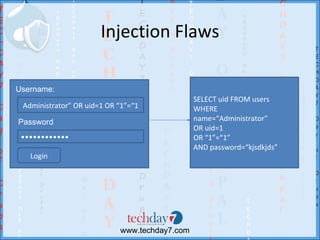



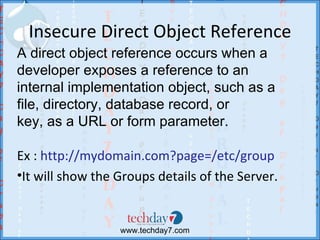










![How Drupal prevents...
• As a PHP-based system, Drupal can use
Apache’s widely-trusted SSL support.
• If only part of the site is behind SSL,
administrators can install modules to make
certain URLs available only through a secure
connection.
Ex: $conf['https'] = TRUE need to be in settings.php
www.techday7.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupalsecurity-120424045506-phpapp01/85/Drupal-security-21-320.jpg)


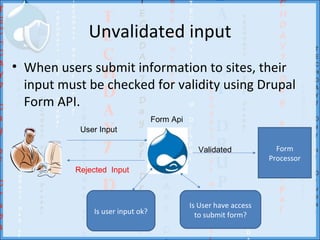

![Use the database abstraction layer to avoid SQL injection attacks
For example, never concatenate data directly into SQL queries, like this:
<?php db_query('SELECT foo FROM {table} t WHERE t.name = '. $_GET['user']); ?
>
<?php db_query("SELECT foo FROM {table} t WHERE t.name = '%s' ",
$_GET['user']); ?>
Use db_rewrite_sql to respect node access restrictions.
<?php
$result = db_query(db_rewrite_sql("SELECT n.nid, n.title FROM {node} n"));
?>
www.techday7.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/drupalsecurity-120424045506-phpapp01/85/Drupal-security-26-320.jpg)
