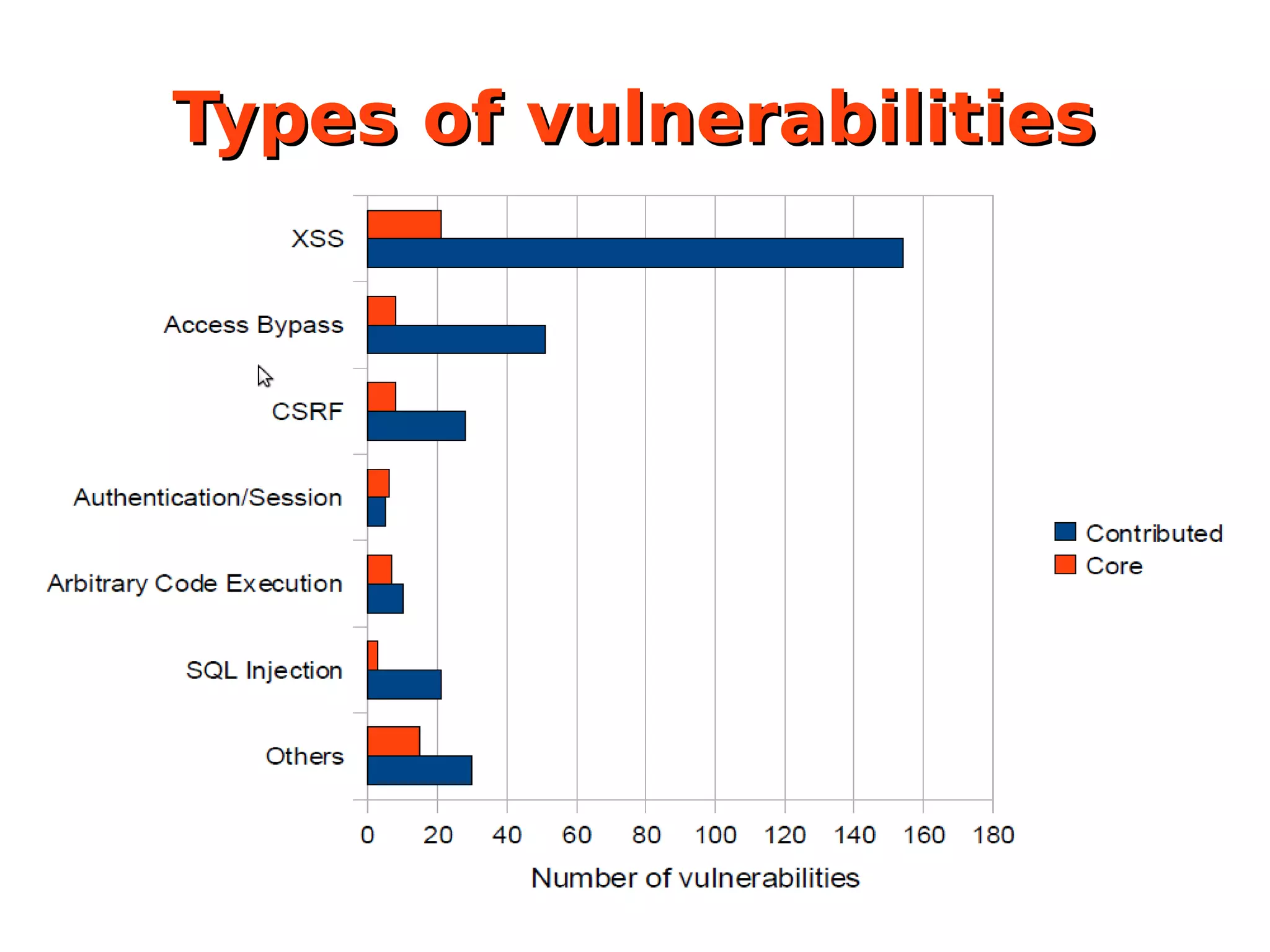
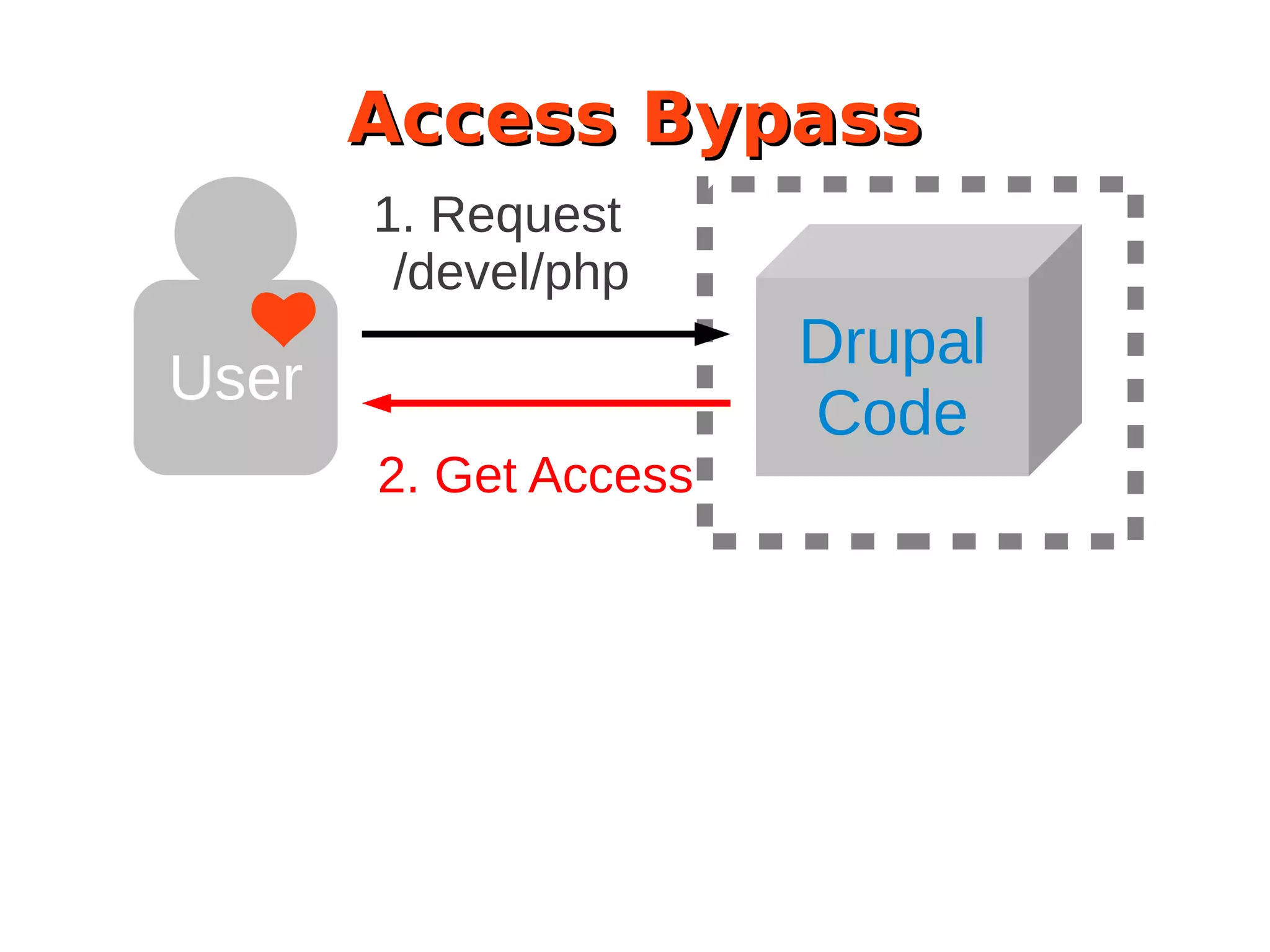
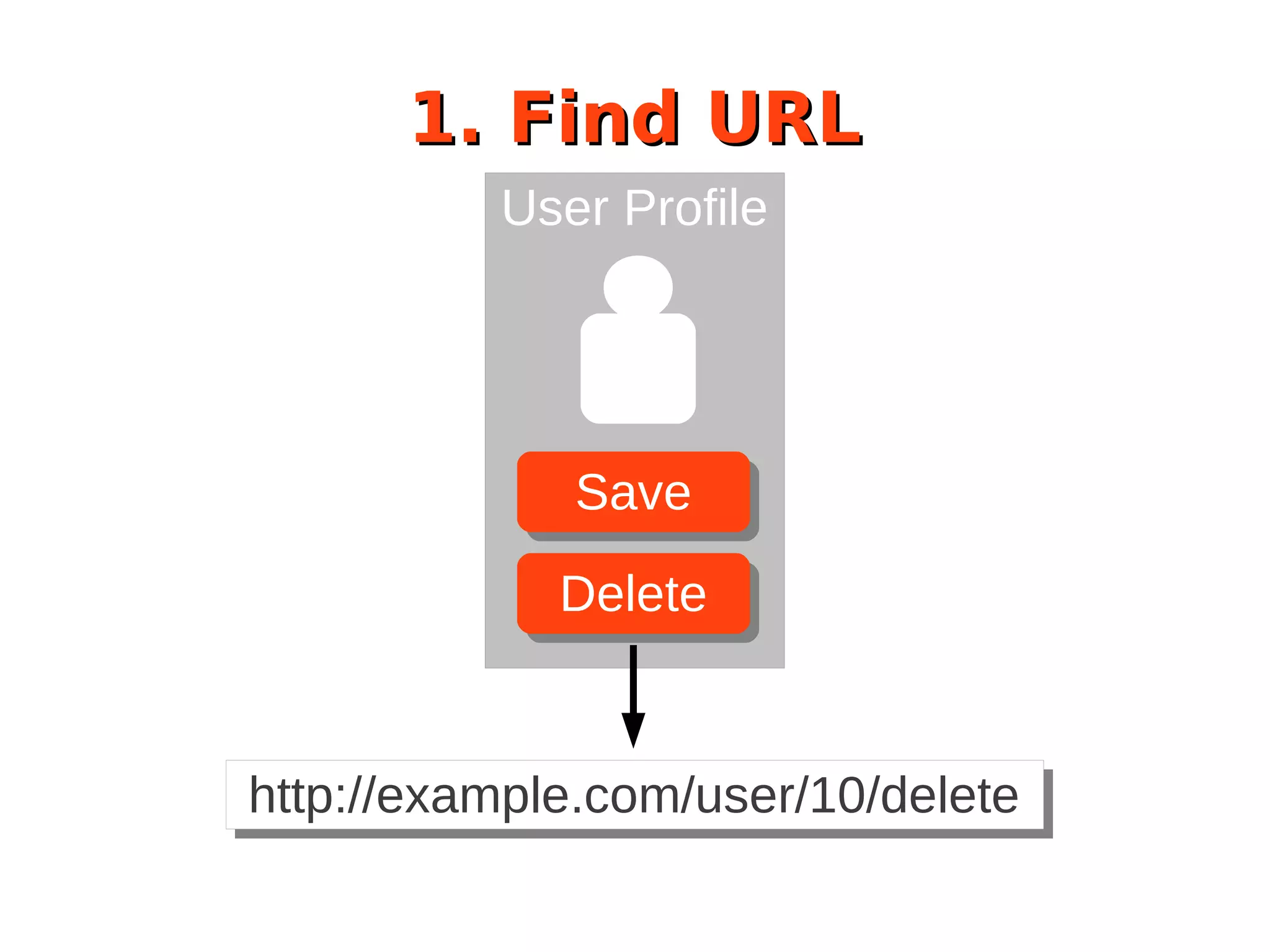
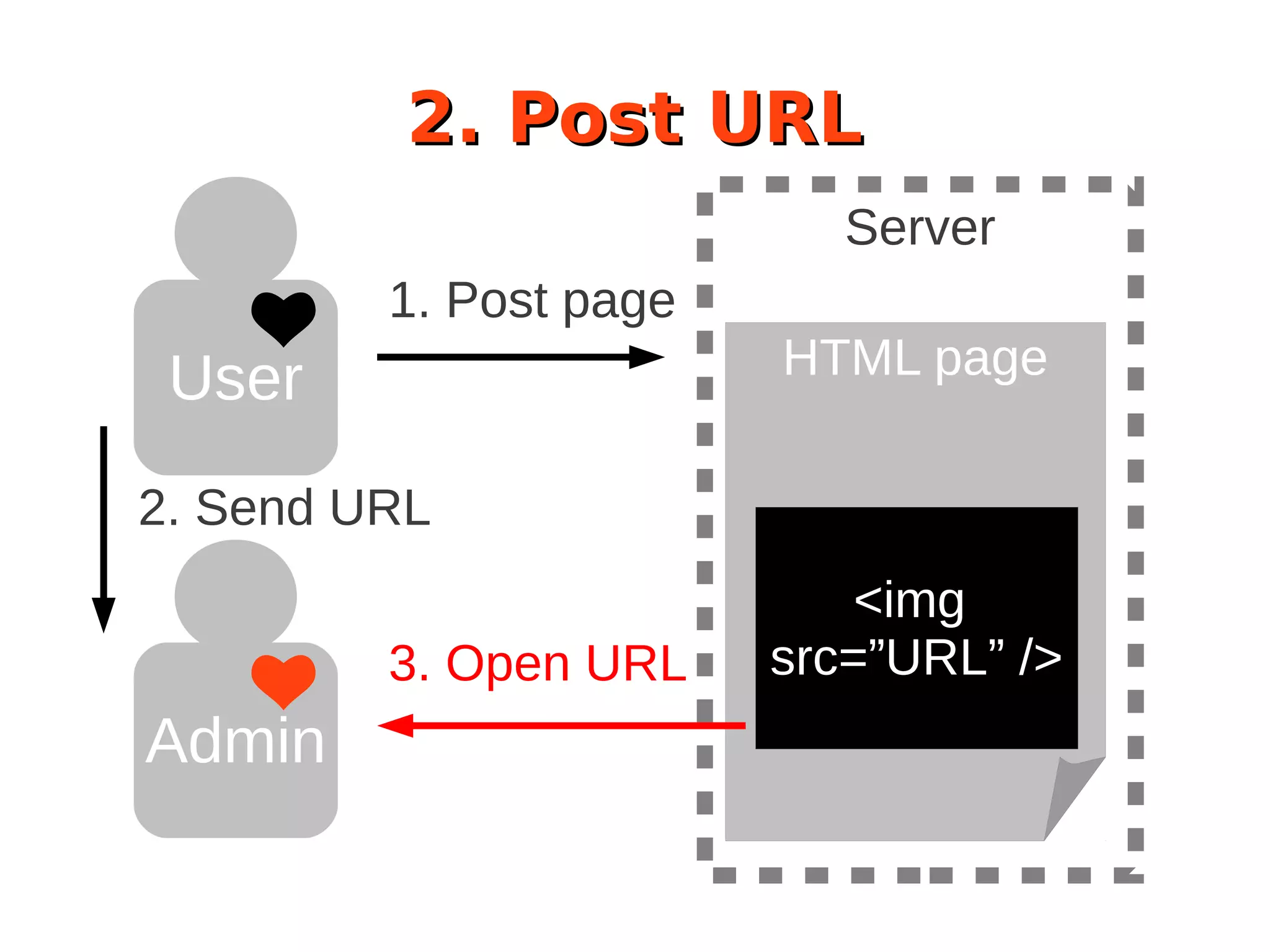
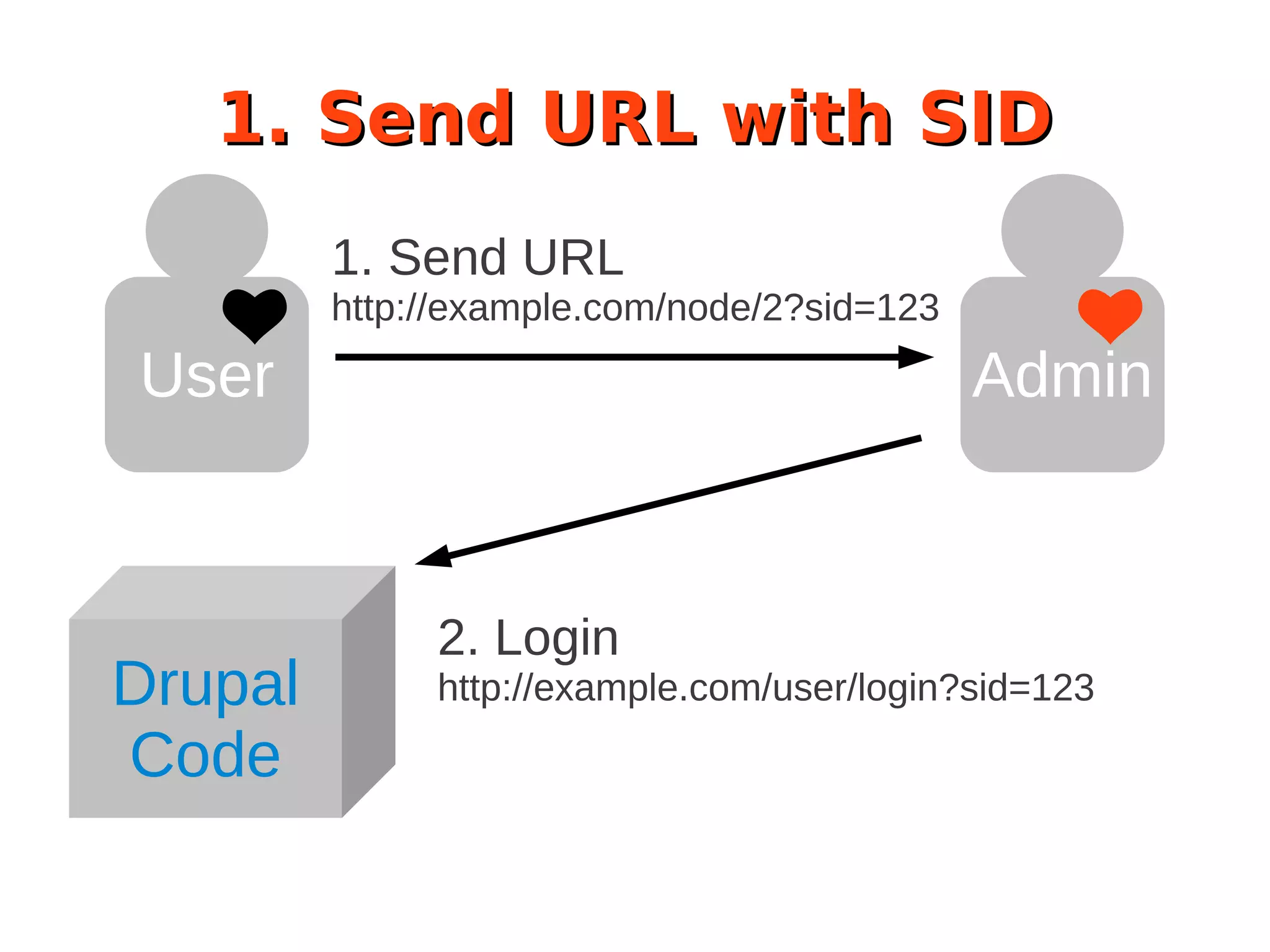
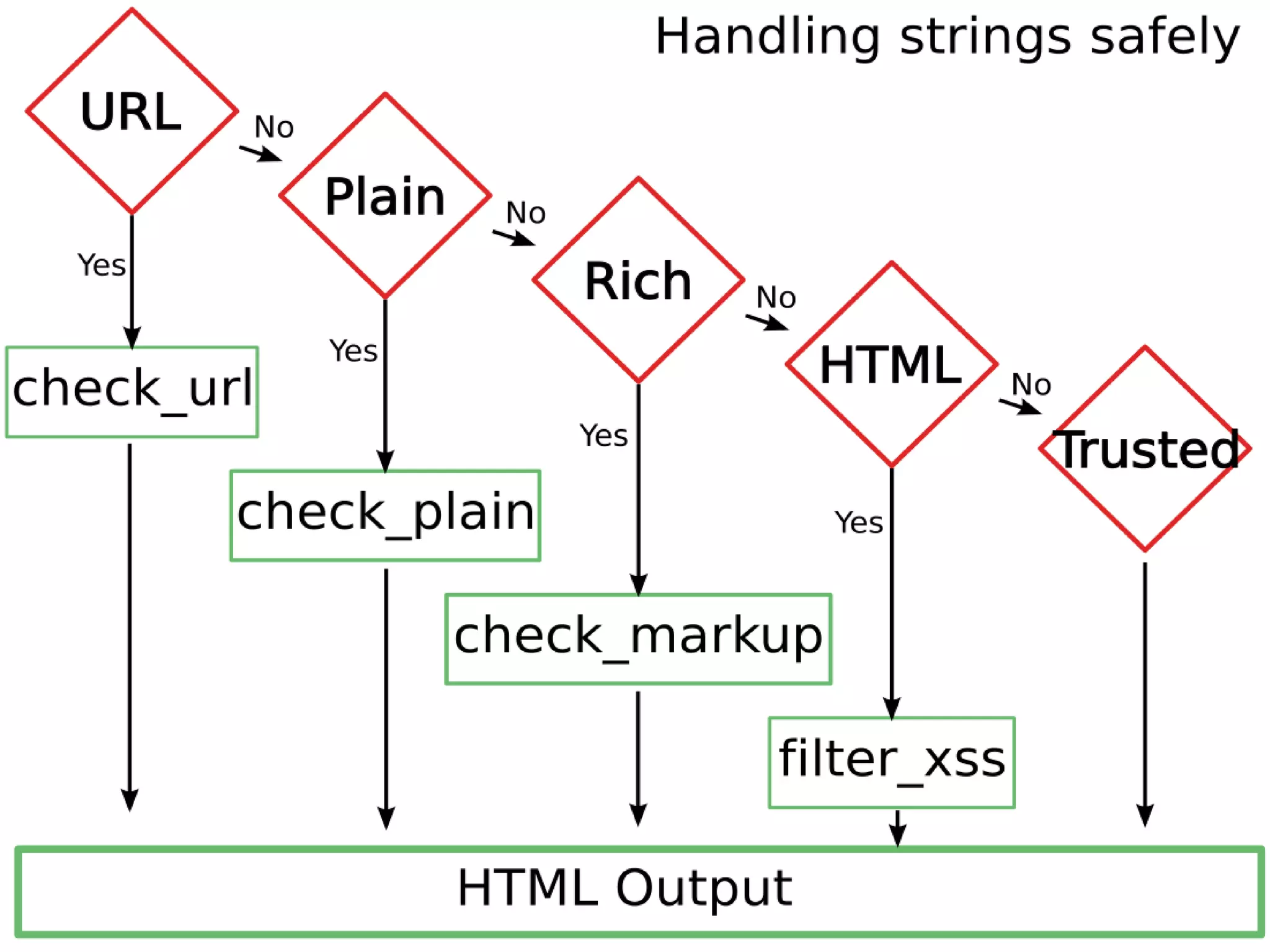
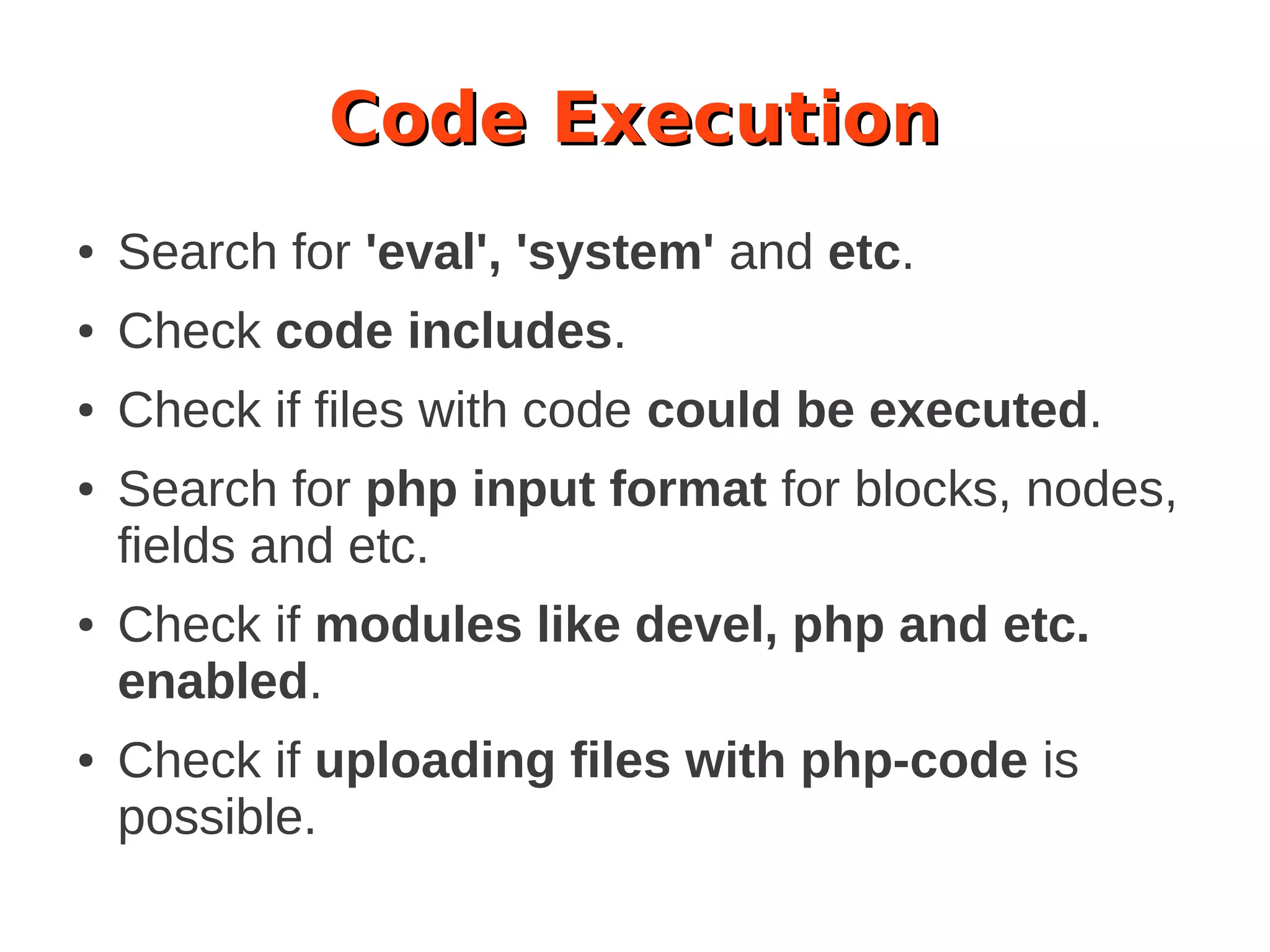
The document discusses the security of Drupal sites, addressing vulnerabilities such as XSS, CSRF, and session fixation, and emphasizes the importance of secure coding practices and regular updates. It outlines how to identify these security issues, report vulnerabilities, and the responsibilities of the Drupal security team in resolving them. Additionally, it provides resources for both securing Drupal sites and writing secure code.