1. This document outlines the teaching and learning plan for a Calculus 2 course, including course description, intended learning outcomes at the institute, program, and course level, as well as content, activities, and assessments for each topic covered over the semester.
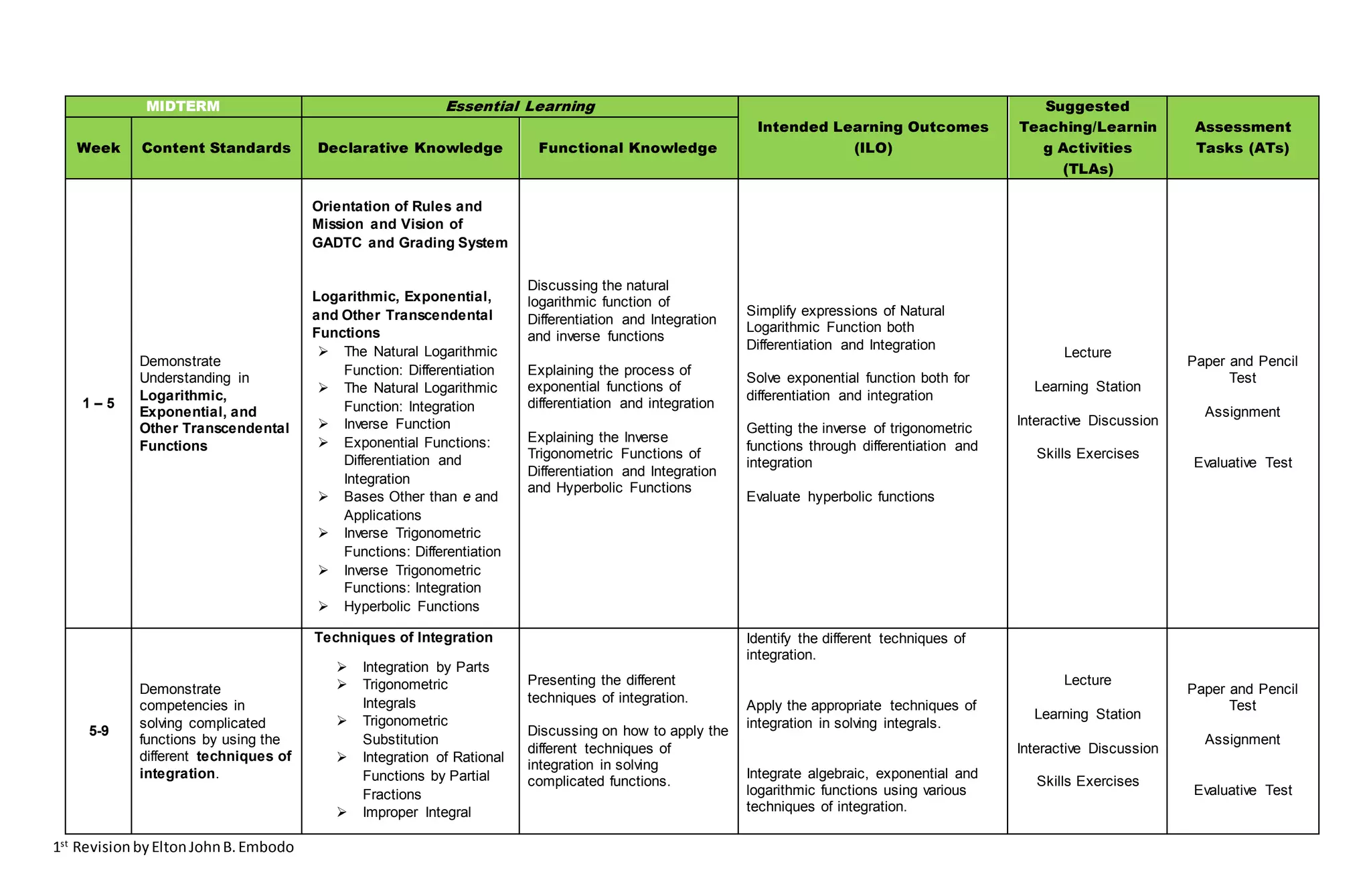
2. The course aims to further develop students' understanding of differential and integral calculus, covering integration methods and techniques, indeterminate forms, and improper integrals of various functions.
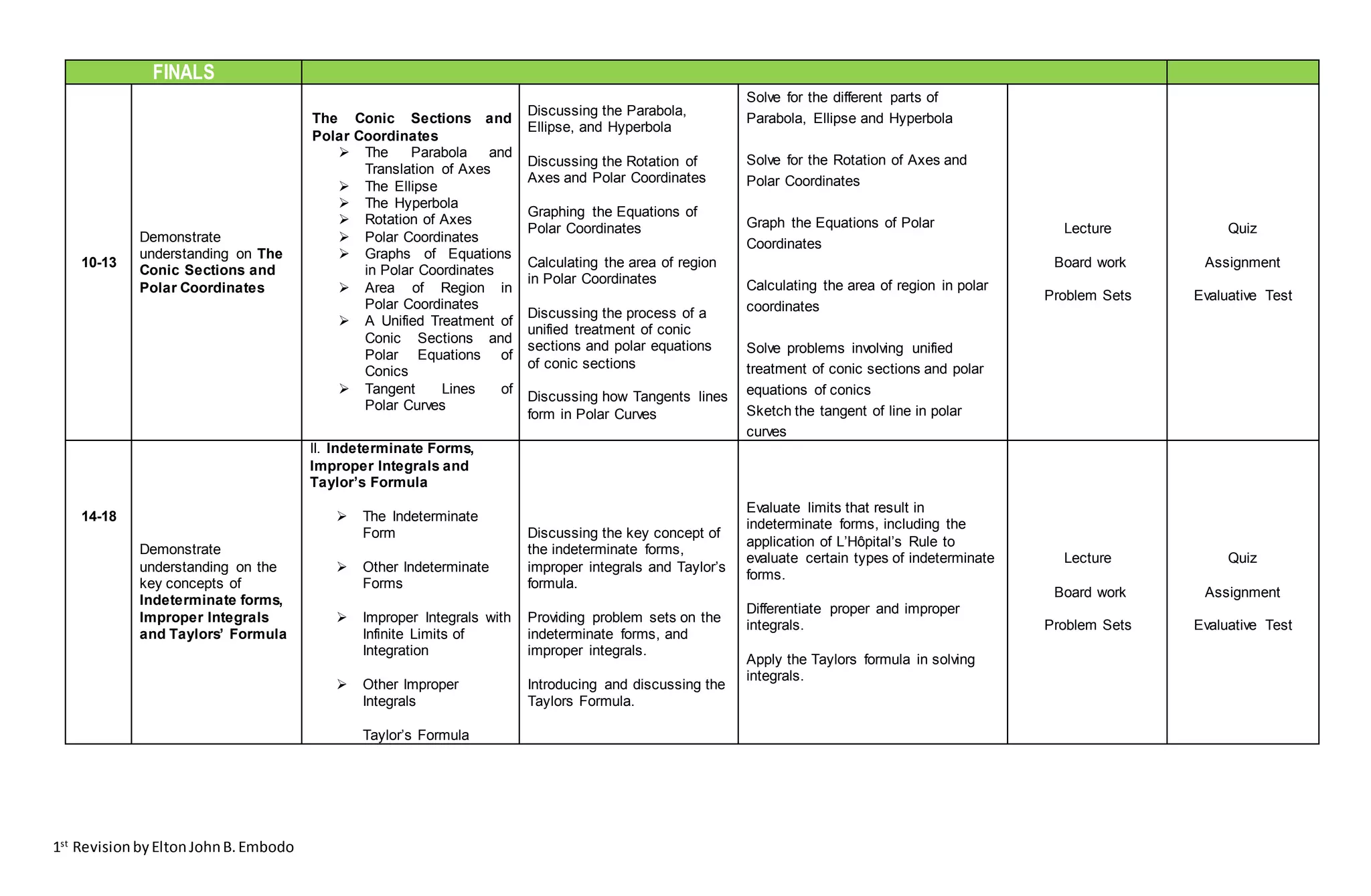
3. Over the semester, students will learn about logarithmic, exponential, and other transcendental functions; various integration techniques; conic sections and polar coordinates; indeterminate forms, improper integrals; and Taylor's formula through lectures, exercises, assignments and evaluations.