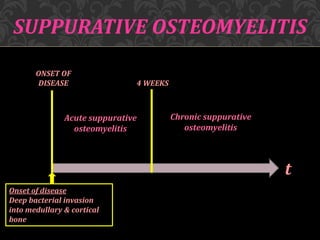
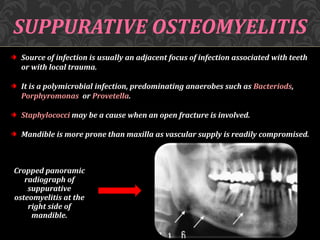
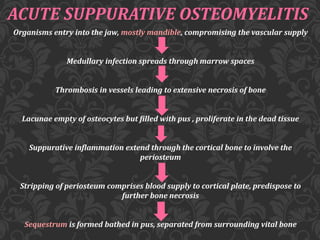
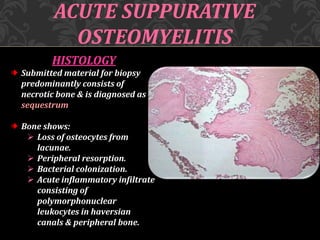
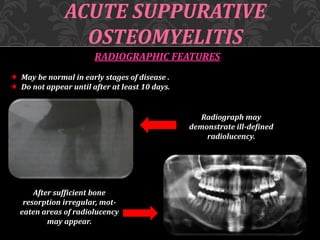
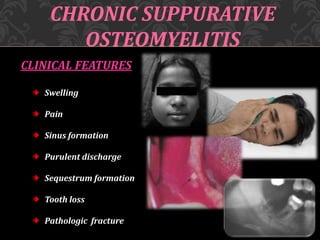
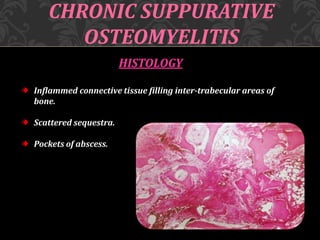
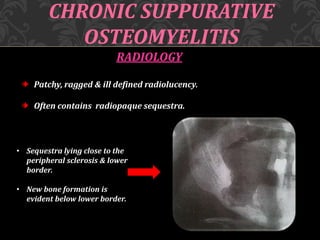
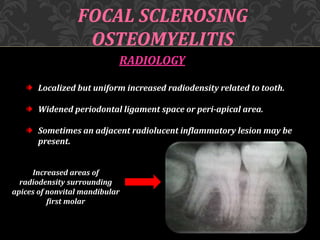
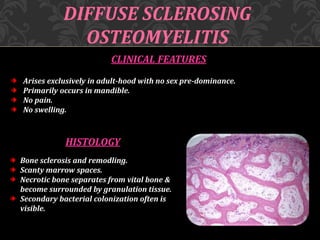
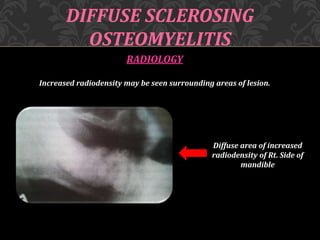
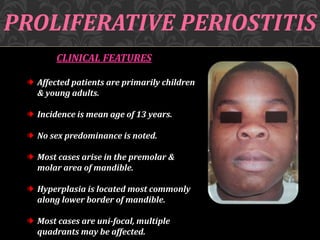
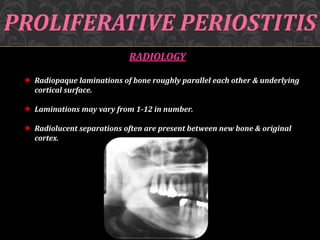
This document discusses osteomyelitis, including its pathogenesis and management. It begins by defining osteomyelitis as an inflammatory process in bone that extends away from the initial site of involvement. It then covers predisposing local and systemic factors, pathogenesis, and the main types - suppurative, focal sclerosing, diffuse sclerosing, and proliferative perositis. For each type, it discusses pathogenesis, clinical features, histology, radiology, and management. The document provides detailed information on acute and chronic suppurative osteomyelitis and emphasizes the importance of thorough debridement and appropriate antibiotic treatment.