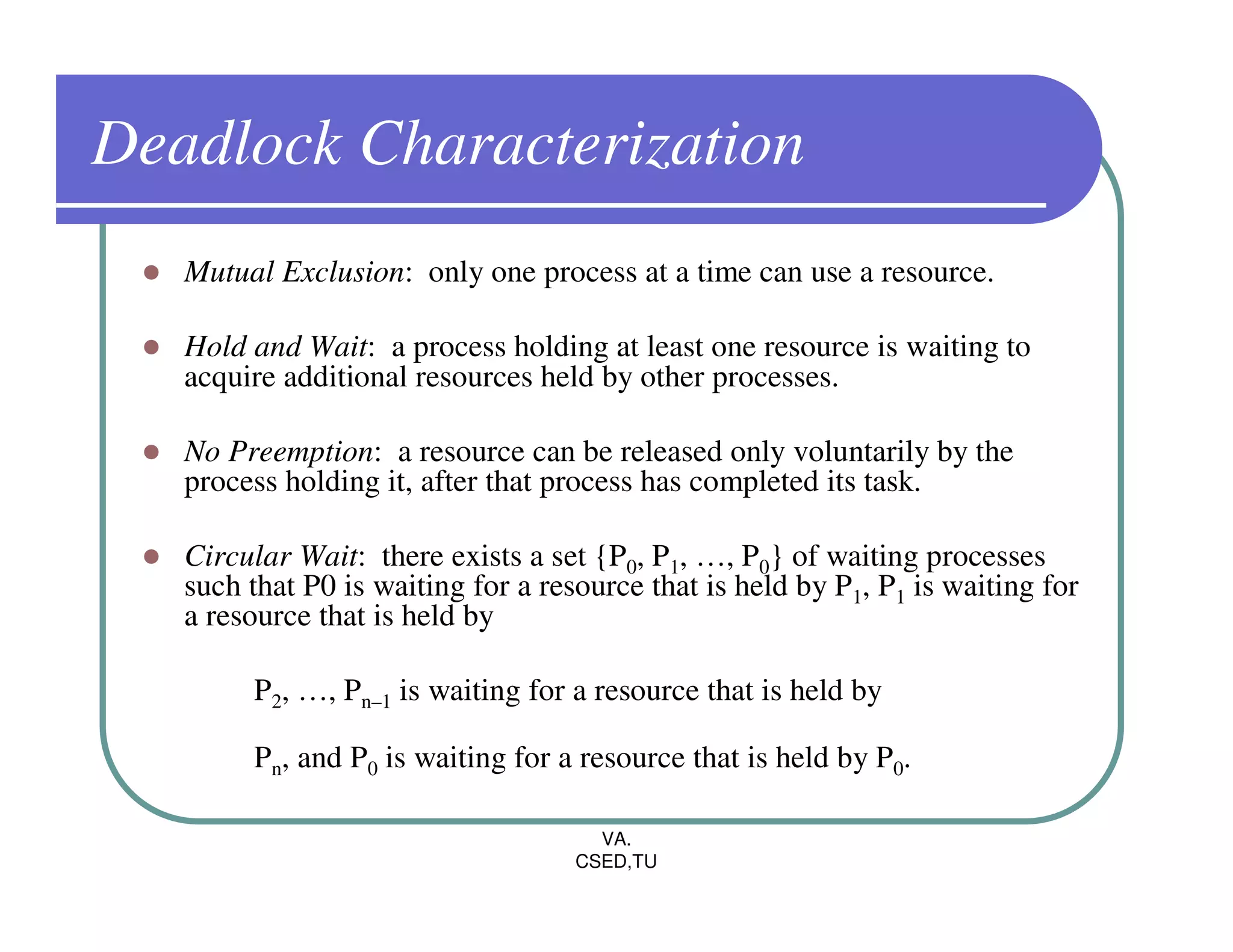
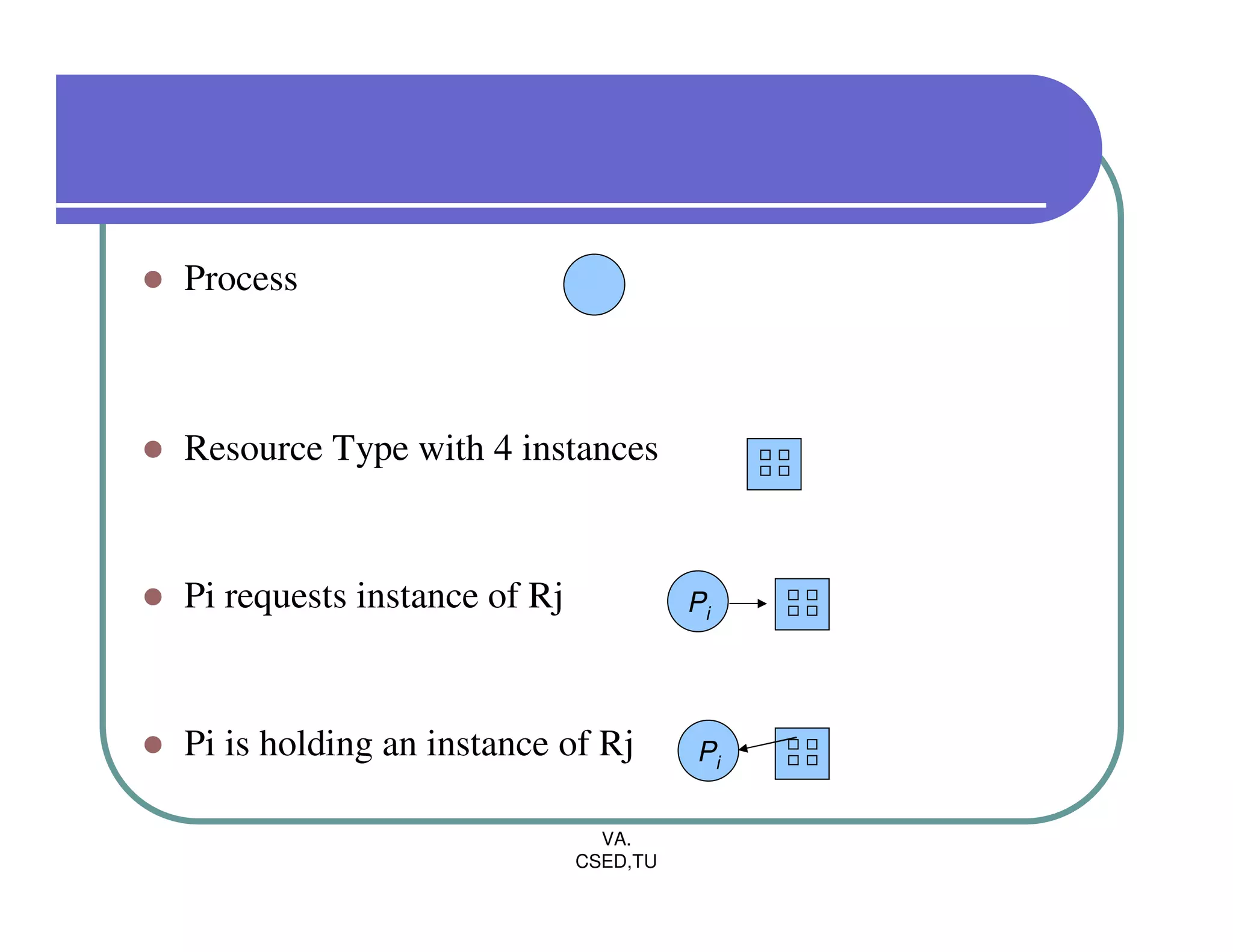
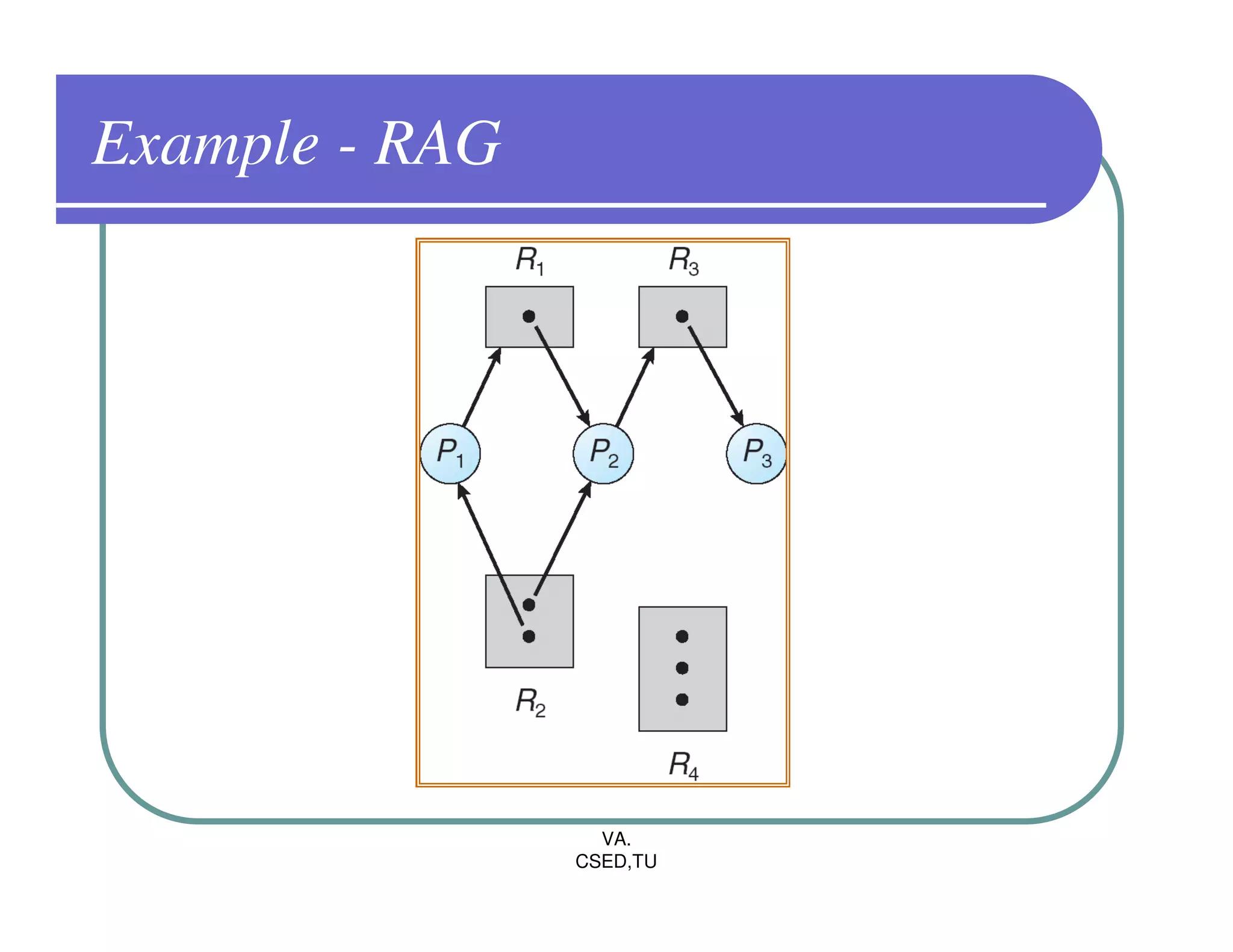
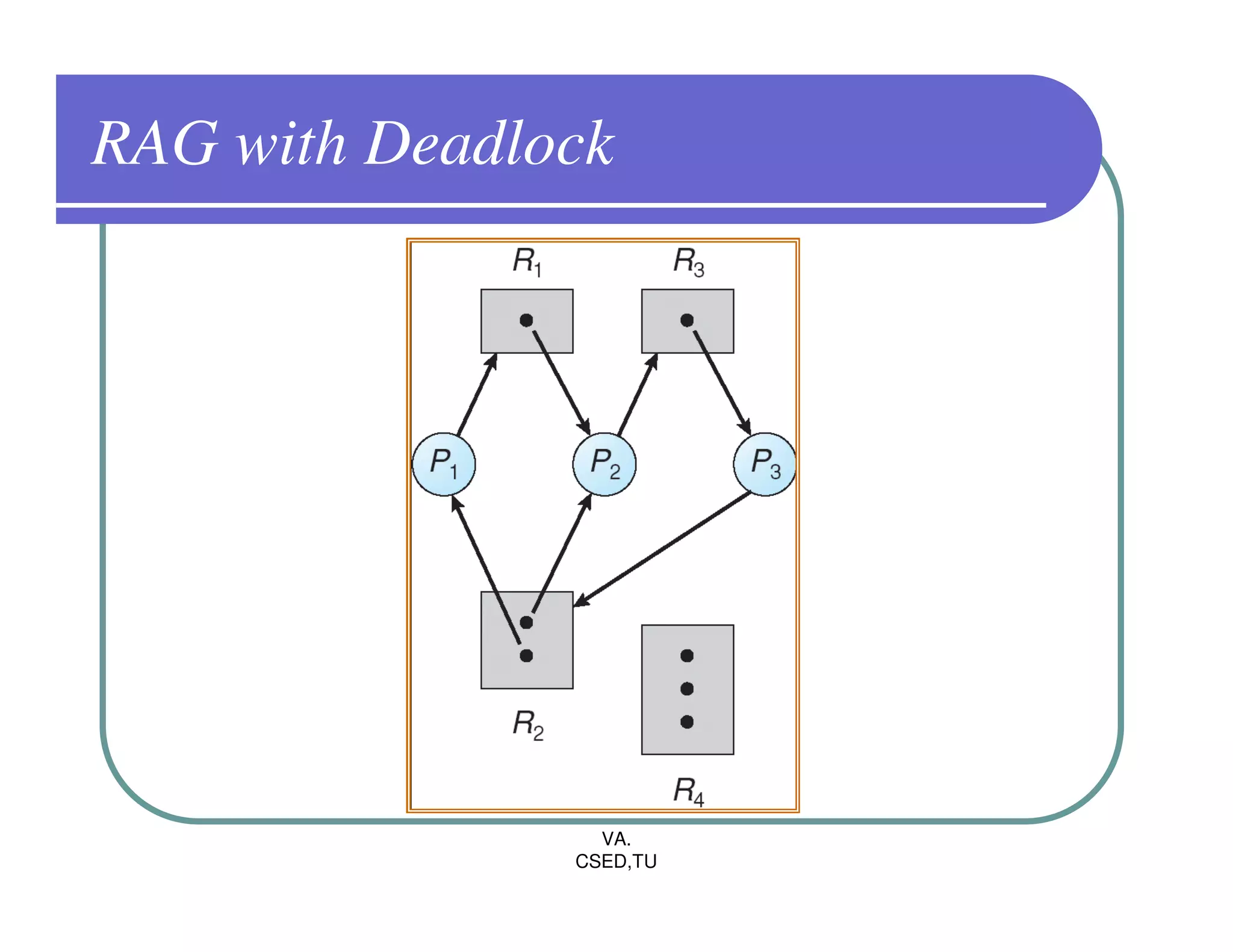
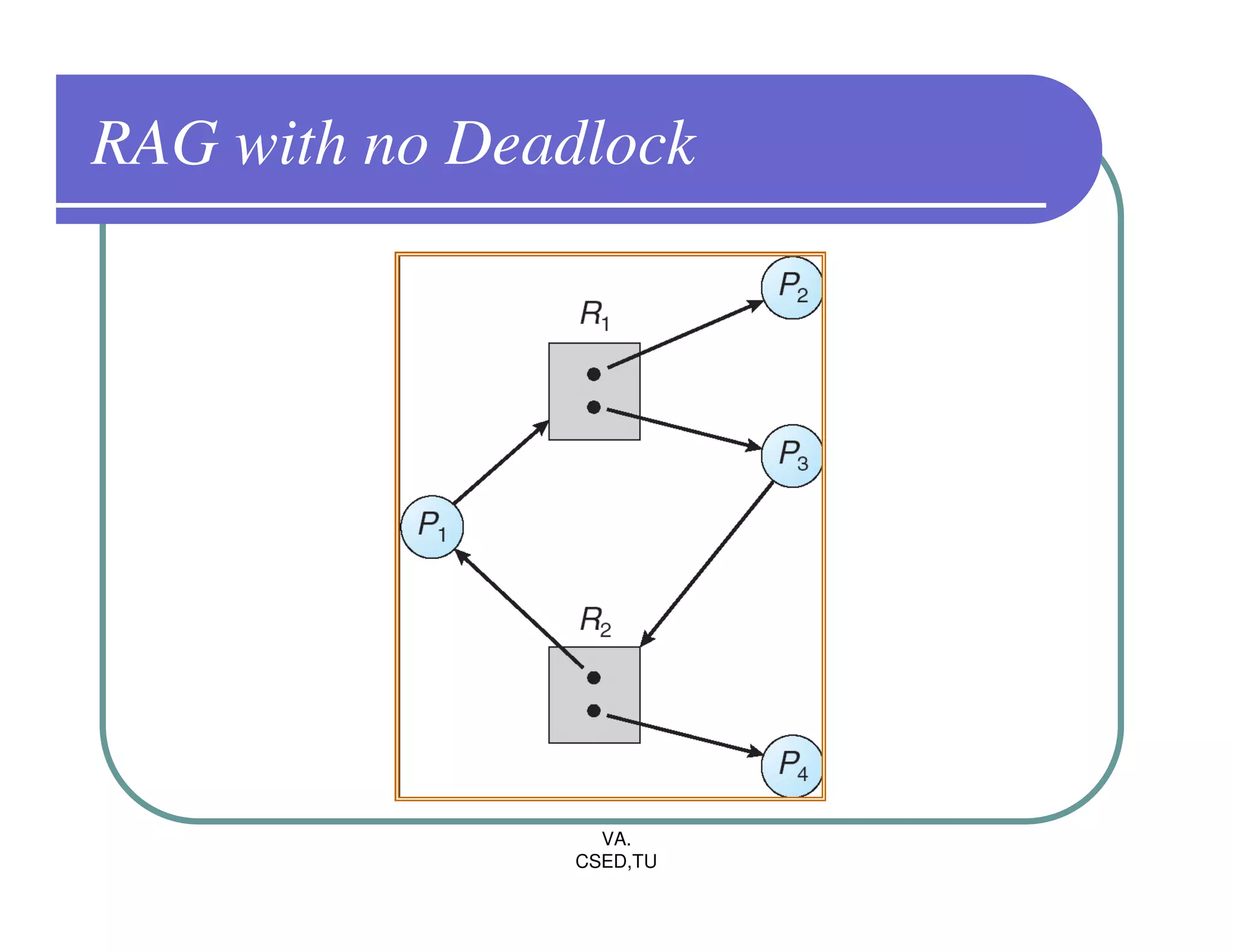
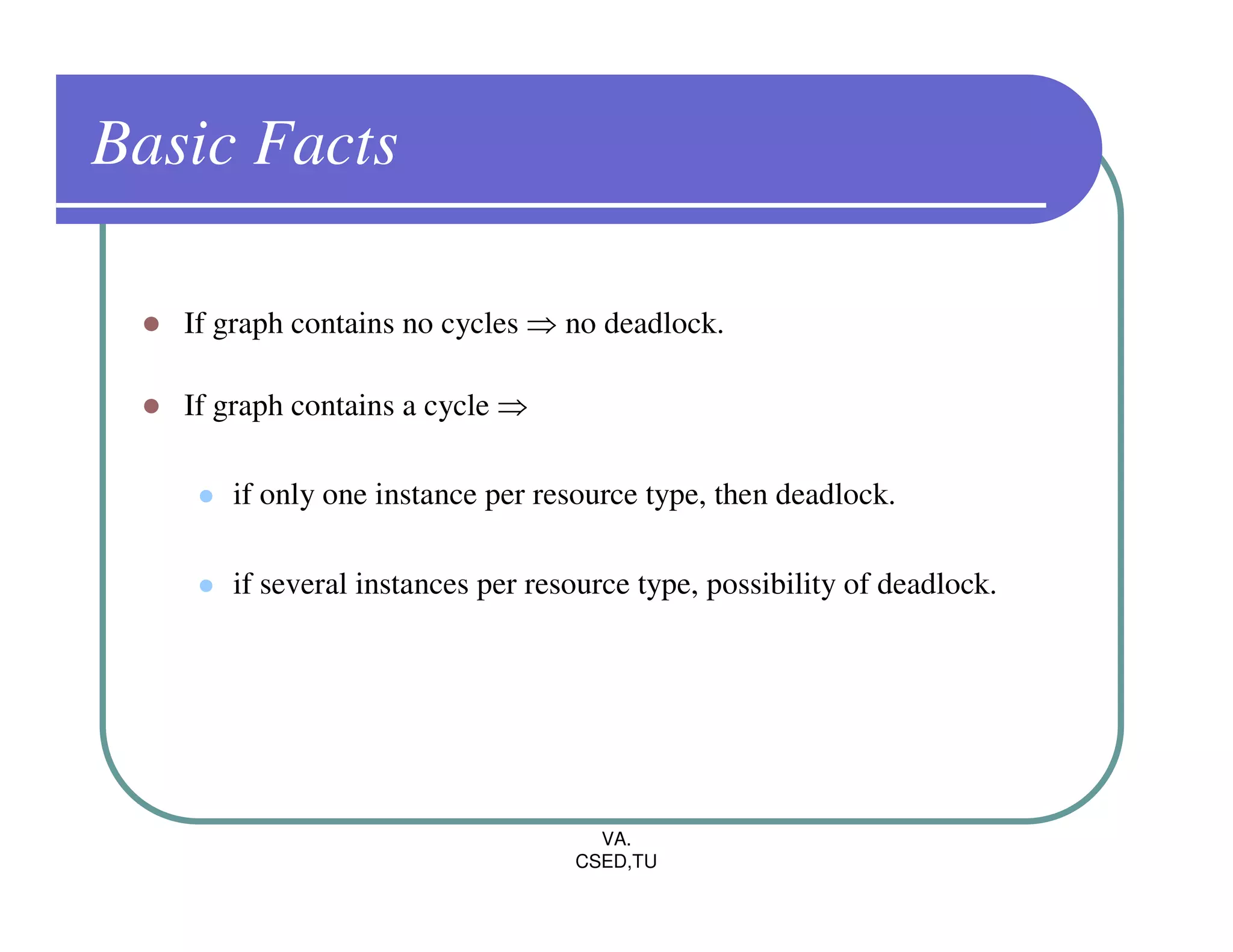
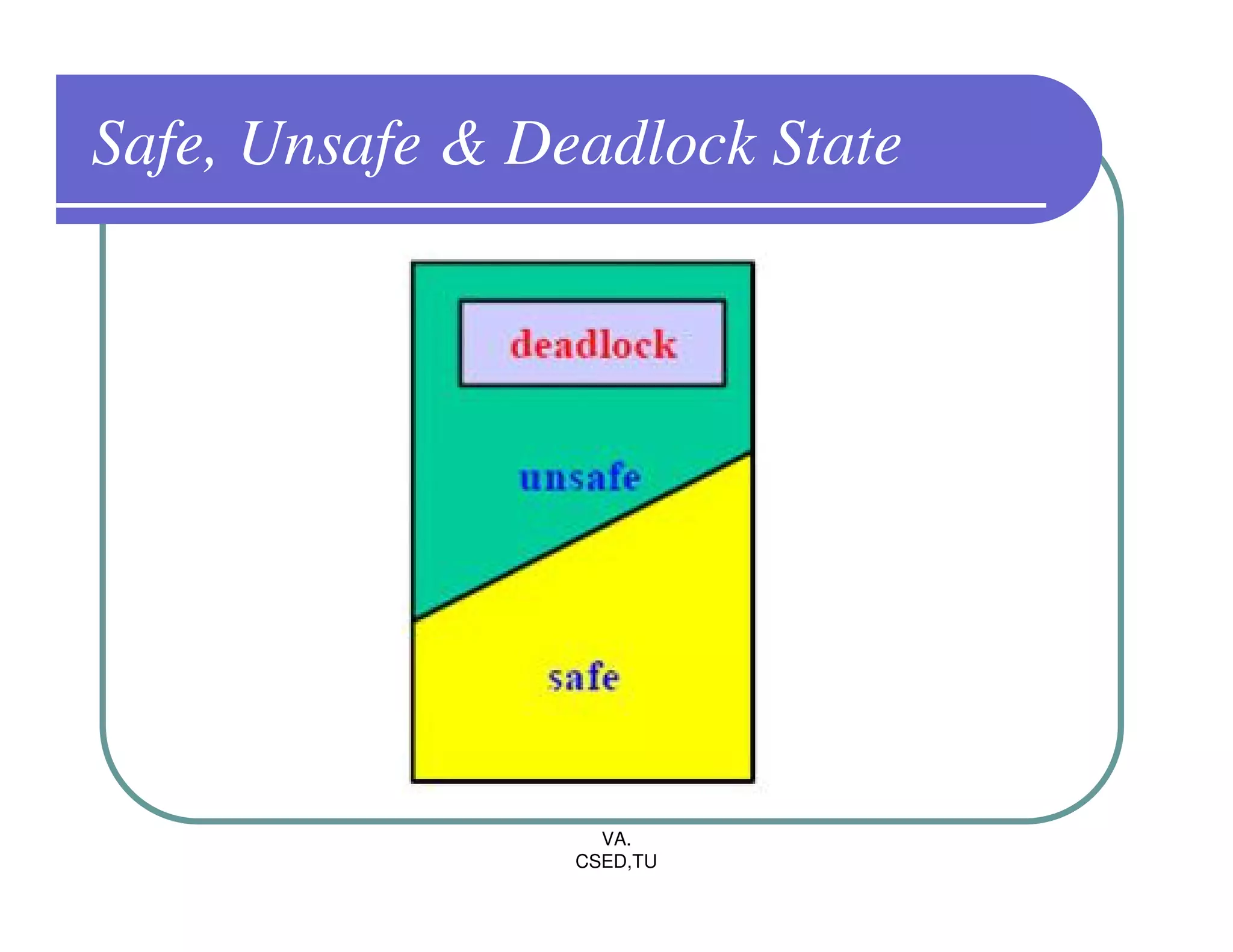
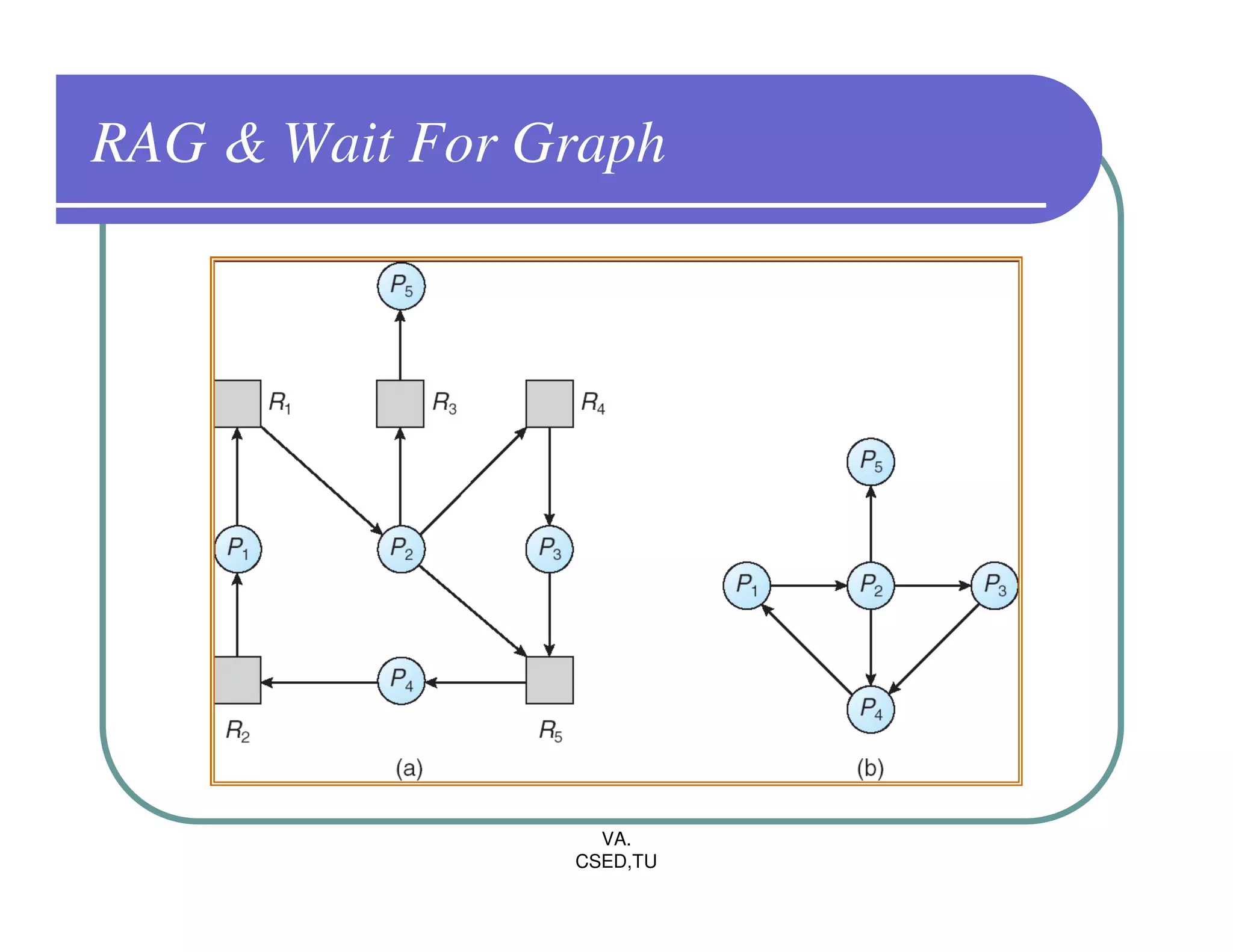
The document discusses deadlocks in operating systems. It defines the four conditions for deadlock - mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. It explains resource allocation graphs and how they can be used to detect deadlocks. The document also covers deadlock prevention methods like mutual exclusion, holding and waiting, preemption, and imposing a total ordering of resources. It describes Banker's algorithm for deadlock prevention and detection with multiple instances of resources. Finally, it discusses different approaches for deadlock recovery like process termination and resource preemption.





![Banker’s Algorithm – Safety Algo.
1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n, respectively.
Initialize Work = Available and Finish[i]=False for i=0,1,2……,n-1
2. Find an index i such that both
Finish[i] = = False
Needi < Work
If No such i exists, go to step 4.
3. Work = Work + Allocationi
Finish[i] = True
Go to Step 2.
4. If Finish[i] = = true for all i, then the system is in a Safe State.
VA.
CSED,TU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os-6-deadlock-111129011644-phpapp02/75/OS-Deadlock-15-2048.jpg)

![Several Instances of resource Type
Available: A vector of length m indicates the number of available
resources of each type.
Allocation: An n x m matrix defines the number of resources of each
type currently allocated to each process.
Request: An n x m matrix indicates the current request of each process.
If Request [ij] = k, then process Pi is requesting k more instances of
resource type. Rj.
VA.
CSED,TU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os-6-deadlock-111129011644-phpapp02/75/OS-Deadlock-21-2048.jpg)
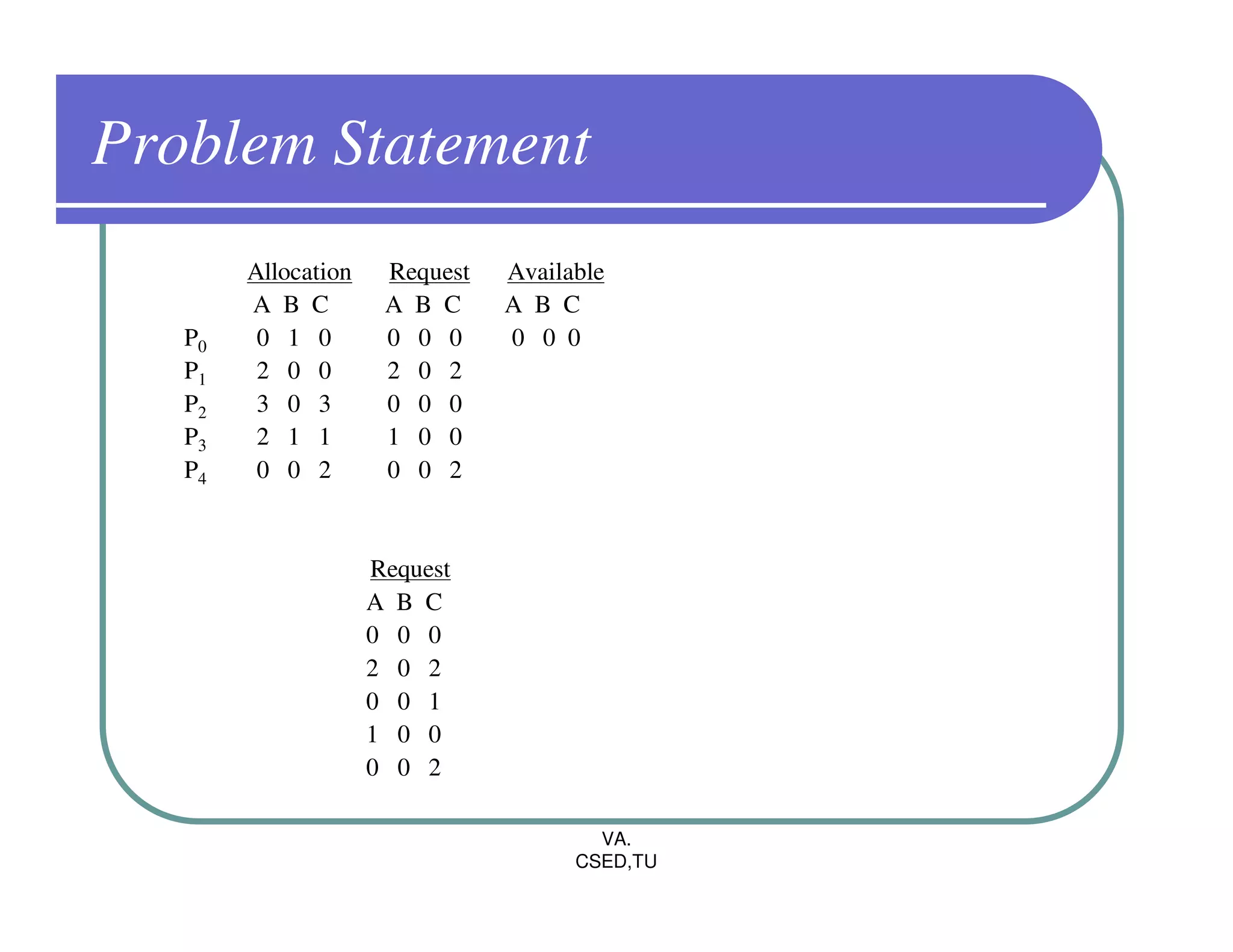
![Deadlock Detection
1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n, respectively.
Initialize Work = Available. For i=0,1,2……,n-1, if Allocationi Not equal
to ZERO, then Finish[i] = False; Otherwise,Finish[i] = True
2. Find an index i such that both
Finish[i] = = False
Requesti < Work
If No such i exists, go to step 4.
3. Work = Work + Allocationi
Finish[i] = True
Go to Step 2.
4. If Finish[i] = = false for some i, then the system is in Deadlock State.
VA.
CSED,TU](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/os-6-deadlock-111129011644-phpapp02/75/OS-Deadlock-22-2048.jpg)