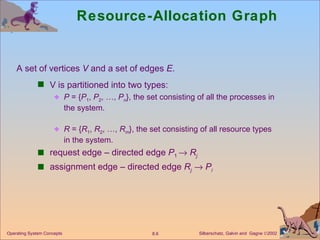
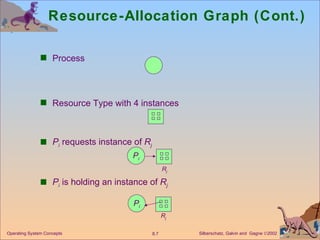
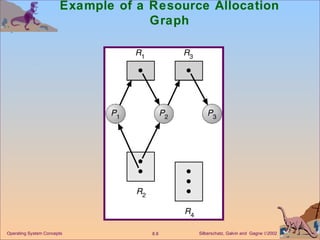
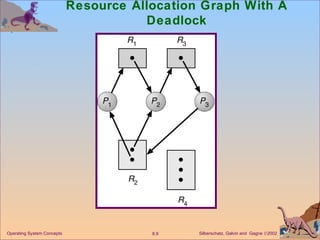
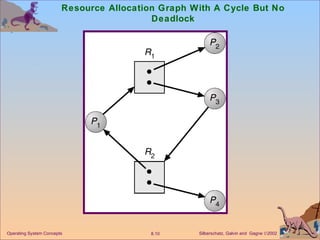
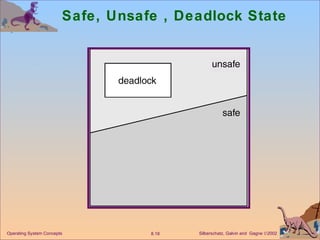
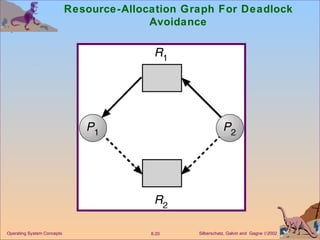
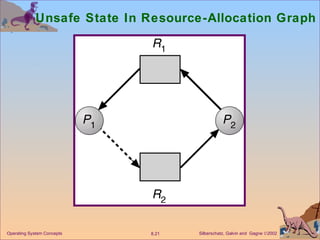
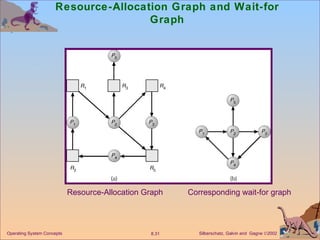
The document discusses various techniques for handling deadlocks in computer systems, including deadlock prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery. It defines the four necessary conditions for deadlock, and describes resource-allocation graphs and wait-for graphs that can be used to model deadlock states. Detection algorithms periodically check the resource-allocation graph for cycles that indicate a deadlock. Upon detection, various recovery techniques can be used like terminating processes, preempting resources, or rolling back to a previous safe state. An optimal approach combines prevention, avoidance and detection tailored for each resource class.












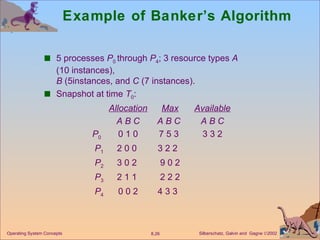
![Data Structures for the Banker’s Algorithm Available: Vector of length m . If available [ j ] = k , there are k instances of resource type R j available. Max: n x m matrix. If Max [ i,j ] = k , then process P i may request at most k instances of resource type R j . Allocation: n x m matrix. If Allocation[ i,j ] = k then P i is currently allocated k instances of R j. Need: n x m matrix. If Need [ i,j ] = k , then P i may need k more instances of R j to complete its task. Need [ i,j] = Max [ i,j ] – Allocation [ i,j ]. Let n = number of processes, and m = number of resources types.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-23-320.jpg)
![Safety Algorithm 1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n , respectively. Initialize: Work = Available Finish [ i ] = false for i - 1,3, …, n. 2. Find and i such that both: (a) Finish [ i ] = false (b) Need i Work If no such i exists, go to step 4. 3. Work = Work + Allocation i Finish [ i ] = true go to step 2. 4. If Finish [ i ] == true for all i , then the system is in a safe state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-24-320.jpg)
![Resource-Request Algorithm for Process P i Request = request vector for process P i . If Request i [ j ] = k then process P i wants k instances of resource type R j . 1. If Request i Need i go to step 2. Otherwise, raise error condition, since process has exceeded its maximum claim. 2. If Request i Available , go to step 3. Otherwise P i must wait, since resources are not available. 3. Pretend to allocate requested resources to P i by modifying the state as follows: Available = Available = Request i ; Allocation i = Allocation i + Request i ; Need i = Need i – Request i;; If safe the resources are allocated to P i . If unsafe P i must wait, and the old resource-allocation state is restored](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-25-320.jpg)


![Several Instances of a Resource Type Available: A vector of length m indicates the number of available resources of each type. Allocation: An n x m matrix defines the number of resources of each type currently allocated to each process. Request: An n x m matrix indicates the current request of each process. If Request [ i j ] = k , then process P i is requesting k more instances of resource type. R j .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-32-320.jpg)
![Detection Algorithm 1. Let Work and Finish be vectors of length m and n , respectively Initialize: (a) Work = Available (b) For i = 1,2, …, n , if Allocation i 0, then Finish [i] = false;otherwise, Finish [i] = true . 2. Find an index i such that both: (a) Finish [ i ] == false (b) Request i Work If no such i exists, go to step 4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-33-320.jpg)
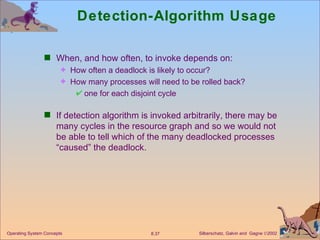
![Detection Algorithm (Cont.) 3. Work = Work + Allocation i Finish [ i ] = true go to step 2. 4. If Finish [ i ] == false, for some i , 1 i n , then the system is in deadlock state. Moreover, if Finish [ i ] == false , then P i is deadlocked. Algorithm requires an order of O( m x n 2) operations to detect whether the system is in deadlocked state.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-34-320.jpg)
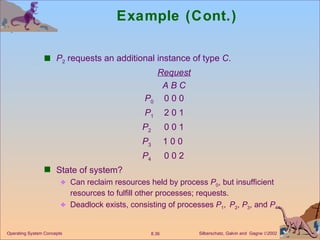
![Example of Detection Algorithm Five processes P 0 through P 4 ; three resource types A (7 instances), B (2 instances), and C (6 instances). Snapshot at time T 0 : Allocation Request Available A B C A B C A B C P 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 P 1 2 0 0 2 0 2 P 2 3 0 3 0 0 0 P 3 2 1 1 1 0 0 P 4 0 0 2 0 0 2 Sequence < P 0 , P 2 , P 3 , P 1 , P 4 > will result in Finish [ i ] = true for all i .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch8-110928045107-phpapp02/85/OS_Ch8-35-320.jpg)