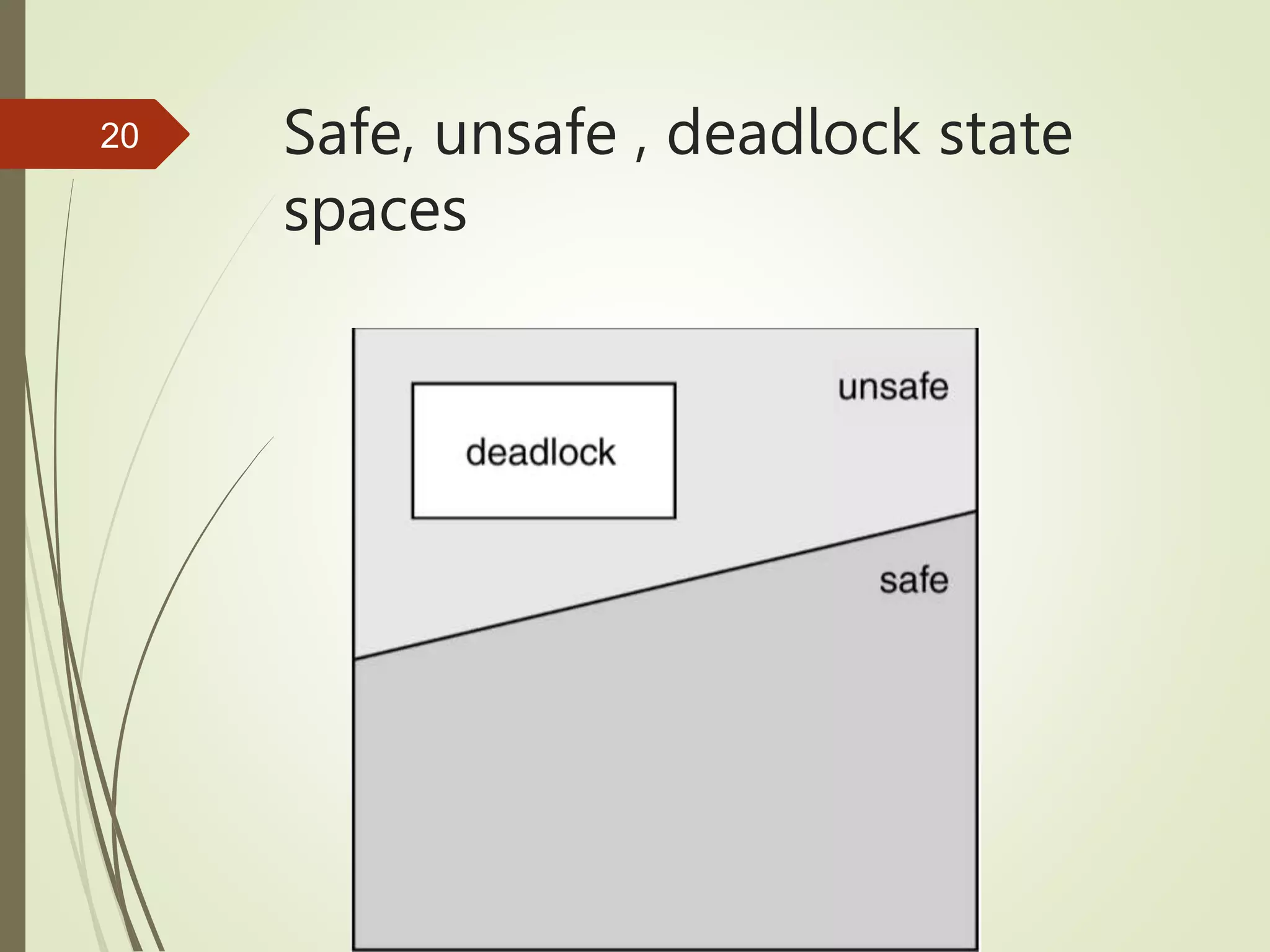
The document summarizes key topics about deadlocks in operating systems including deadlock characterization, prevention, and avoidance. It defines deadlock as a set of blocked processes where each process is waiting for a resource held by another in the set. Four conditions must be met for deadlock to occur: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Deadlock prevention methods ensure systems never enter a deadlock state while avoidance uses a safe state algorithm and resource ordering to dynamically prevent unsafe states.