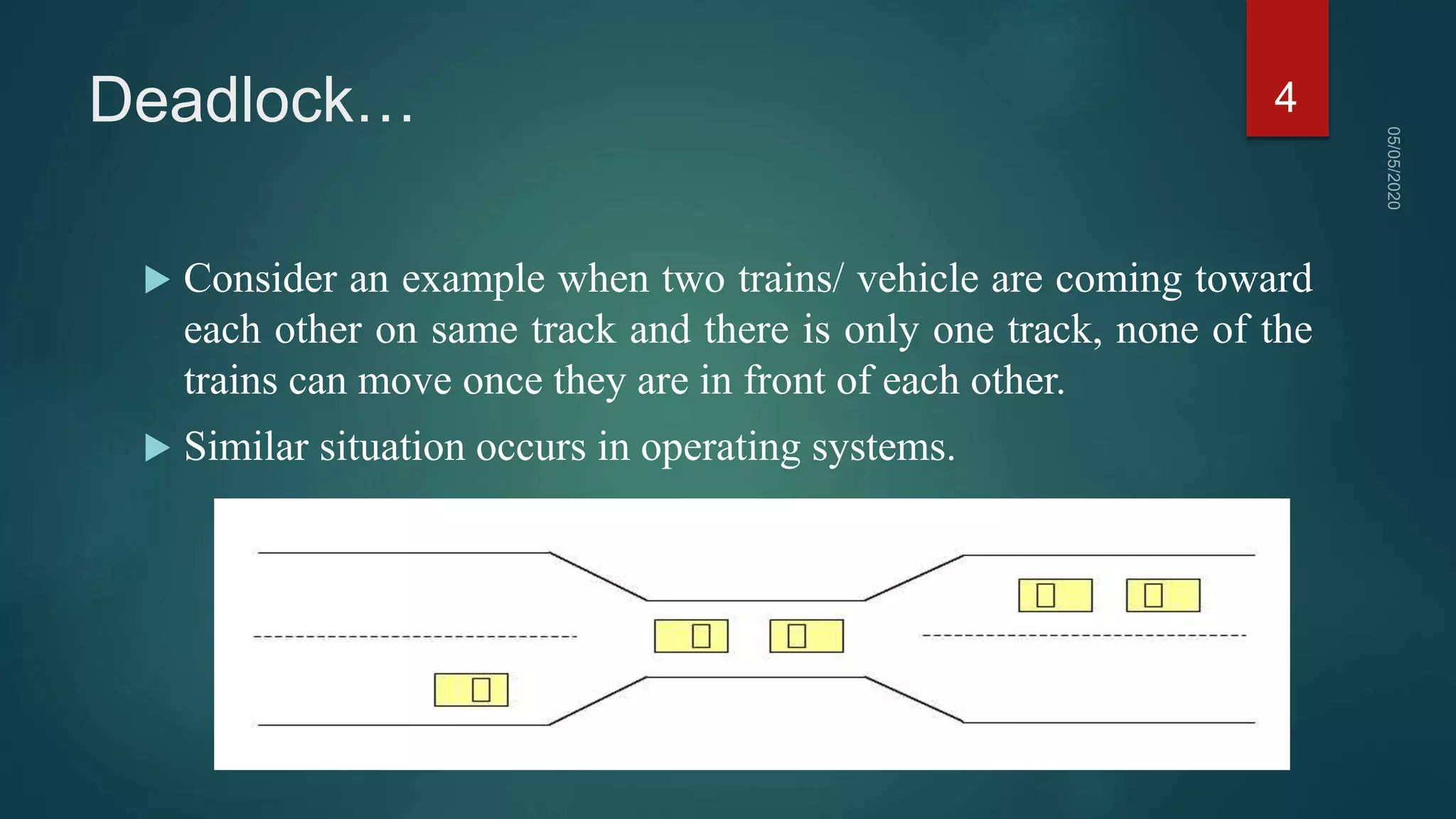
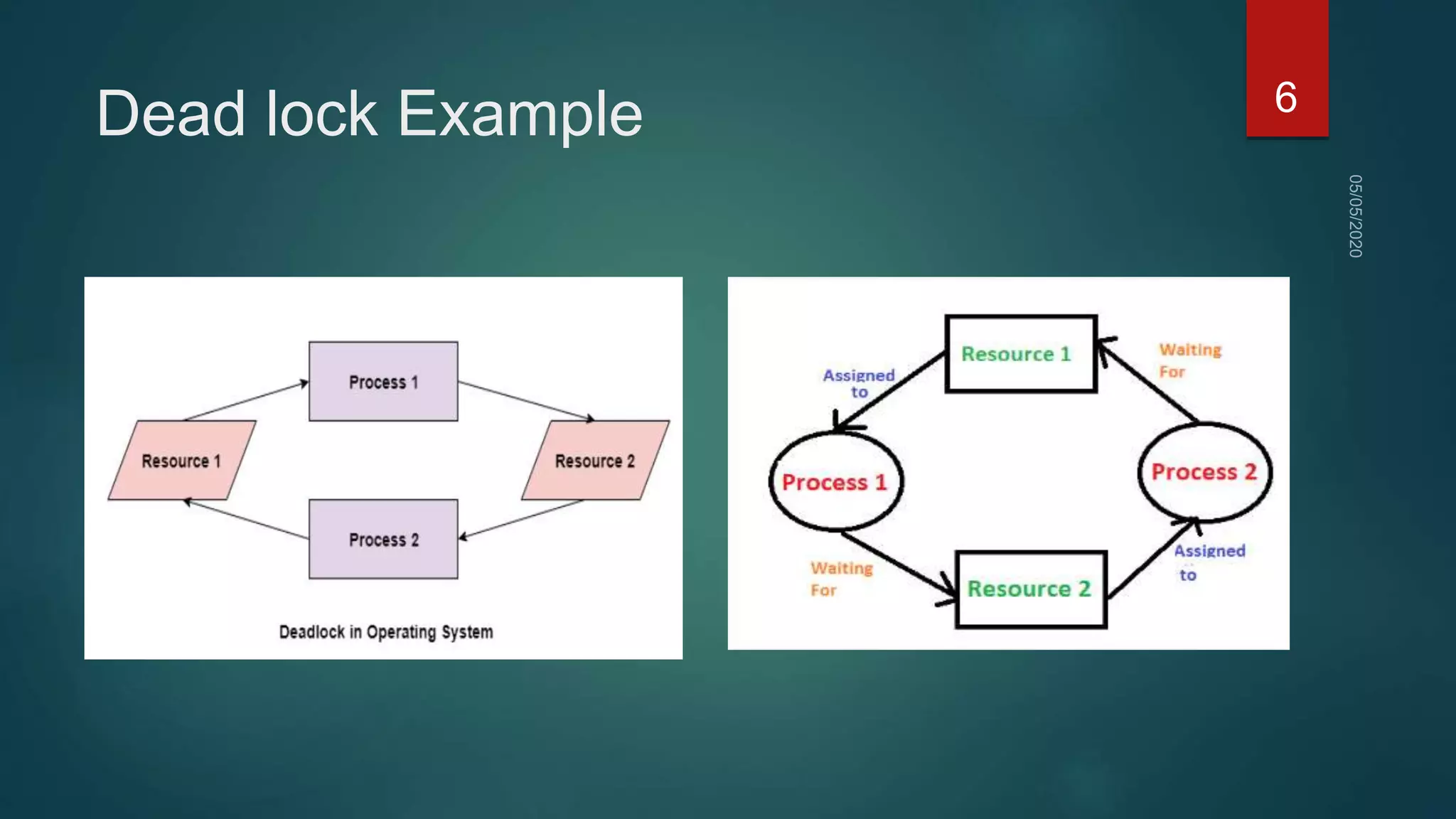
1) A deadlock occurs when a set of processes are blocked waiting for resources held by other processes in the set, forming a circular wait.
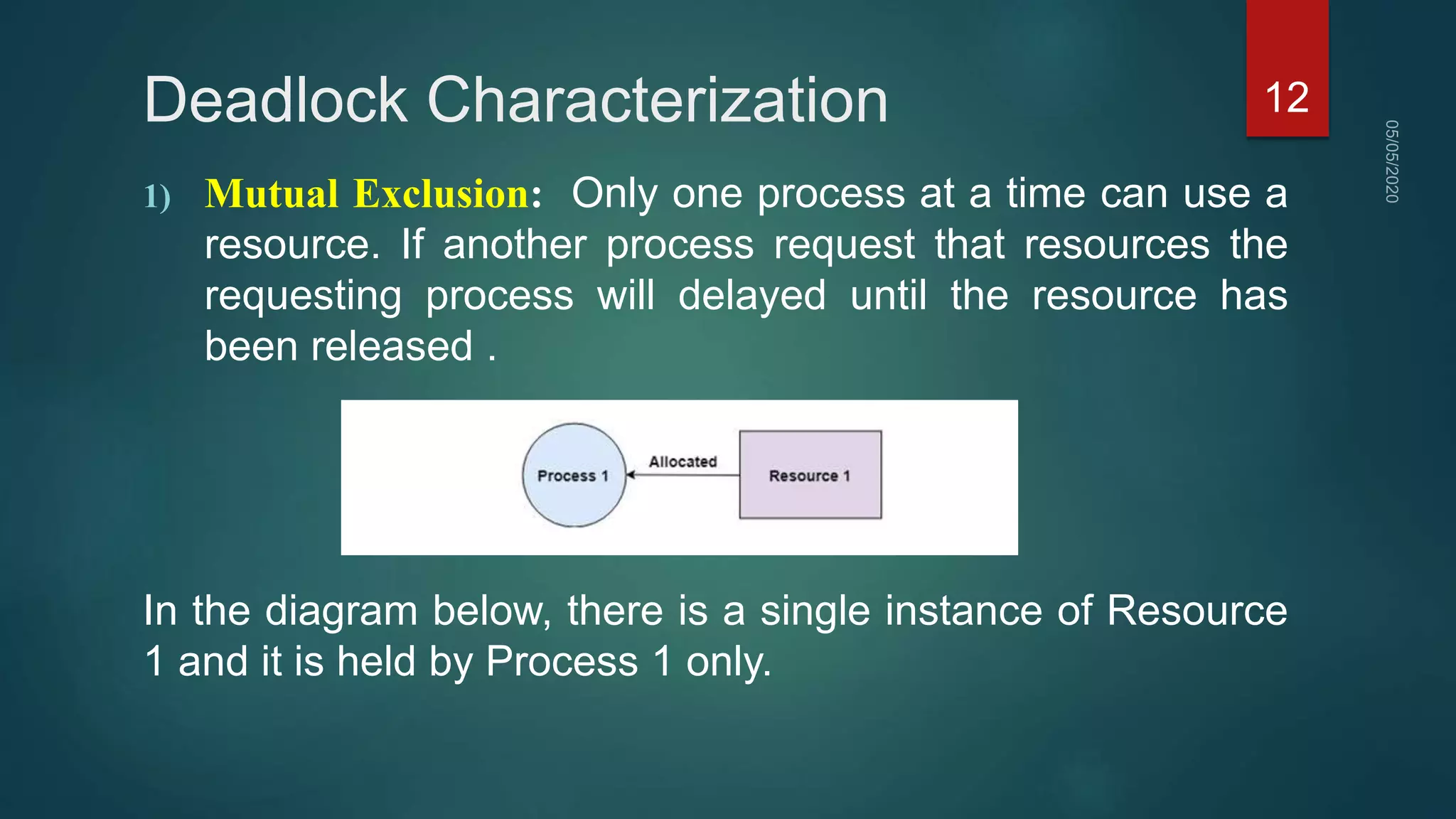
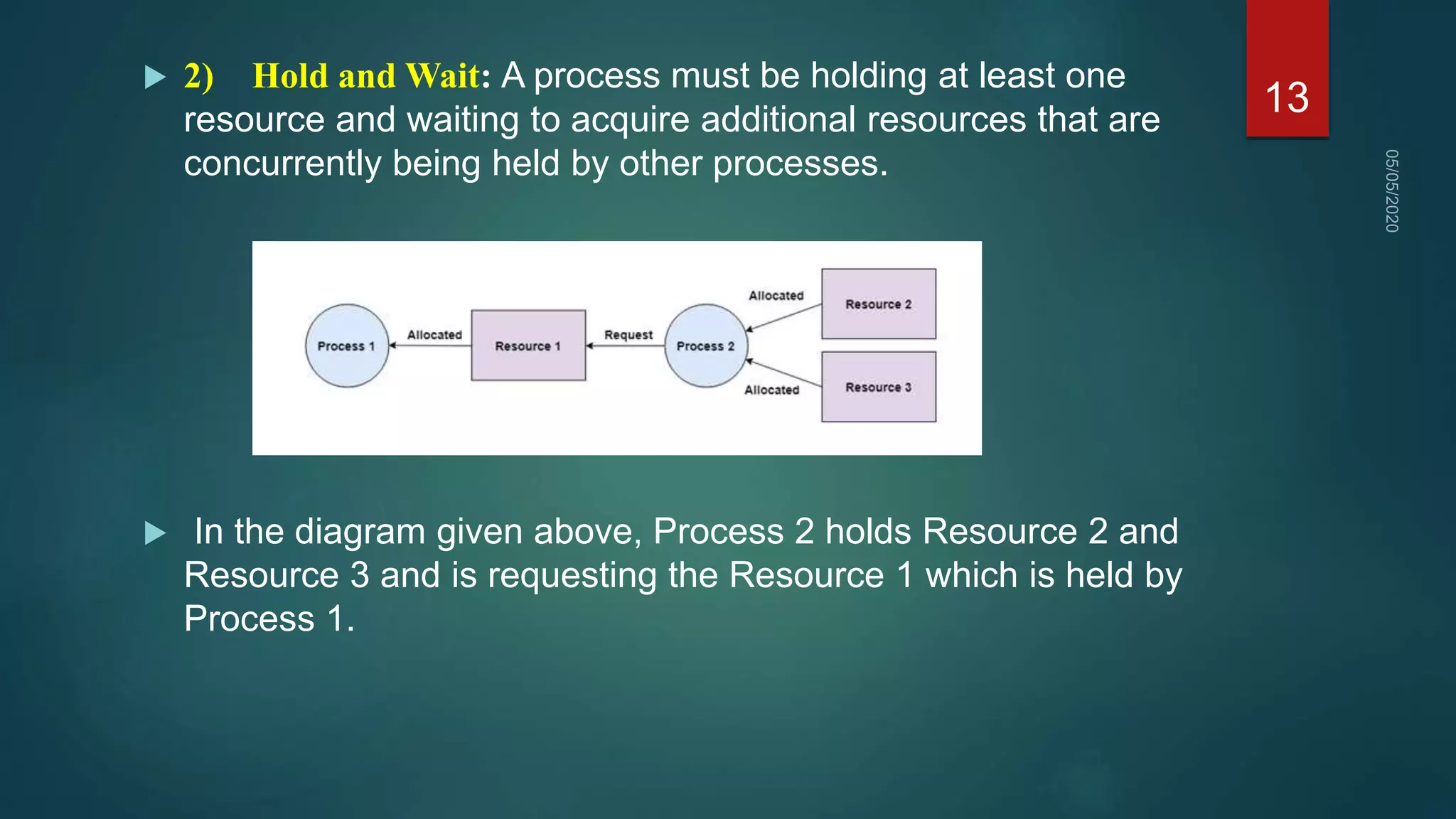
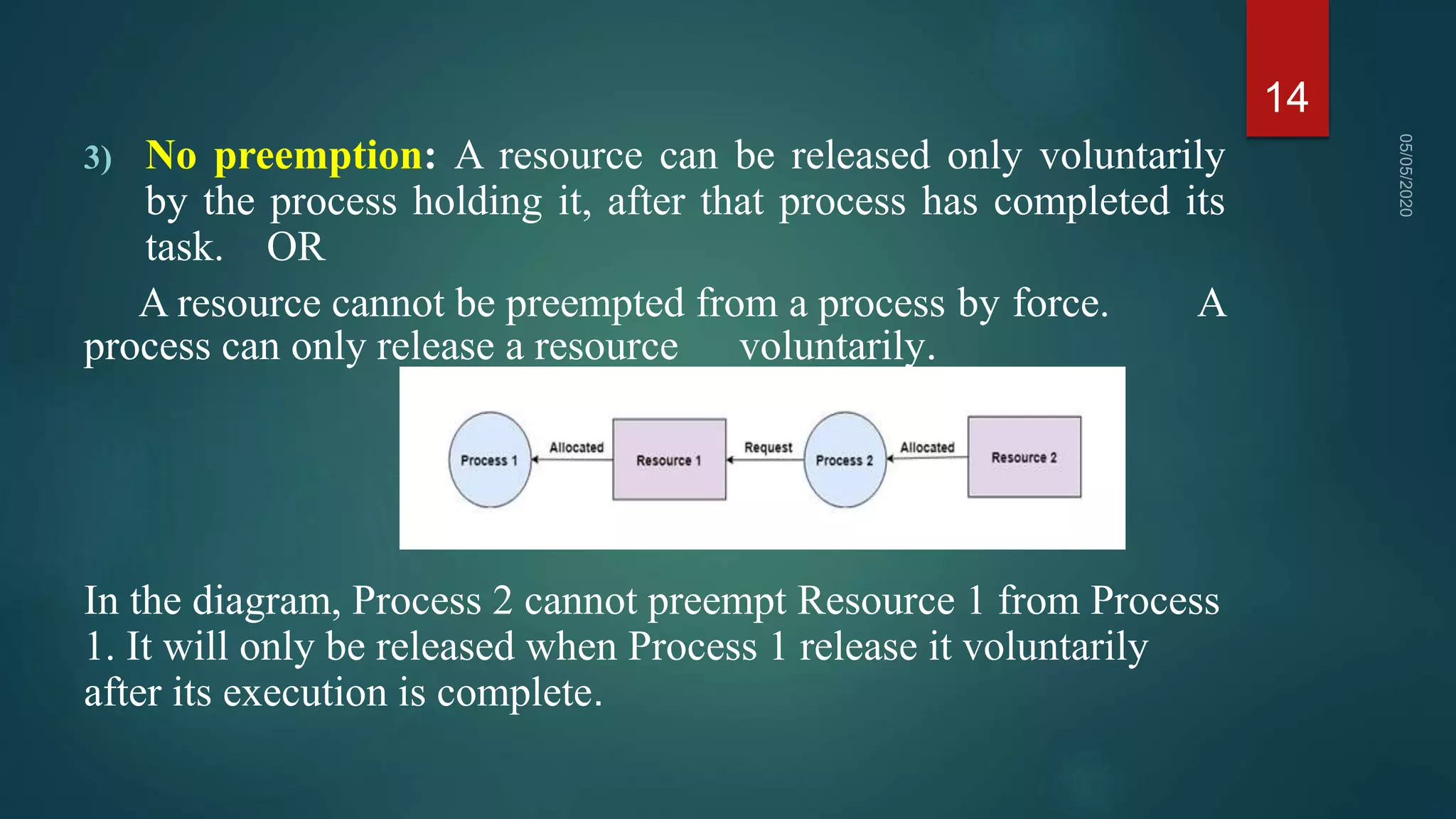
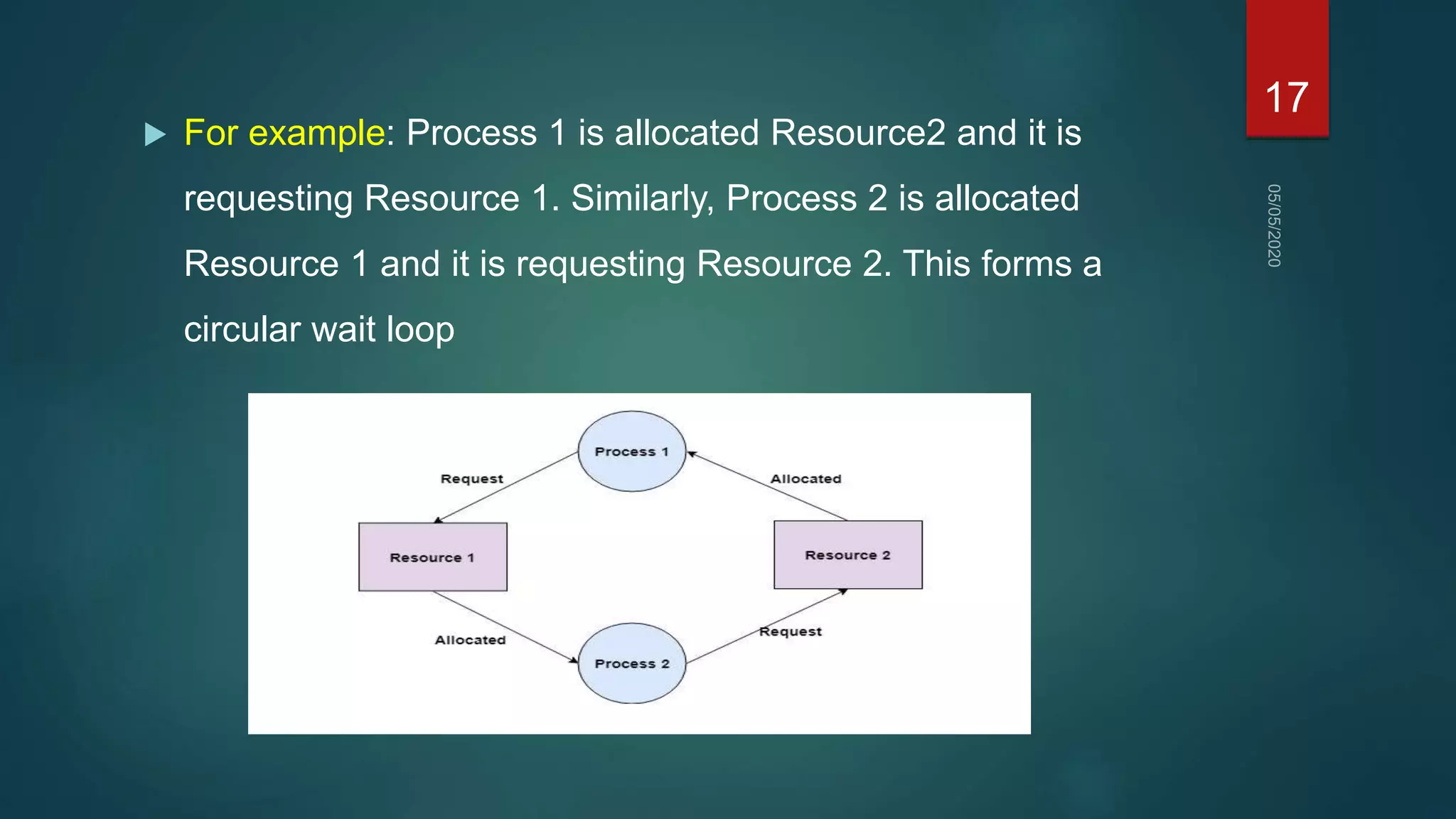
2) For a deadlock to occur, four necessary conditions must be met: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait.
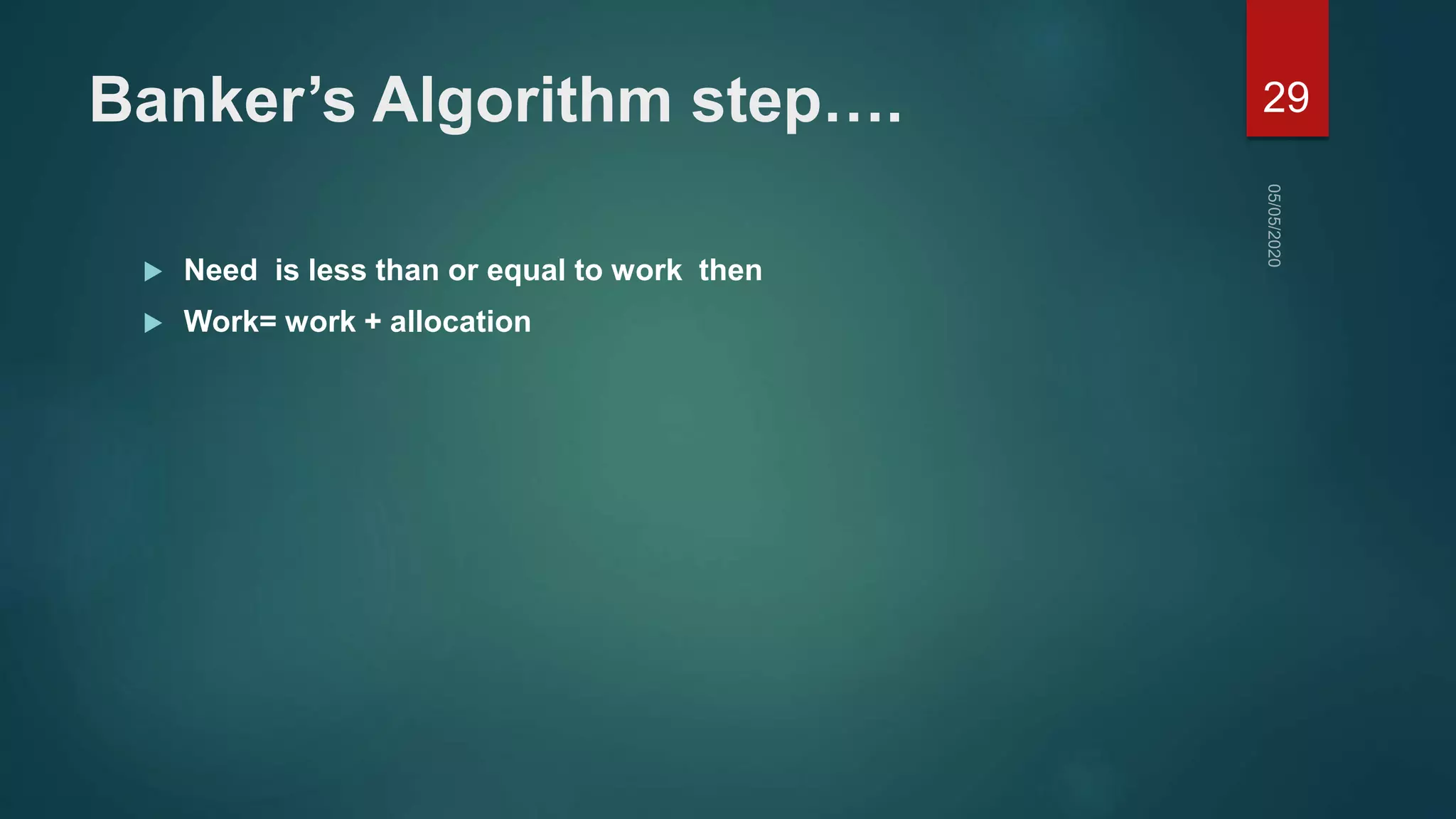
3) Deadlocks can be prevented by ensuring that at least one of the four conditions is not met, such as allowing resource preemption or requiring processes request all resources before starting. Deadlock avoidance uses algorithms like Banker's Algorithm to prevent unsafe states that could lead to deadlock.