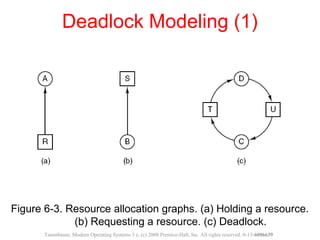
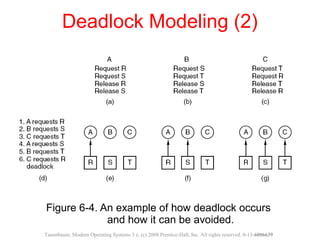
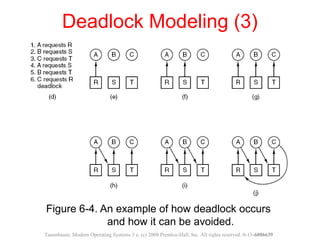
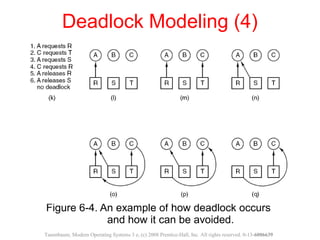
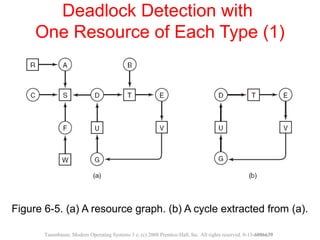
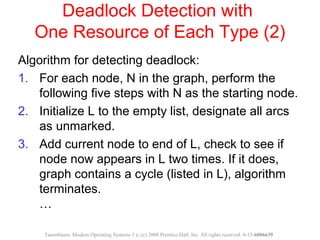
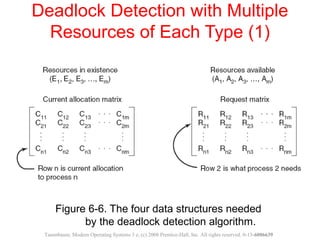
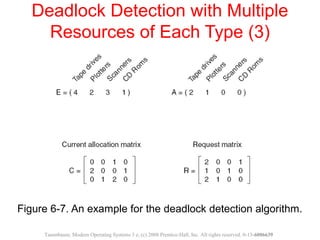
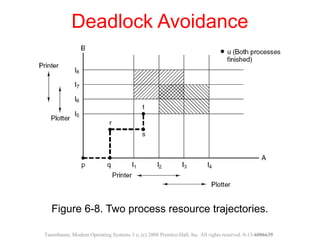
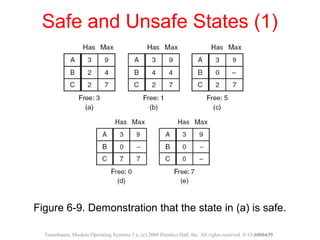
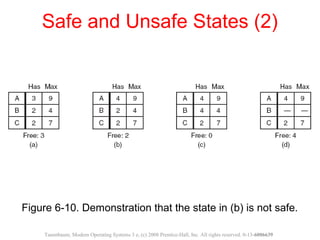
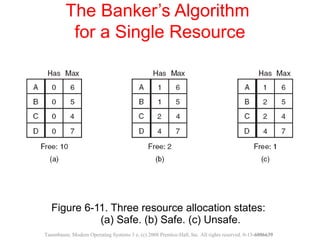
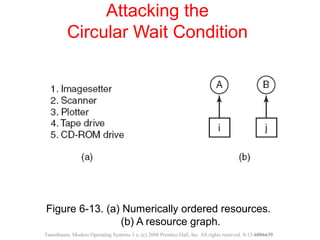
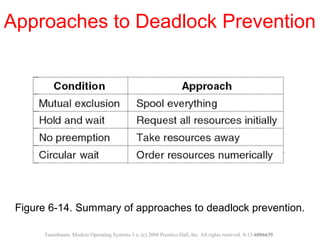
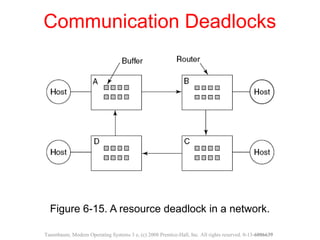
This document discusses deadlocks in operating systems. A deadlock occurs when a set of processes are blocked waiting for resources held by each other in a cyclic manner. Four conditions must be met for a deadlock to occur: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. The document outlines strategies for detecting and avoiding deadlocks such as deadlock detection algorithms, safe state models like the Banker's Algorithm, and techniques for preventing the four deadlock conditions.