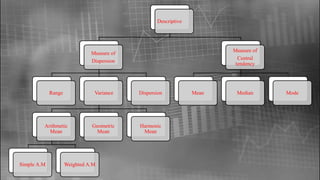
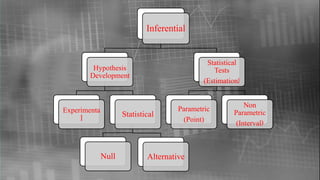
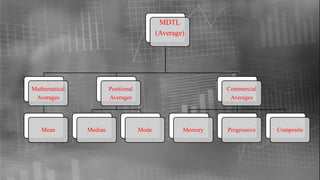
The document outlines the origin and history of statistics, tracing its development from ancient administrative practices to modern statistical theory. It highlights significant milestones and contributors, such as the establishment of vital statistics, the introduction of probability theory, and advancements by key figures like Karl Pearson and Ronald Fisher. The document also categorizes different types of statistics and discusses various statistical methods and measures.