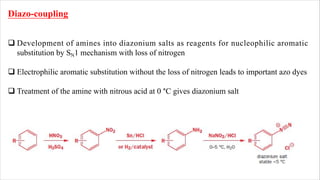
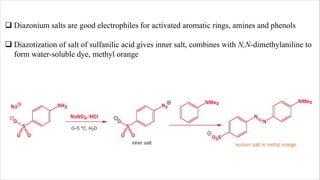
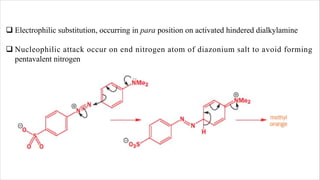
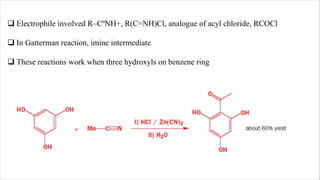
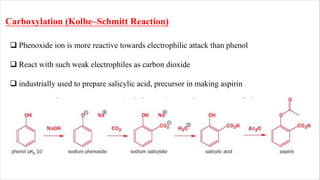
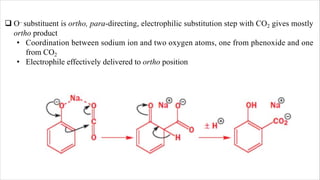
The document discusses three reactions: diazocoupling, formylation, and carboxylation. Diazocoupling involves converting amines into diazonium salts that act as electrophiles in aromatic substitution reactions. Formylation uses protonated hydrogen cyanide or alkyl cyanides to introduce aldehyde groups via an imine intermediate. Carboxylation uses phenoxide ions, which are more reactive than phenols, to react with carbon dioxide via electrophilic substitution, delivering the electrophile to the ortho position through coordination with sodium ions.