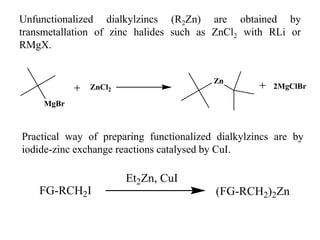
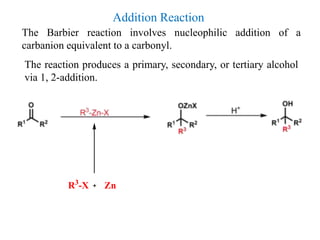
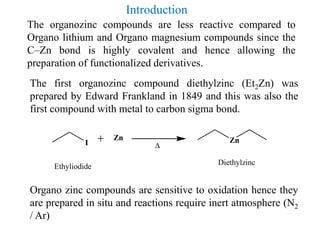
1) Organozinc compounds are less reactive than organolithium and organomagnesium compounds due to their more covalent C-Zn bond, allowing preparation of functionalized derivatives.
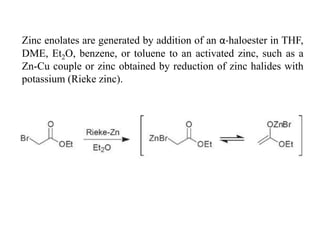
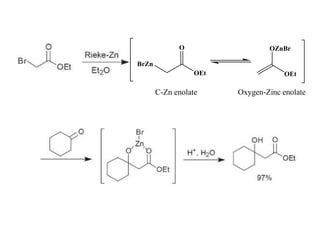
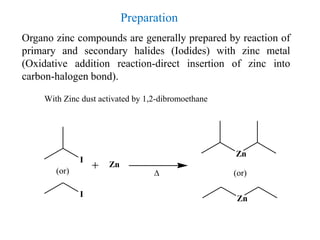
2) Organozinc compounds are commonly prepared by reacting primary or secondary halides with zinc metal or Rieke zinc under inert atmosphere due to their sensitivity to oxidation.
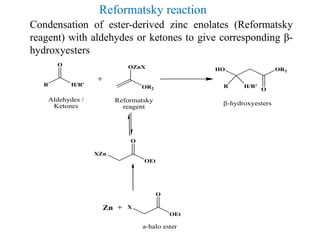
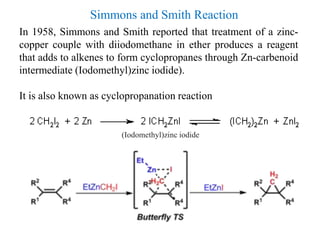
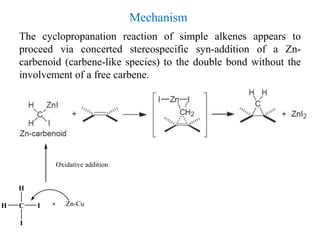
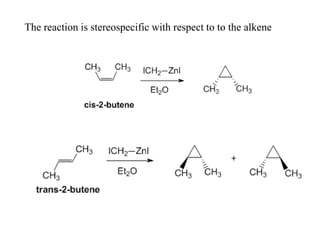
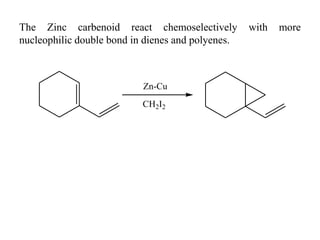
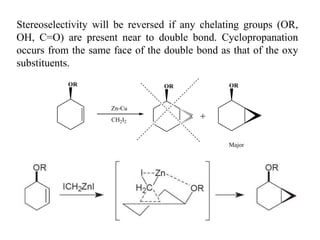
3) Organozinc reagents are useful in organic syntheses such as Reformatsky reactions, Simmons-Smith cyclopropanation reactions, and cross-coupling reactions like Negishi and Fukuyama couplings.


![With Rieke Zinc
ZnCl2 Zn
Li-naphthalenide
LiLi-naphthalenide
FG-RX
[FG-RZnX]
Rieke Zinc
R= Alkyl, Aryl, Benzyl
X = Br, I
FG = CO2R, CN, halide
Organo zinc halides are also prepared by reaction of primary
and secondary halides (Iodides) with Rieke Zinc.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/organozinccompounds-200410072220/85/Organozinc-compounds-5-320.jpg)