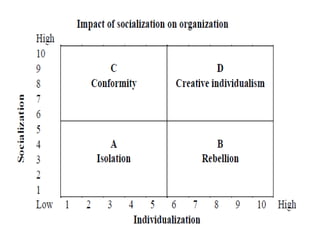
This document outlines the management strategies in educational institutions, focusing on the concept of organizational behavior (OB) and related behavioral management techniques. It covers different levels of OB, various organizational models, and the importance of behavior-based safety and communication in improving organizational performance. Furthermore, it emphasizes the need for ethical leadership and engagement in open communication within organizations.