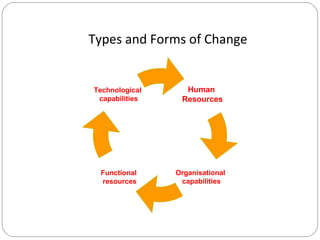
Organizational change involves moving an organization from its current state to a desired future state to increase effectiveness. There are forces that drive change, such as competitive, economic, demographic, and ethical forces, as well as resistances to change at the organizational, functional, group, and individual levels. Changes can be technological, to human resources, functional resources, or organizational capabilities. Evolutionary change is gradual and incremental, while revolutionary change is rapid and drastic. The change process involves unfreezing the current state, diagnosing needs, planning the future state, implementing changes, evaluating outcomes, and institutionalizing new approaches.