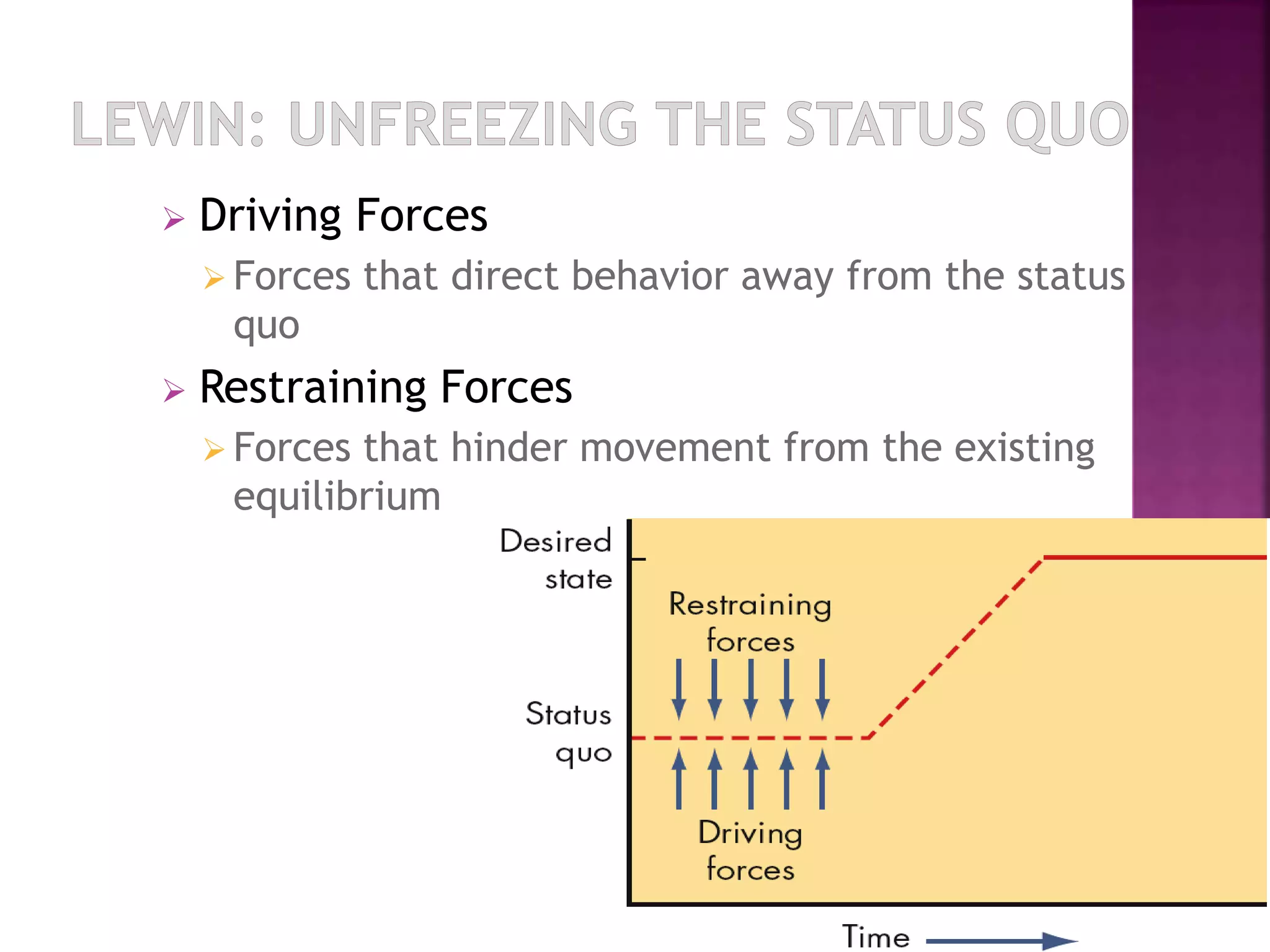
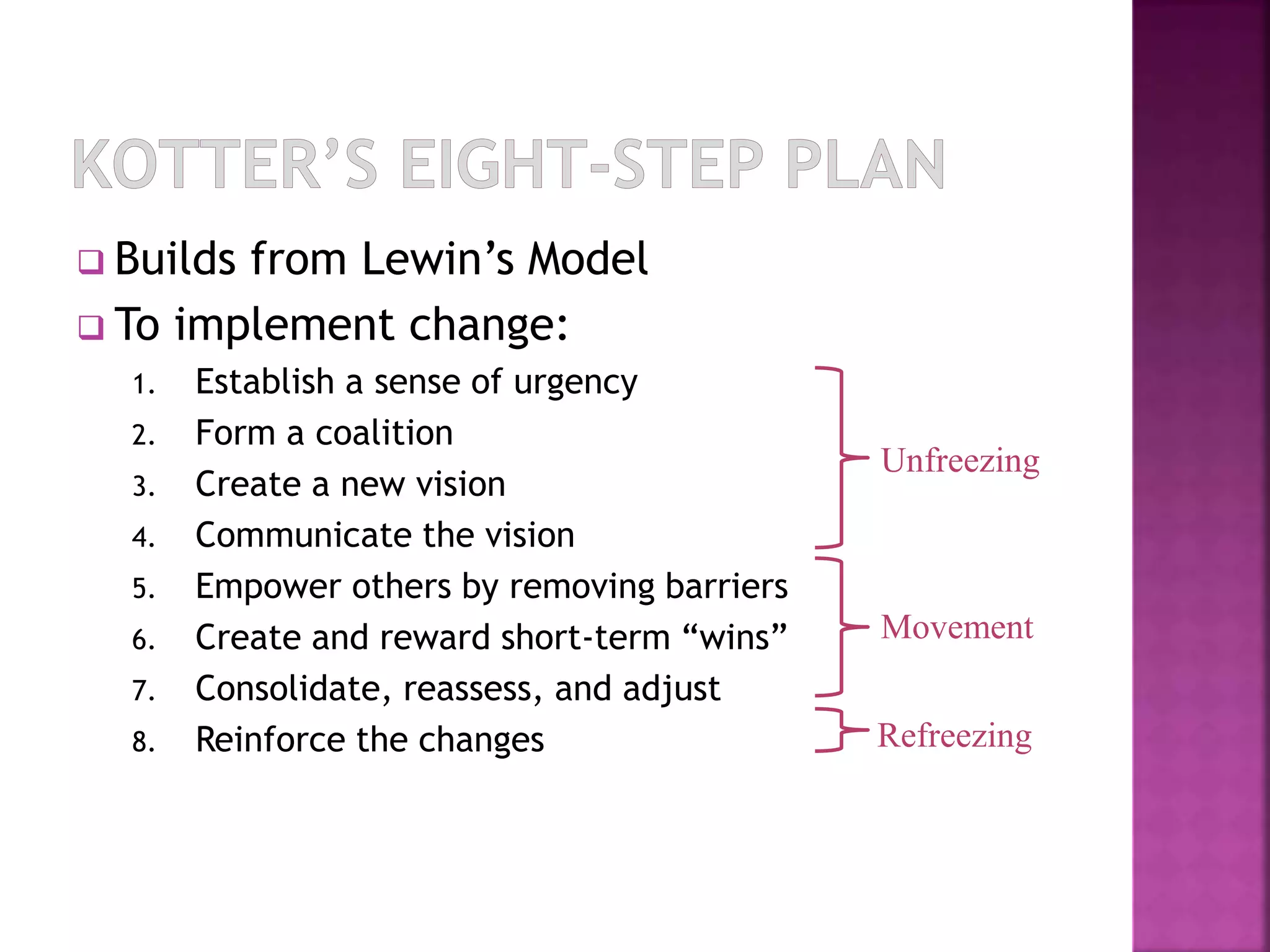
The document discusses several theories and approaches for organizational change management including Lewin's force field theory, Kotter's 8-step change model, action research, and organizational development. Lewin's model involves three steps: unfreezing, moving, and refreezing. Kotter's 8 steps build on Lewin's model and include establishing urgency, forming a coalition, creating a vision, communicating the vision, empowering employees, creating short-term wins, consolidating gains, and reinforcing changes. Action research is a data-driven change process involving diagnosis, analysis, feedback, action, and evaluation. Organizational development seeks to improve effectiveness and well-being through planned interventions based on humanistic values.