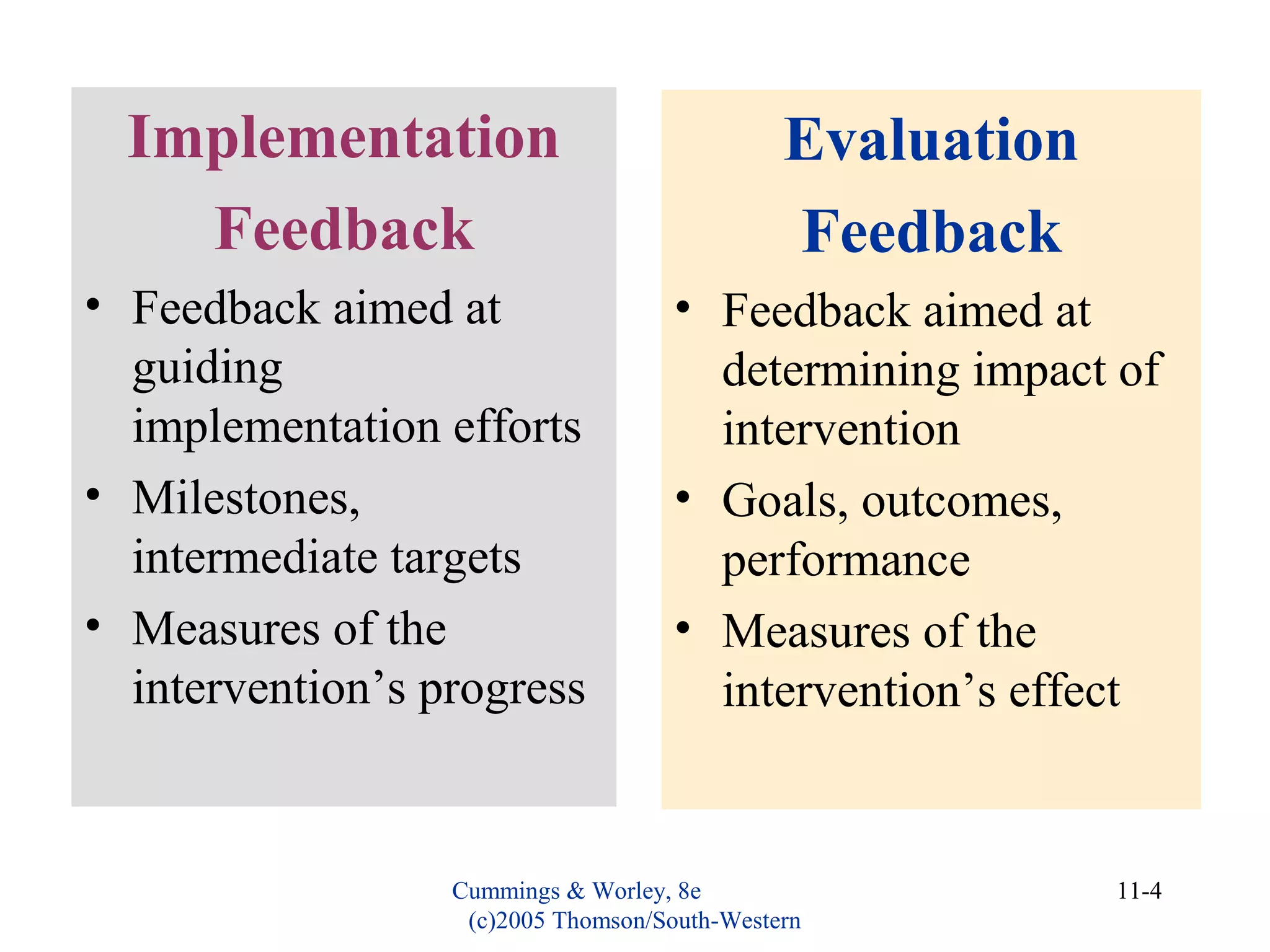
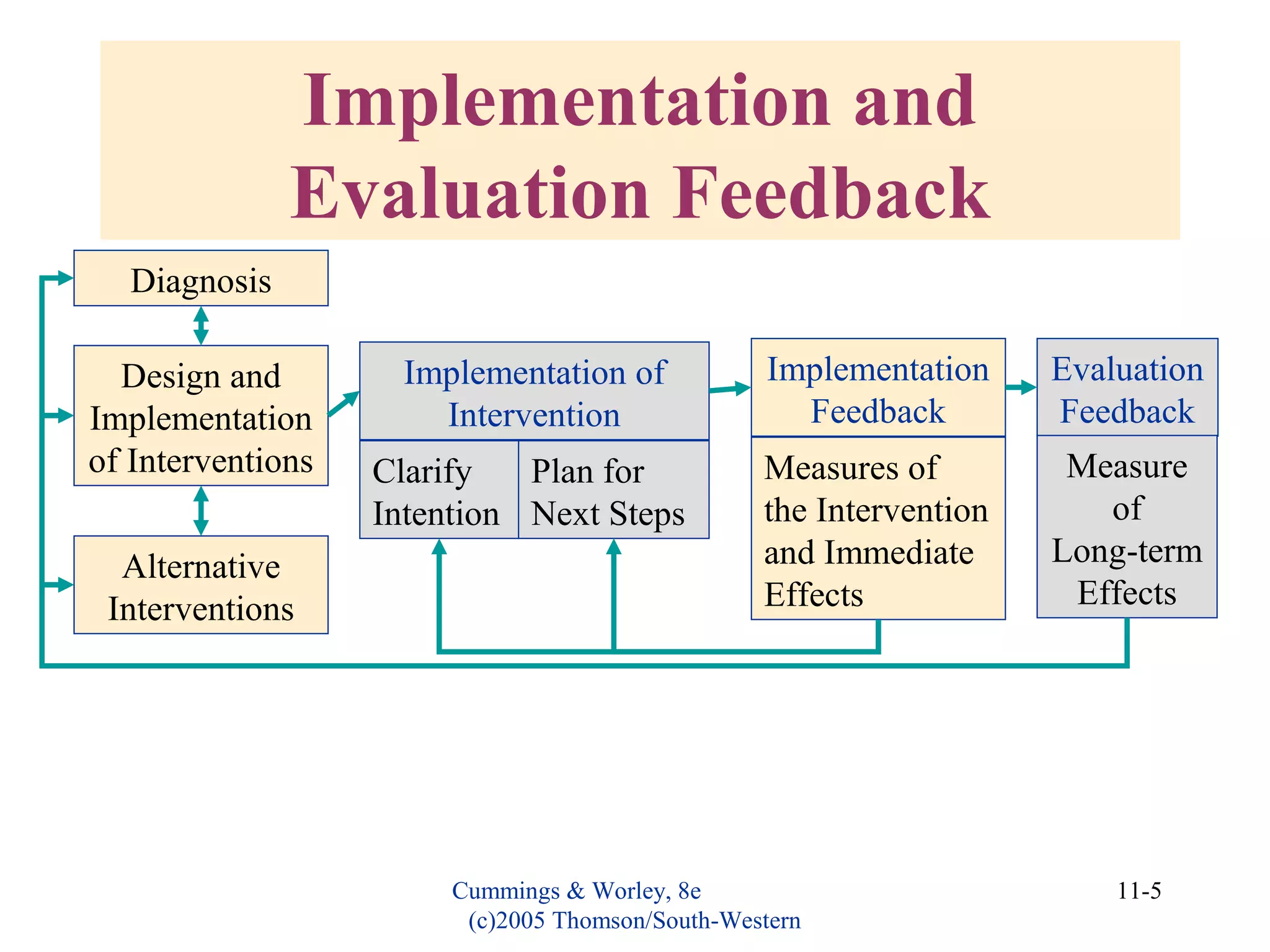
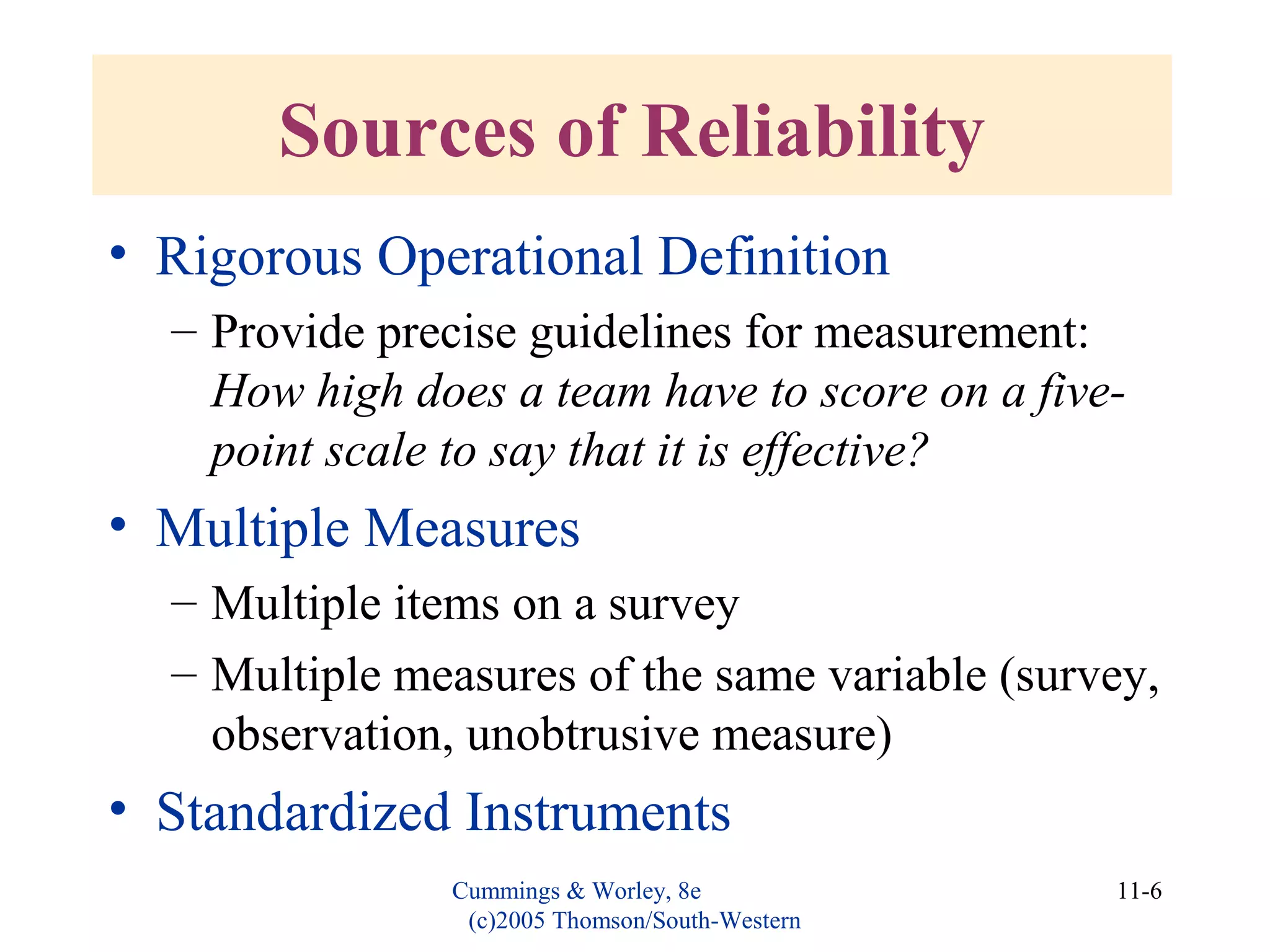
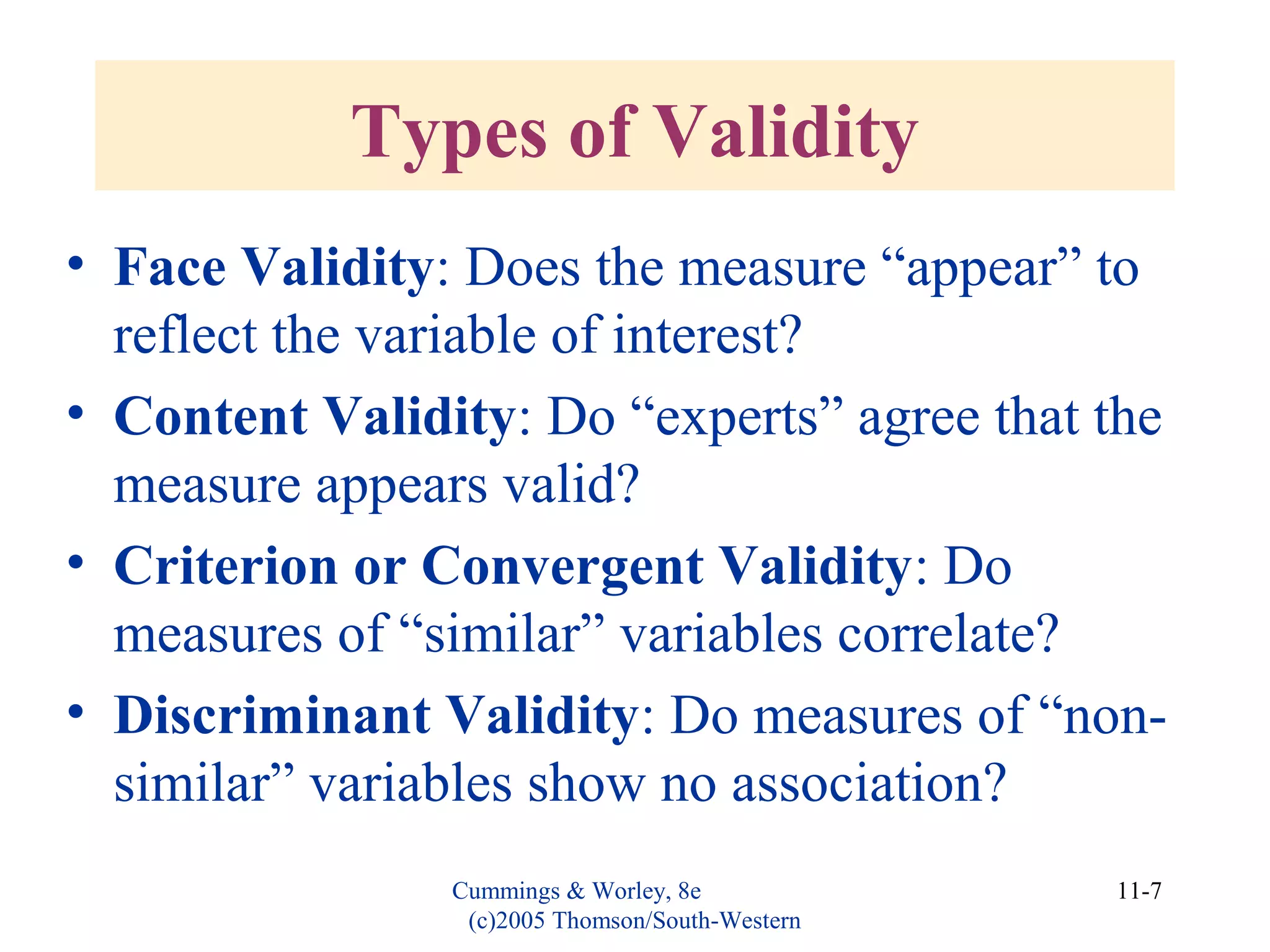
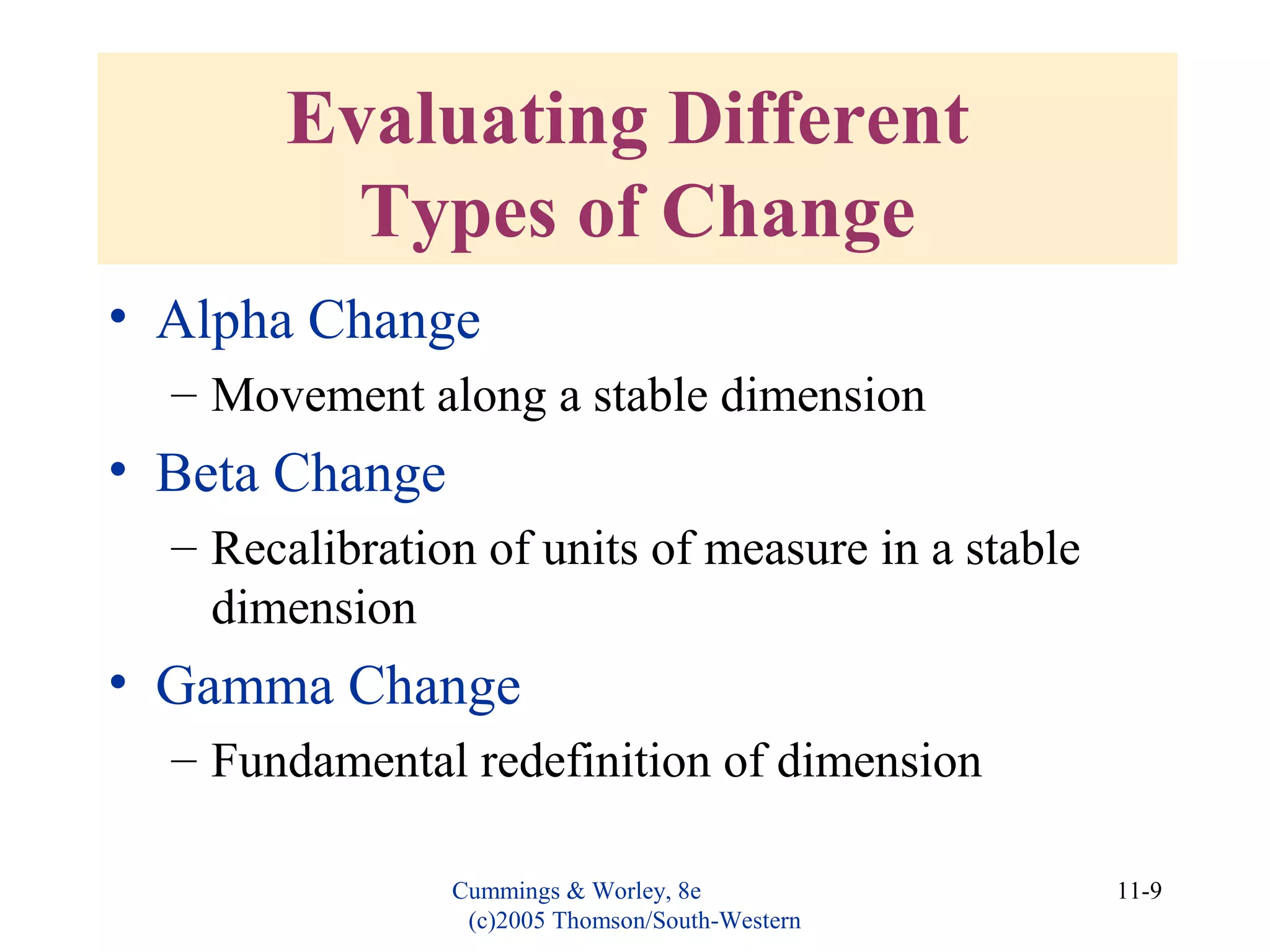
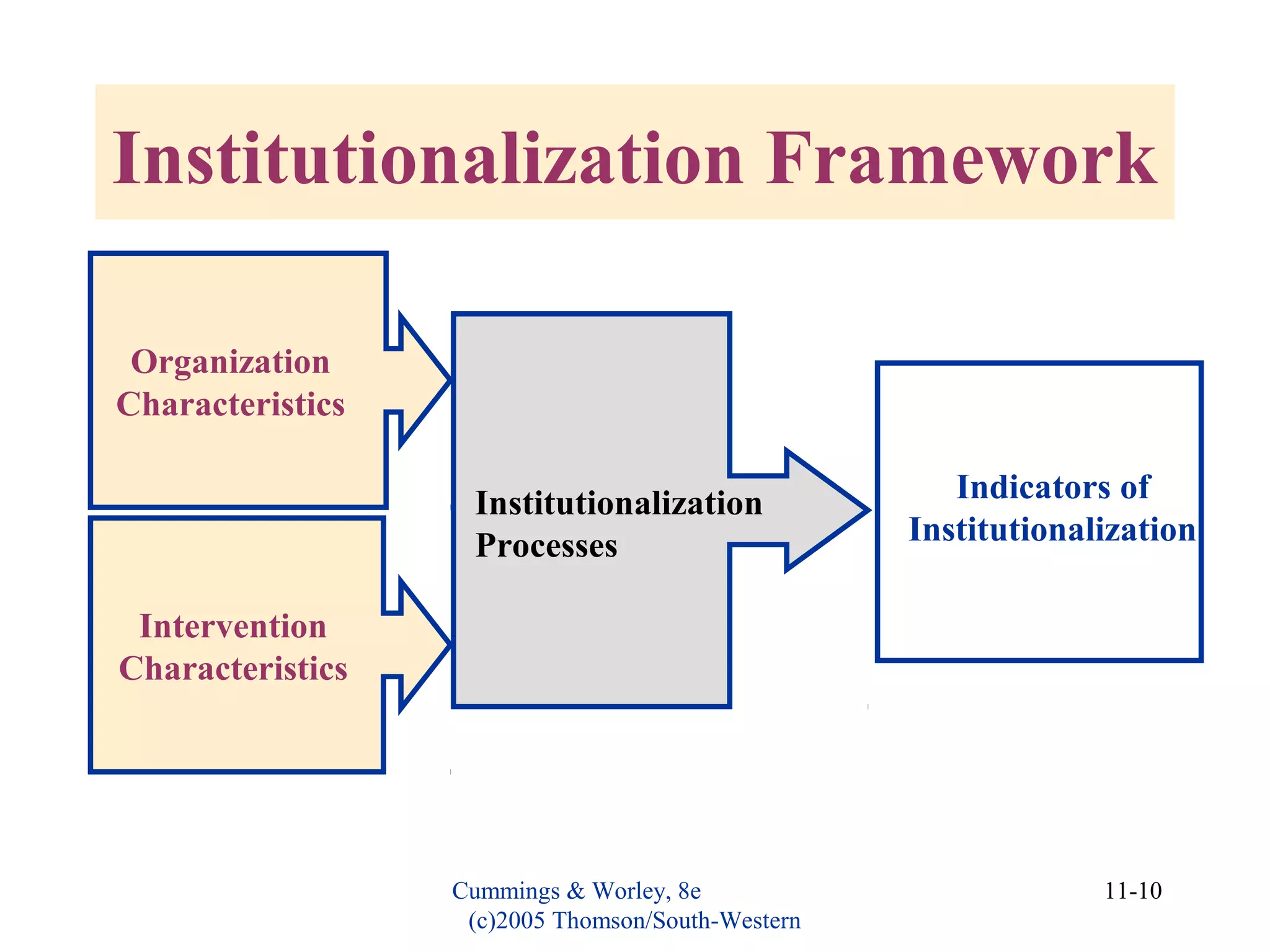
This document discusses evaluating organizational development (OD) interventions and institutionalizing changes from those interventions. It addresses issues in evaluating interventions such as selecting valid and reliable measurement variables and using appropriate research designs. Feedback during and after implementation is important. Factors that influence whether changes are institutionalized include characteristics of the organization, intervention, and processes that socialize and commit people to the changes. Indicators that changes were institutionalized include knowledge, performance, preferences, and consensus around new norms and values.