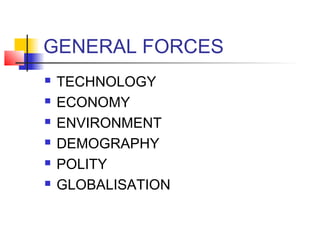
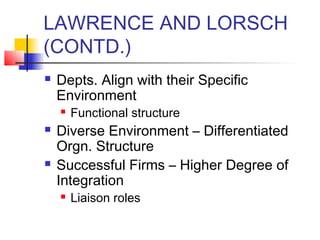
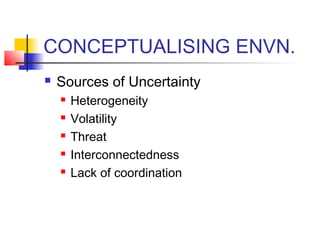
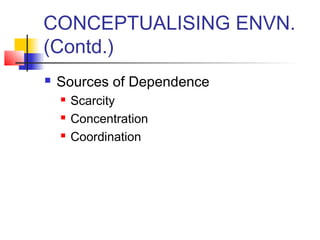
The document discusses organizational environment and its impact on organizations. Organizational environment refers to the set of forces surrounding an organization that can affect its operations and access to resources. These forces include customers, suppliers, competitors, government regulations, technology, the economy, and more. Researchers have found that organizations adapt their structures based on the complexity of their environment - stable environments suit mechanistic structures while unstable environments require more organic structures. Managers can enact strategies to buffer or bridge the organization from its task environment and seek legitimacy from the institutional environment.