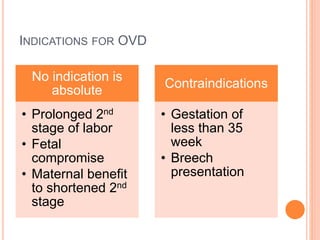
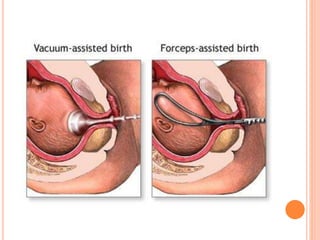
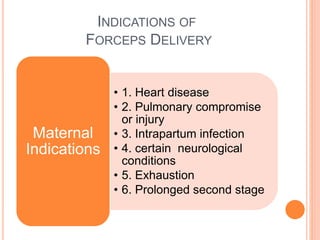
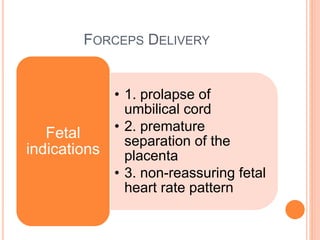
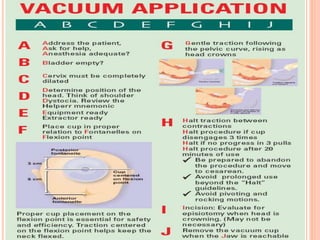
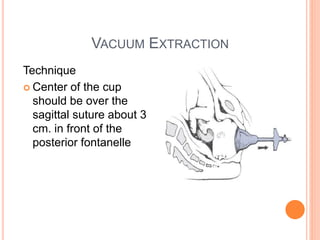
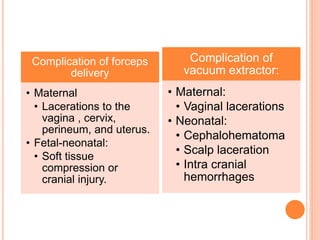
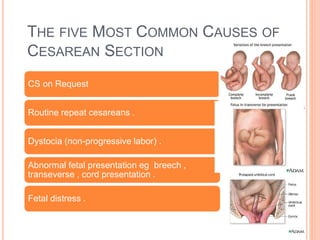
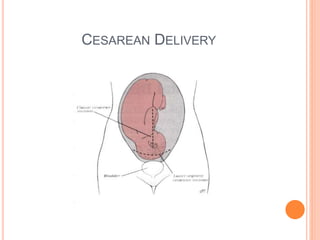
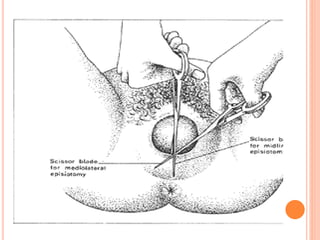
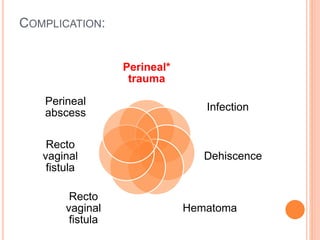
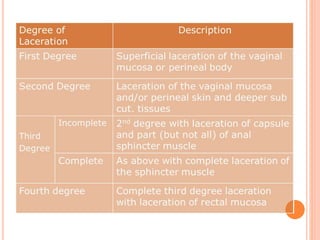
This document discusses various operative obstetric procedures including operative vaginal deliveries, cesarean sections, and episiotomy. Operative vaginal deliveries involve using forceps or vacuum extraction to assist with vaginal birth and may be indicated for prolonged labor, fetal compromise, or maternal benefit. Cesarean sections are performed by making incisions in the abdominal and uterine walls to deliver the fetus and may be indicated for dystocia, abnormal fetal position, or fetal distress. Episiotomy involves surgically enlarging the vaginal opening during birth to prevent tearing, facilitate delivery, and reduce birth time. Complications of these procedures include lacerations, infections, hemorrhage, and injury to the mother