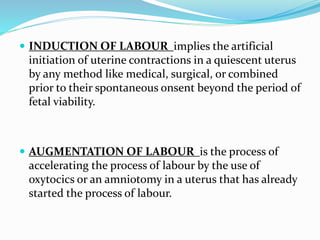
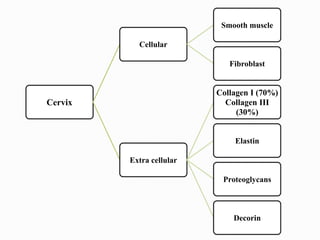
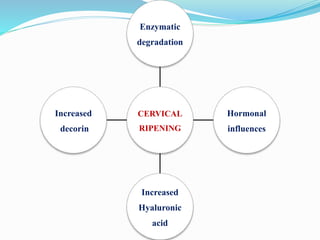
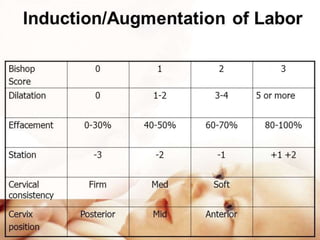
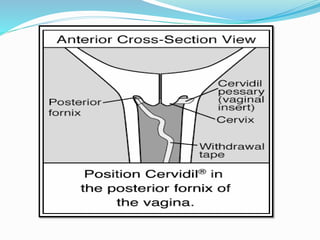
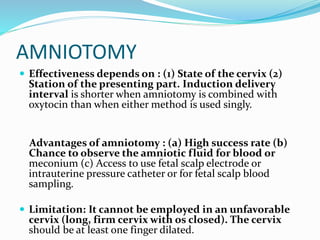
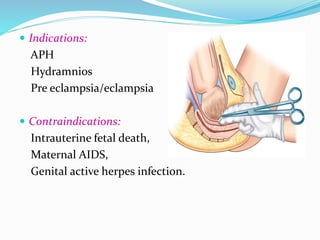
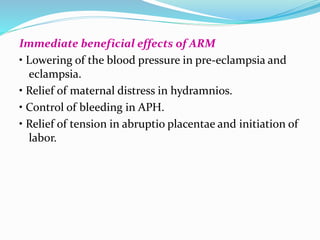
Induction of labour involves artificially initiating uterine contractions in a quiescent uterus prior to spontaneous labour. It requires an indication and favourable cervical conditions. The document discusses evaluating maternal and fetal conditions before induction, WHO recommendations, indications and contraindications. It also discusses risks of induction like increased caesarean rates. Methods of cervical ripening discussed include membrane stripping, hygroscopic dilators, prostaglandins and balloon devices. Having an unfavourable cervix requires ripening to improve outcomes of labour induction.