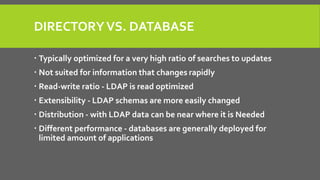
This document compares the directory services OpenLDAP and Active Directory (AD). It finds that OpenLDAP supports more LDAP standards, runs on more platforms, and has significantly better performance than AD, particularly for large user databases. While AD may be easier to use initially, OpenLDAP provides more flexibility, extensibility, and lacks the limitations of AD around schema, data access, indexing, and caching. In conclusion, the document states that while AD excels as a proprietary directory, OpenLDAP is a true standards-compliant LDAP directory.