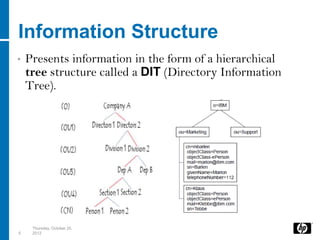
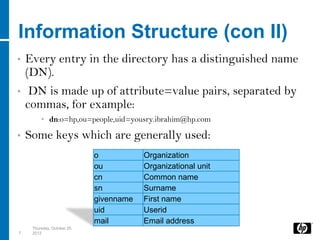
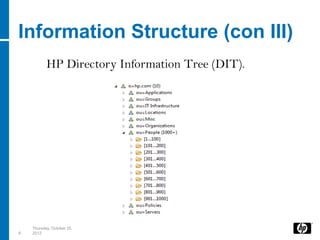
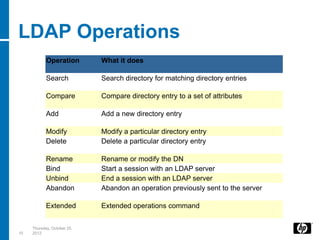
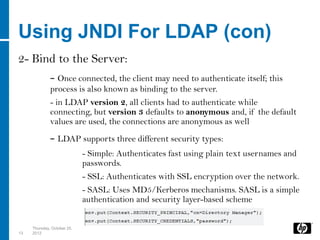
LDAP is a lightweight directory access protocol that provides access to distributed directory services over TCP/IP. It allows directories like Active Directory to be accessed and managed in a standard way without transactions or rollbacks. LDAP uses a hierarchical tree structure and entries with distinguished names and attribute-value pairs to represent information that can then be queried, added, modified, and deleted through LDAP operations. Java applications can use JNDI to connect to and search an LDAP directory by binding with credentials and issuing search requests with filters.