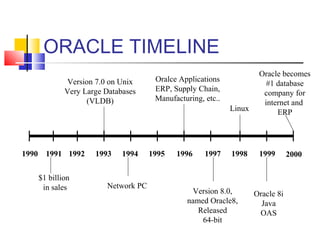
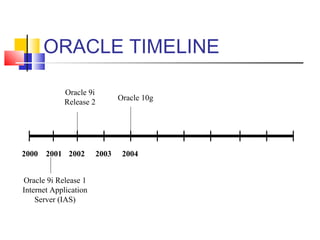
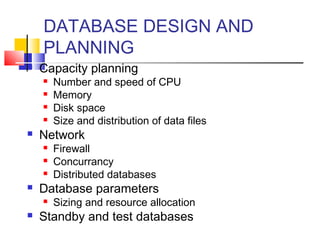
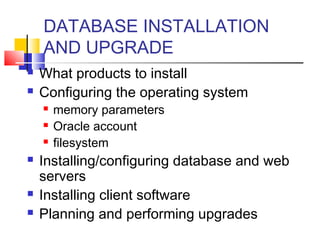
This document provides information about database administration for a course. It outlines the syllabus, software used including Oracle 10g, and skills expected including SQL and database design concepts. The document also summarizes the role of a database administrator and key tasks such as installation, backup and recovery, performance monitoring, security management, and responding to issues.