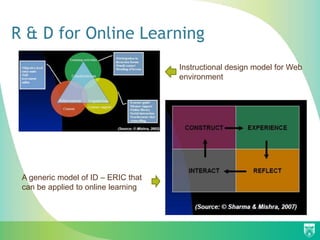
The document discusses the development and implementation of Open Educational Resources (OER) and eLearning in India, highlighting historical initiatives, challenges, and future possibilities. It emphasizes the importance of open licensing for educational material, collaborative course development using wiki-based tools, and the need for teacher capacity building. Additionally, it addresses the digital divide and promotes the integration of ICT in teacher education to enhance educational quality.