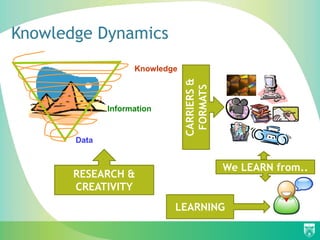
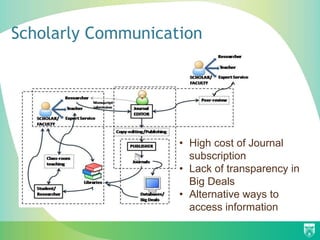
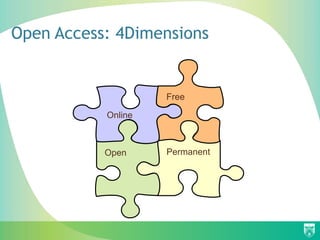
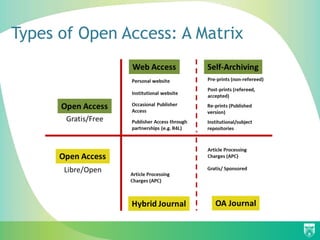
The document discusses the importance of education for sustainable development (ESD) and how it can be integrated into various education systems to prepare individuals for careers related to sustainability. It emphasizes the role of open access in facilitating the free exchange of knowledge essential for developing knowledge societies and addresses challenges like access to information. Additionally, it highlights initiatives and resources that libraries can adopt to support sustainable development and promote open access practices.