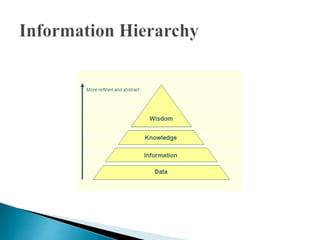
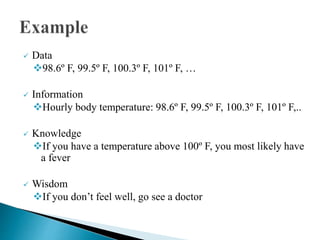
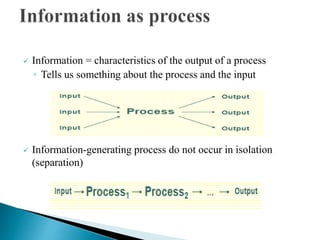
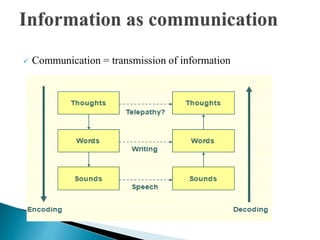
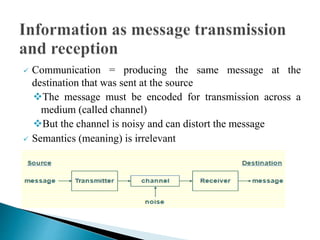
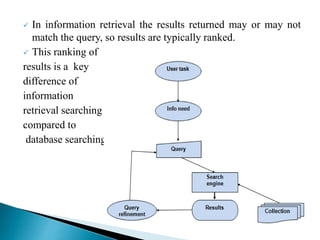
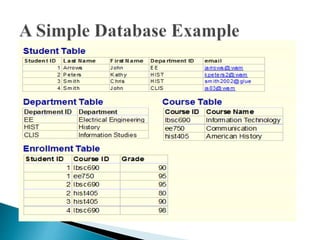
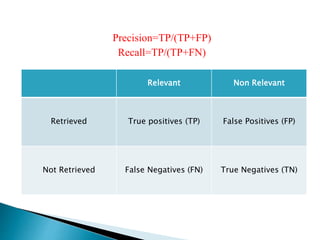
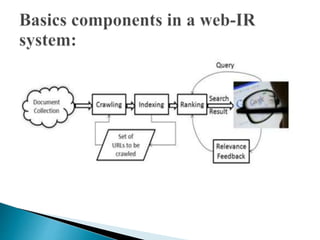
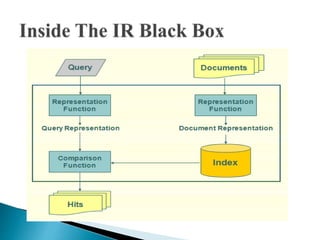
The document discusses key concepts related to information retrieval including data, information, knowledge, and wisdom. It defines information retrieval as the tracing and recovery of specific information from stored data through searching. The main aspects of the information retrieval process are described as querying a collection to retrieve relevant objects that may partially match the query. Precision and recall are discussed as important measures for information retrieval systems.