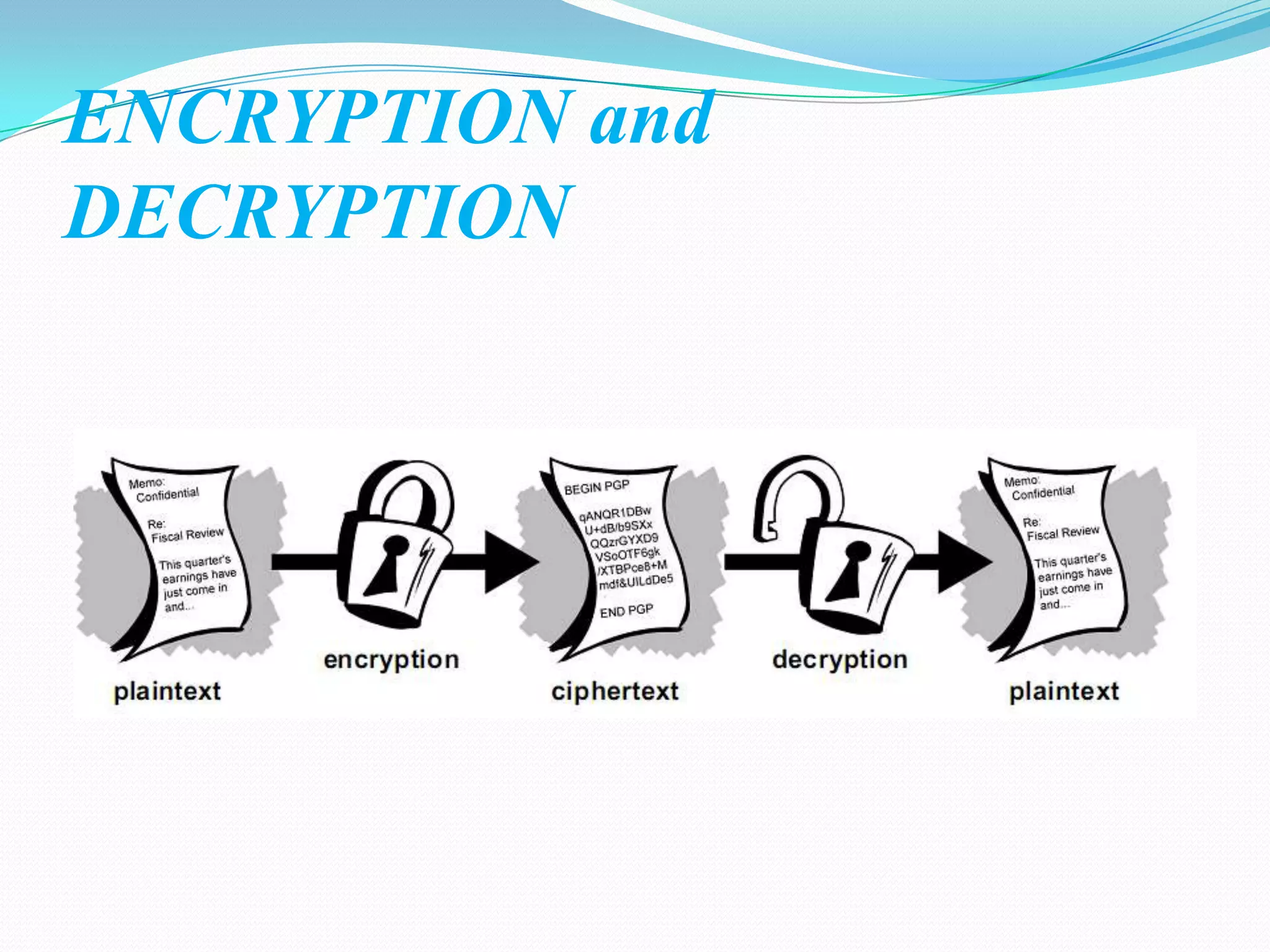
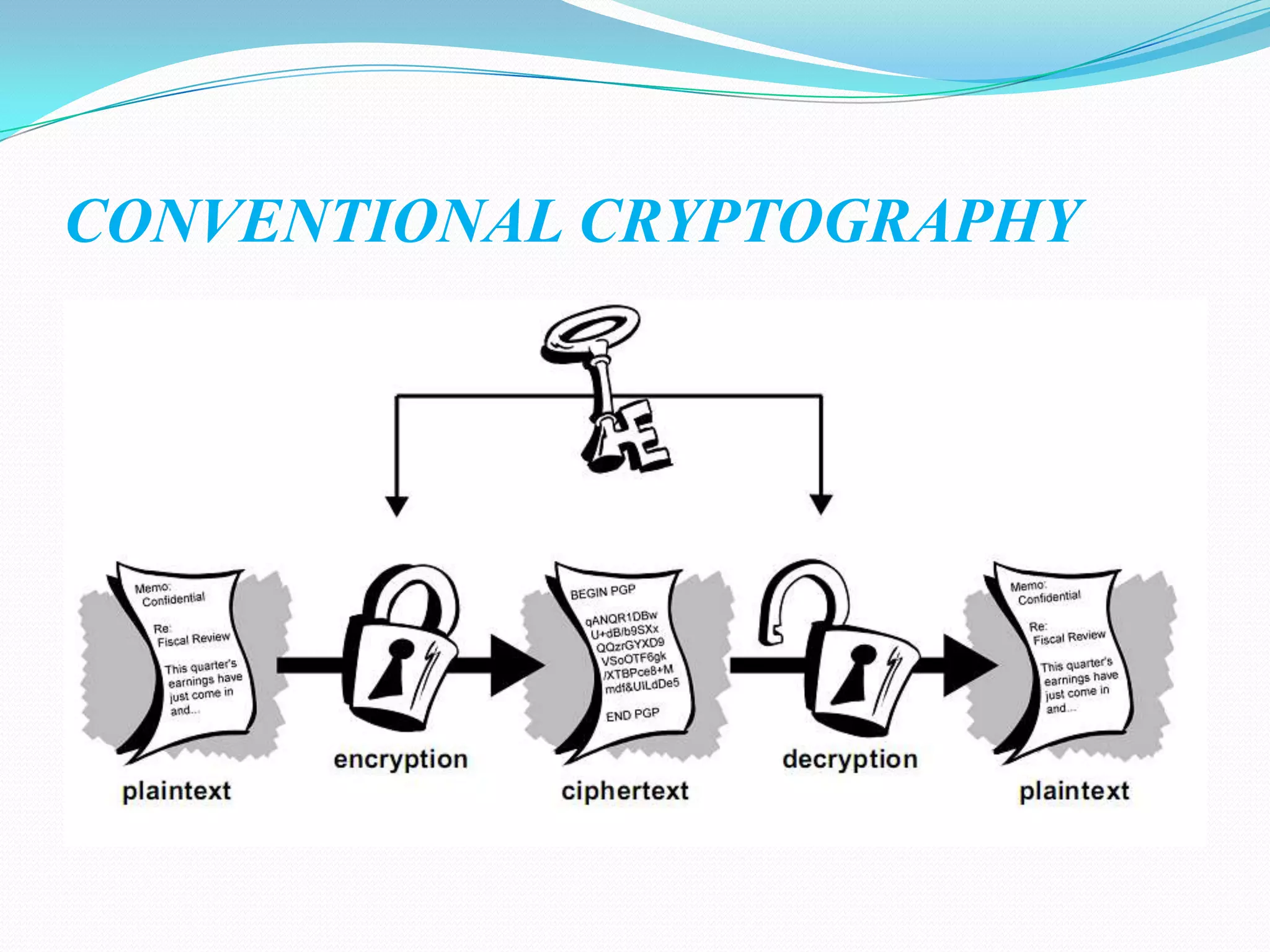
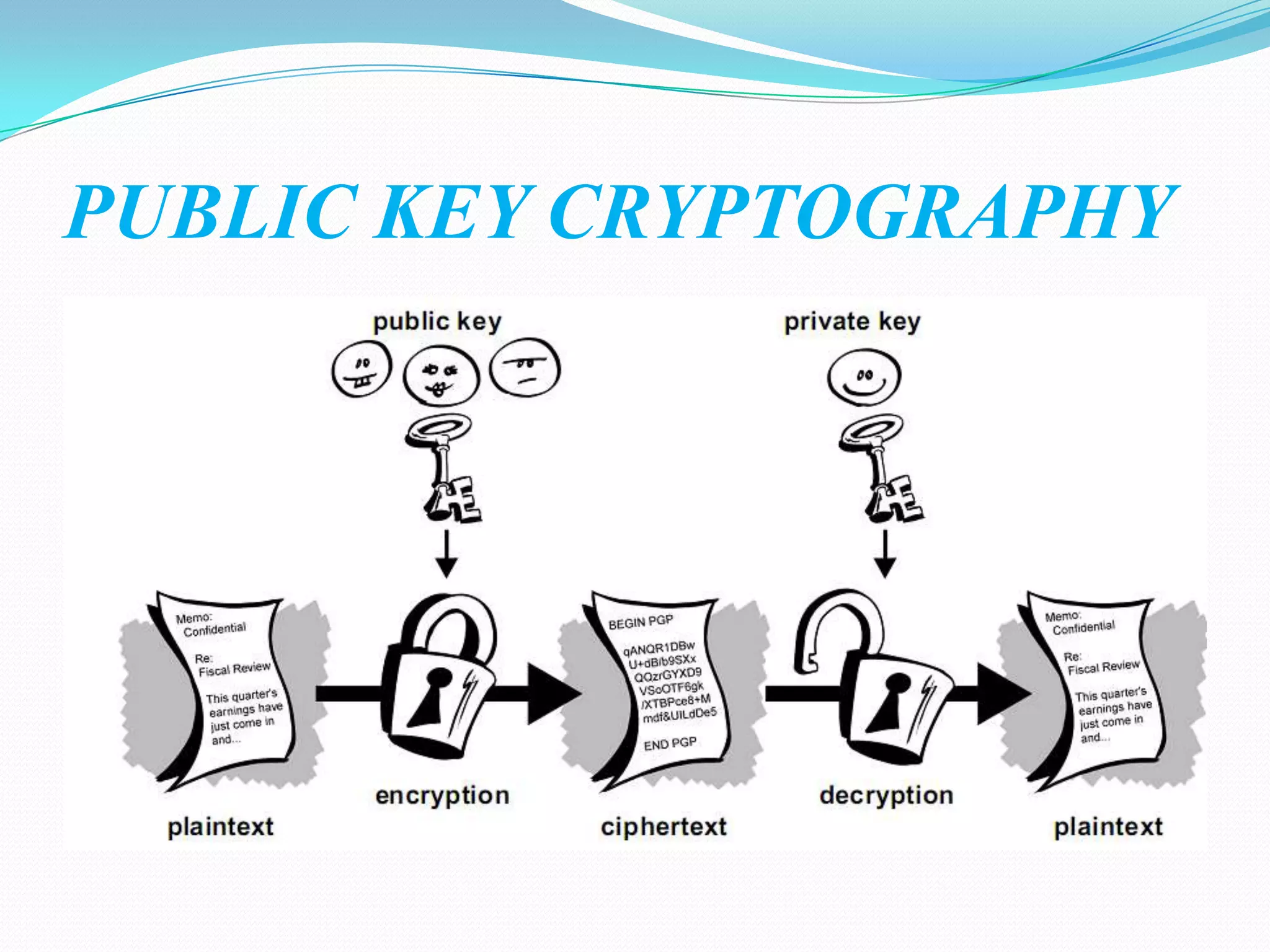
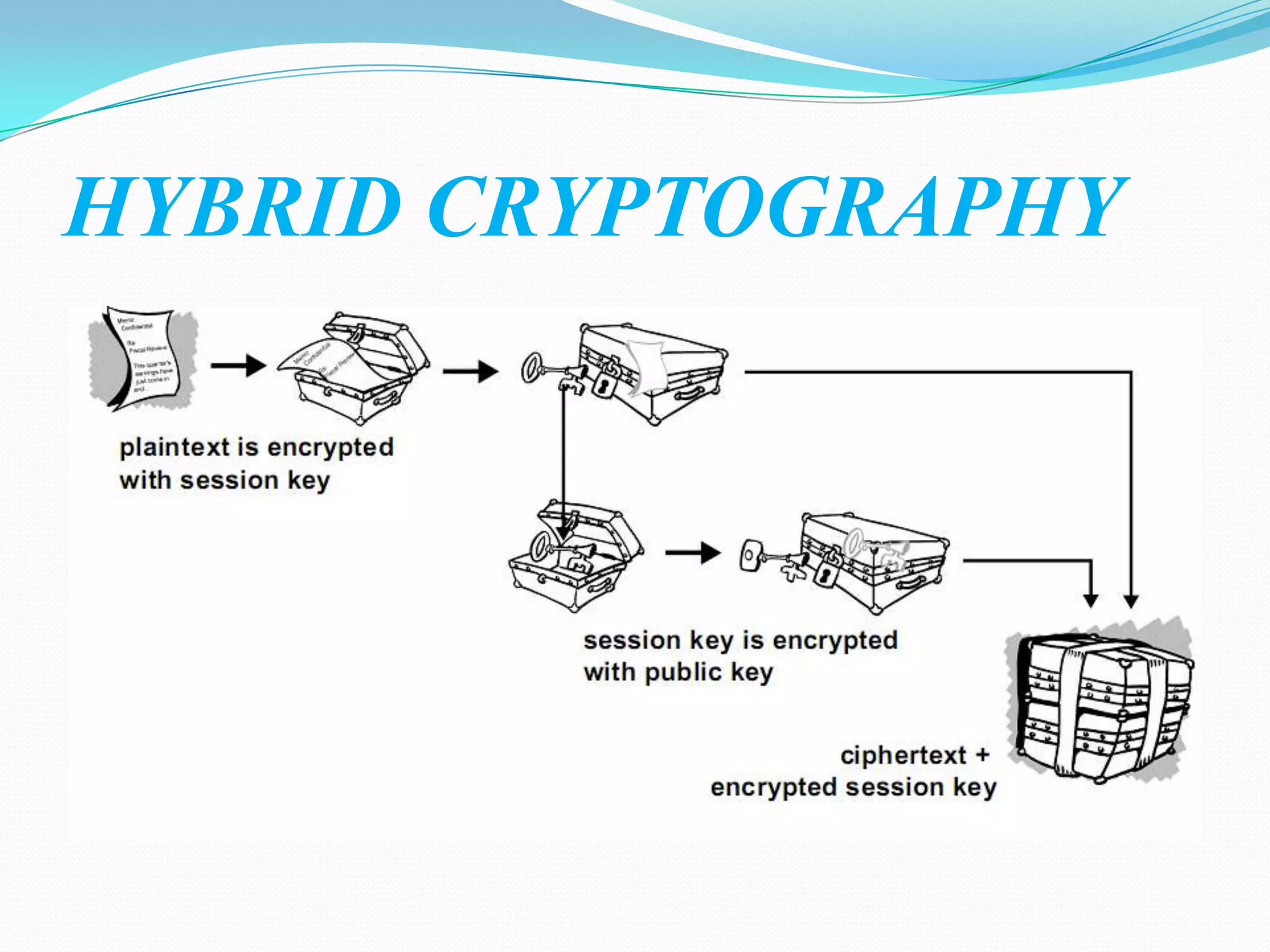
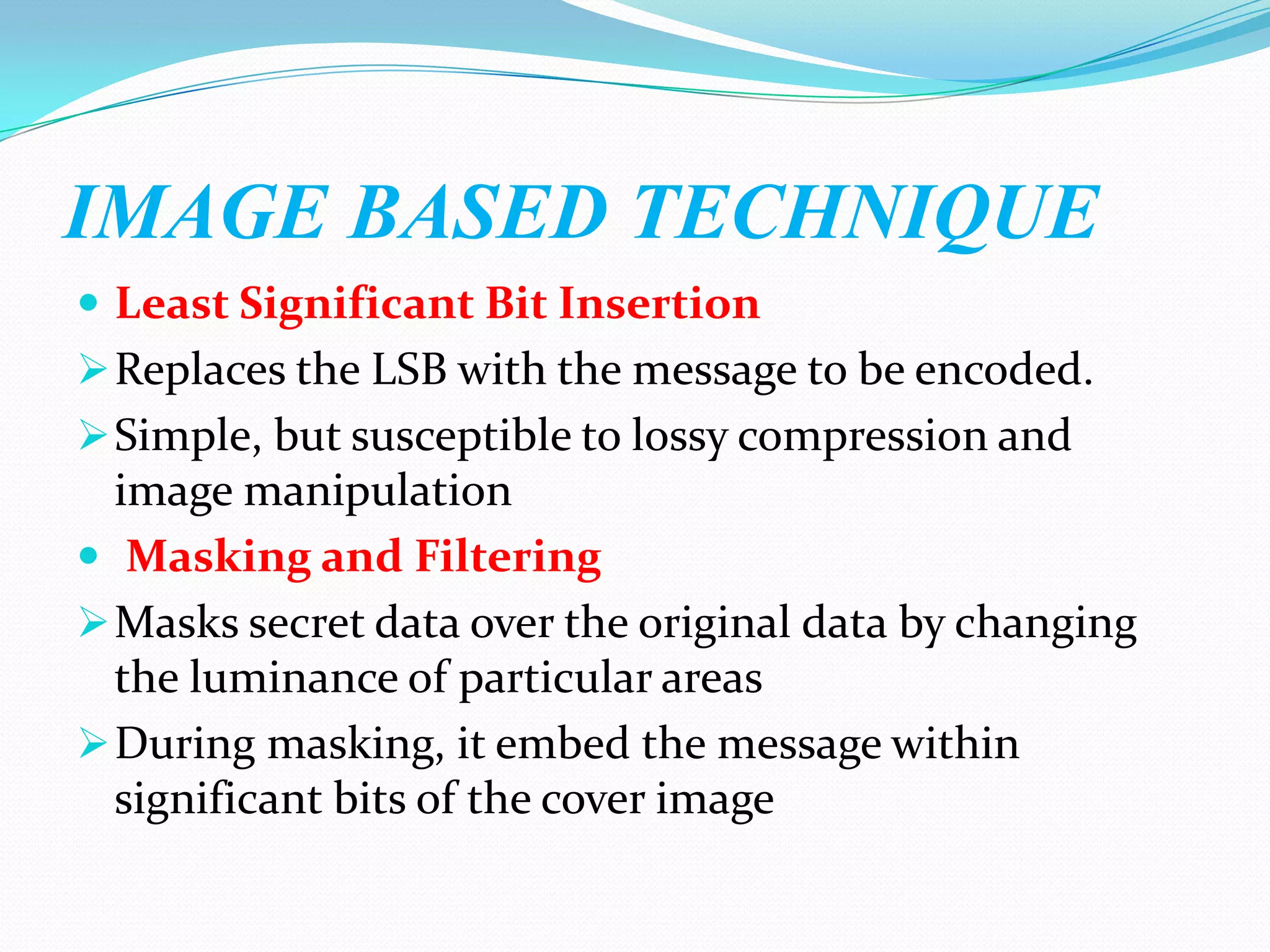
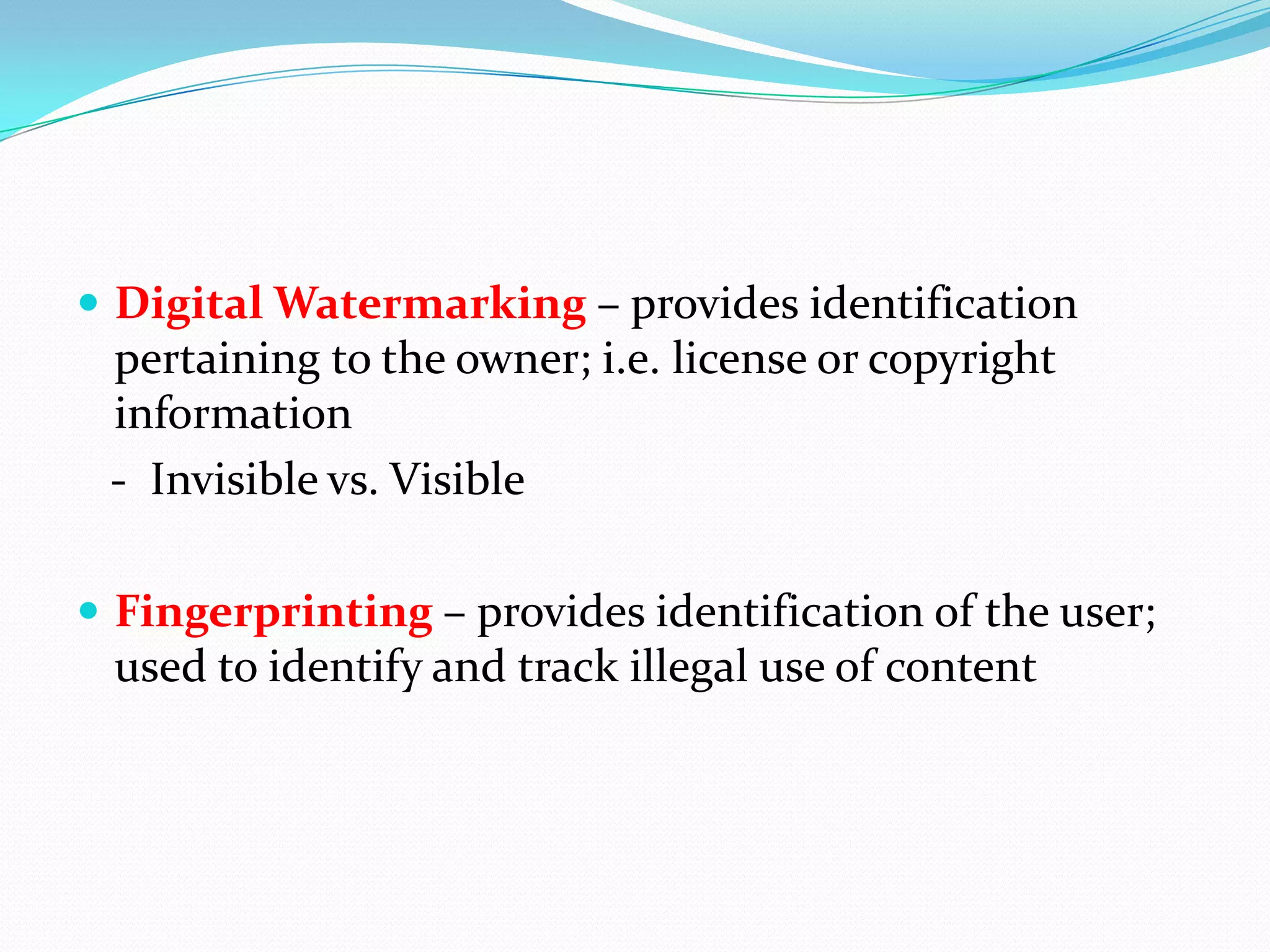
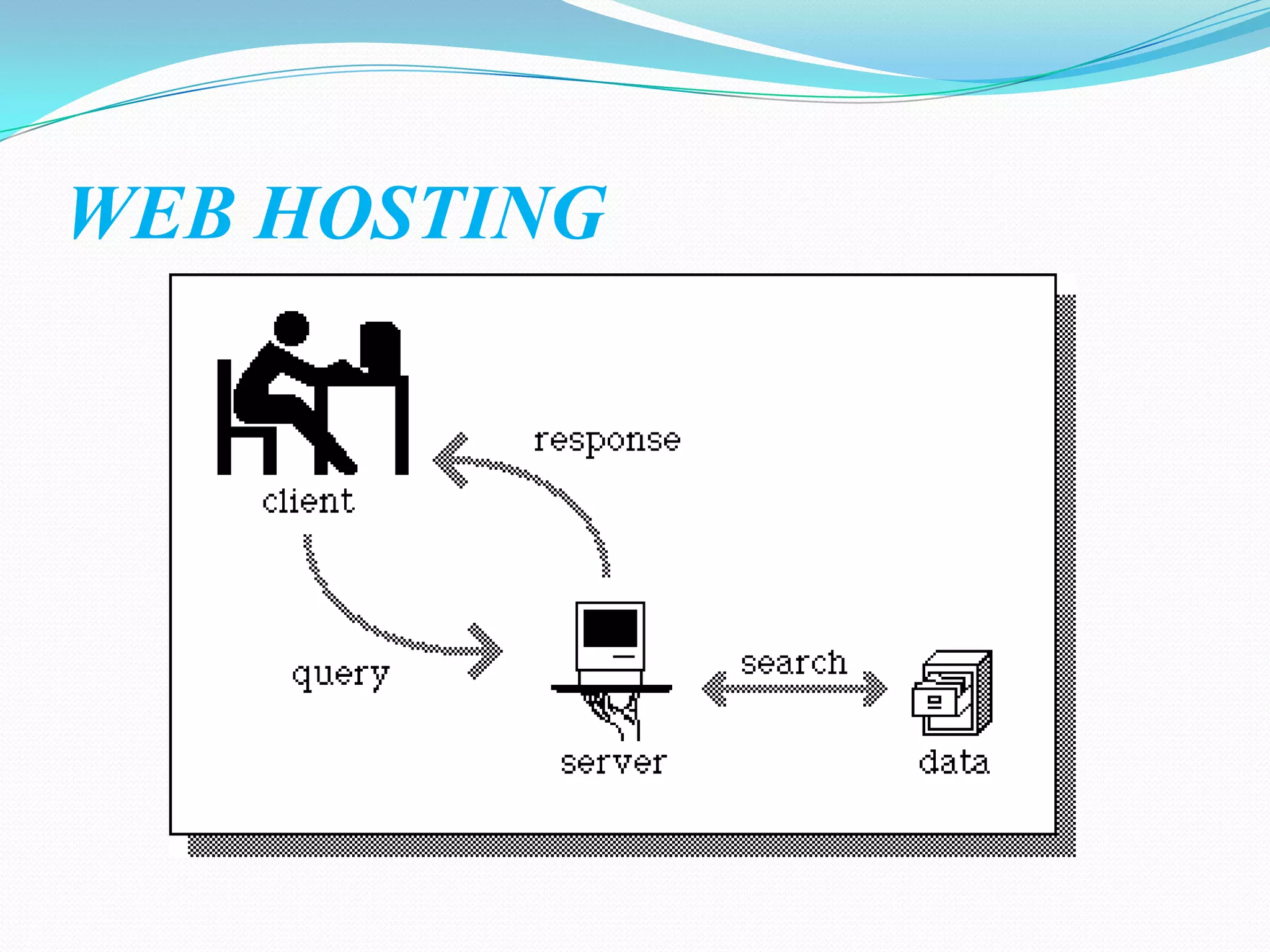
Cryptography involves encrypting data using mathematical algorithms and decrypting it back to plaintext. Encryption scrambles data into ciphertext while decryption returns it to readable text. Conventional cryptography uses a single key for both functions but public key cryptography uses different keys for encryption and decryption, eliminating the need to share secret keys. Hybrid cryptography combines the strengths of both by using asymmetric keys to distribute a symmetric session key for bulk encryption. Cryptanalysis aims to break secure communication while steganography hides messages within innocent-looking files like images and audio.