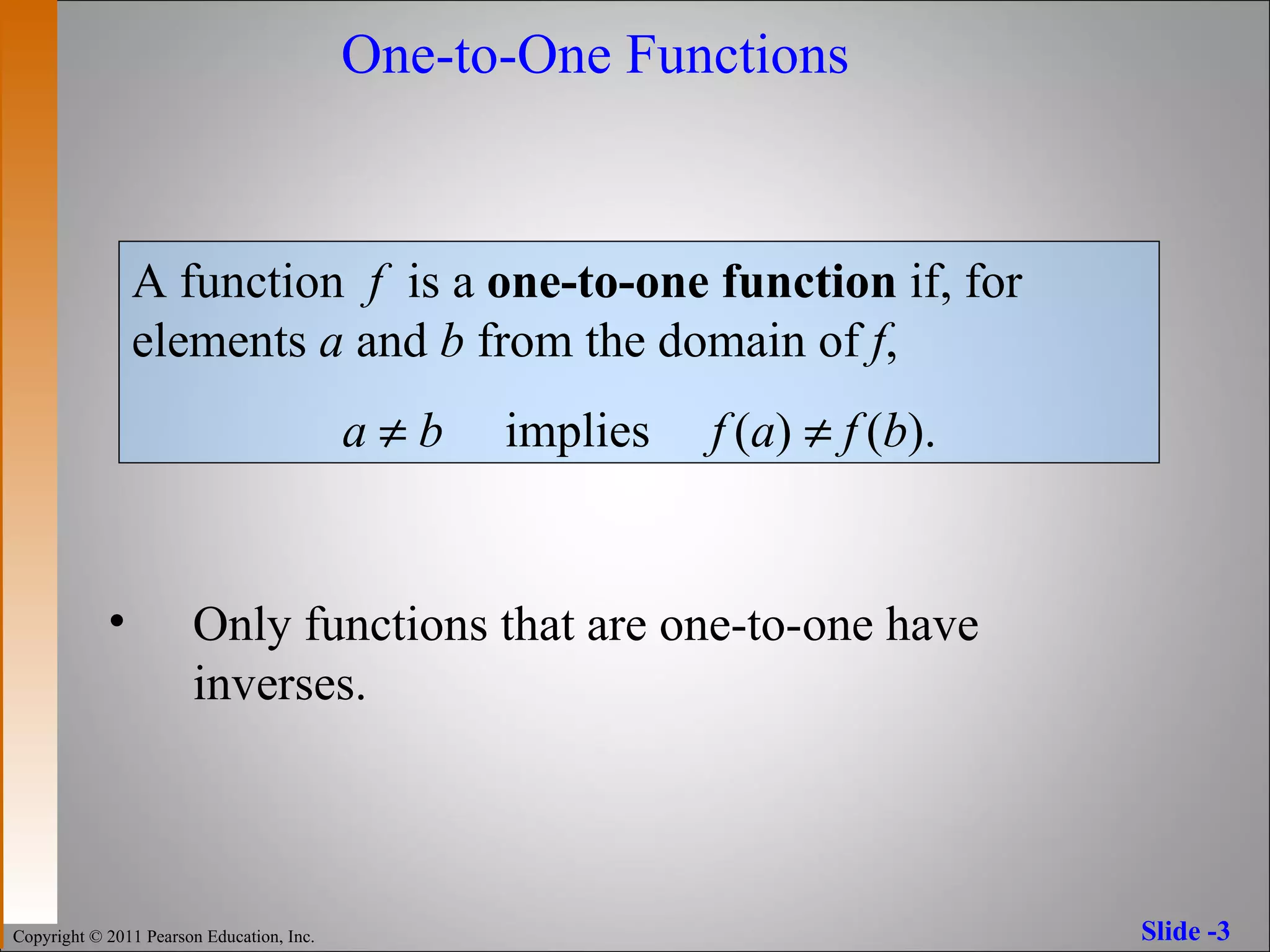
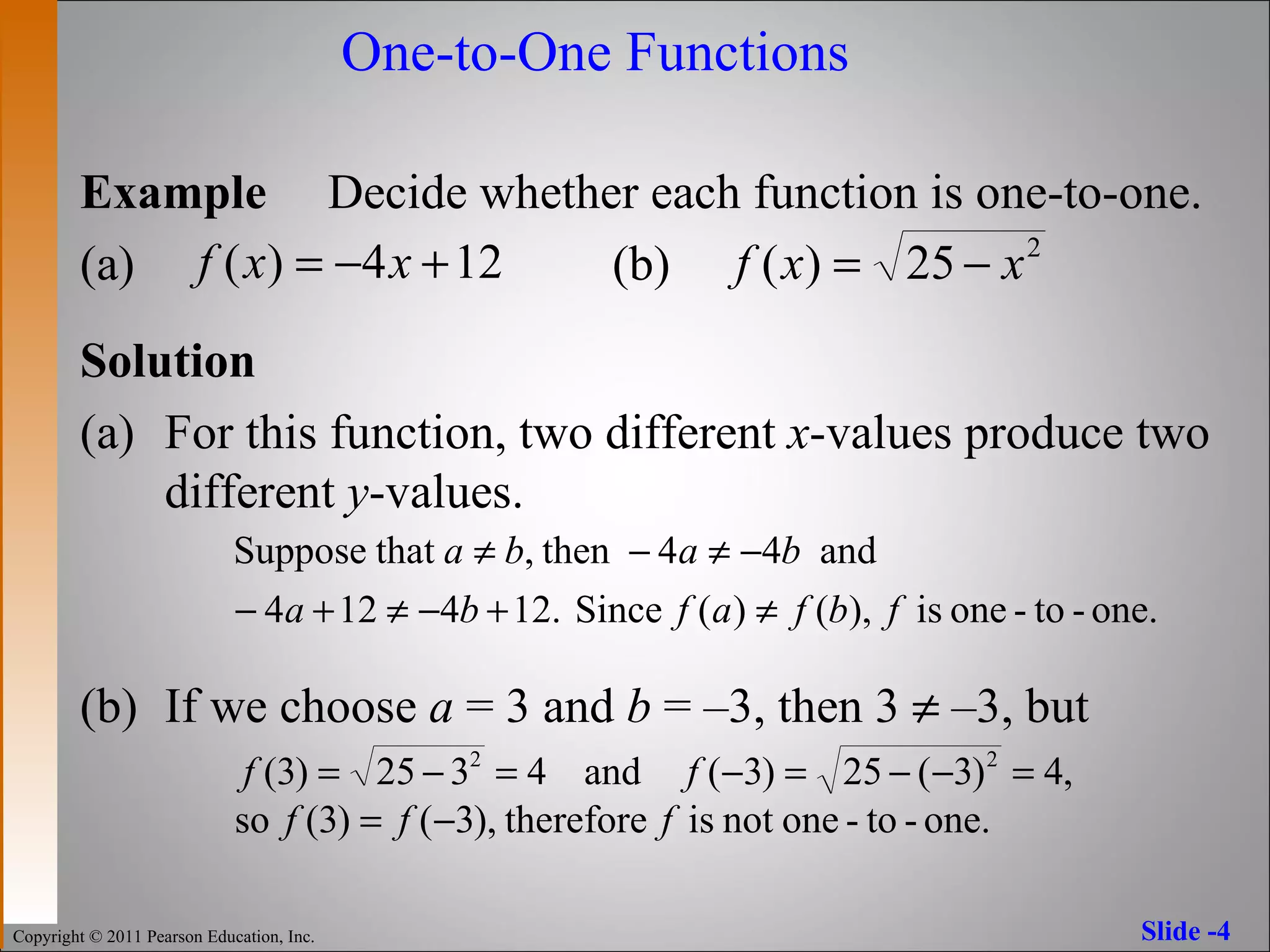
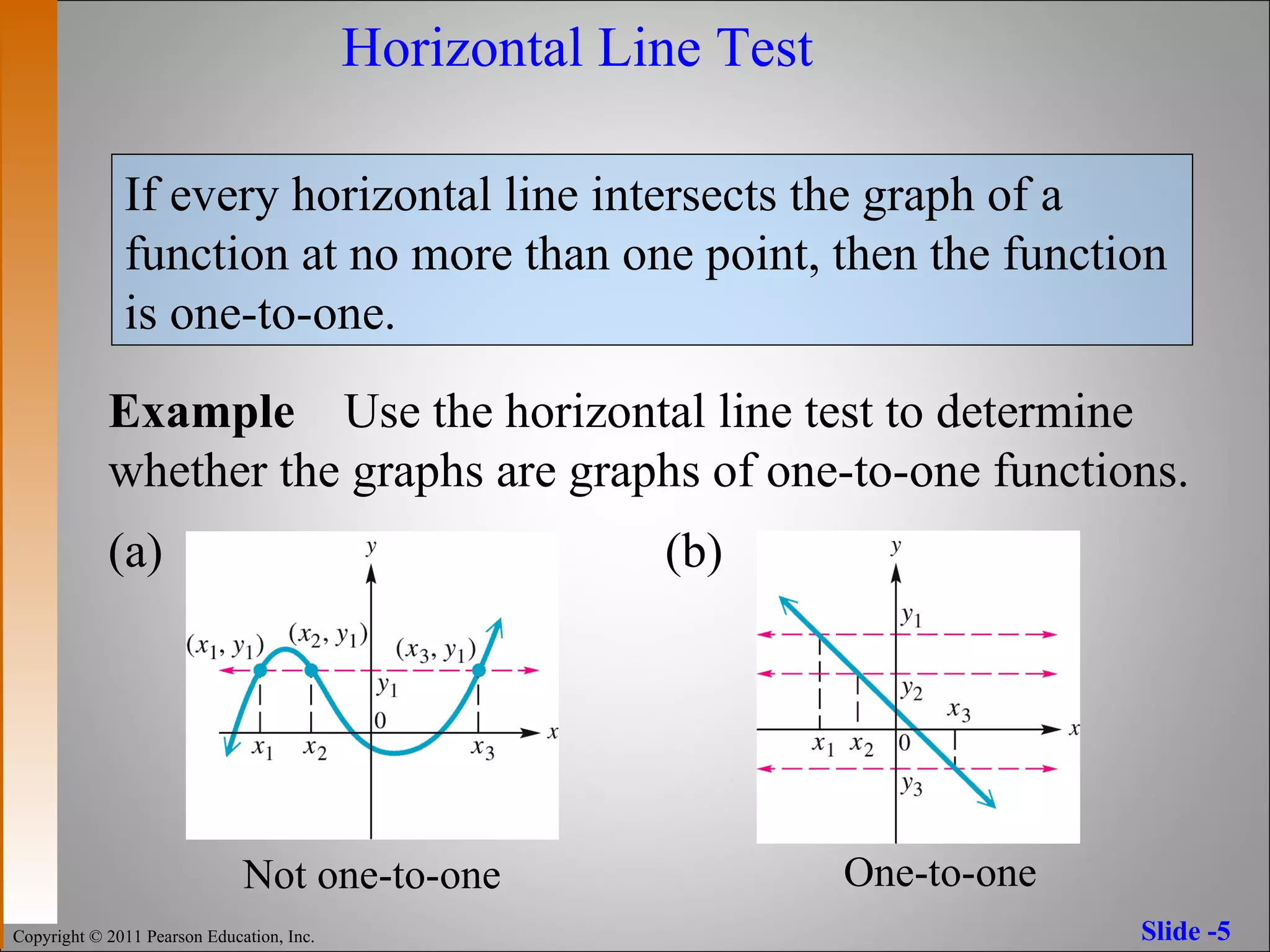
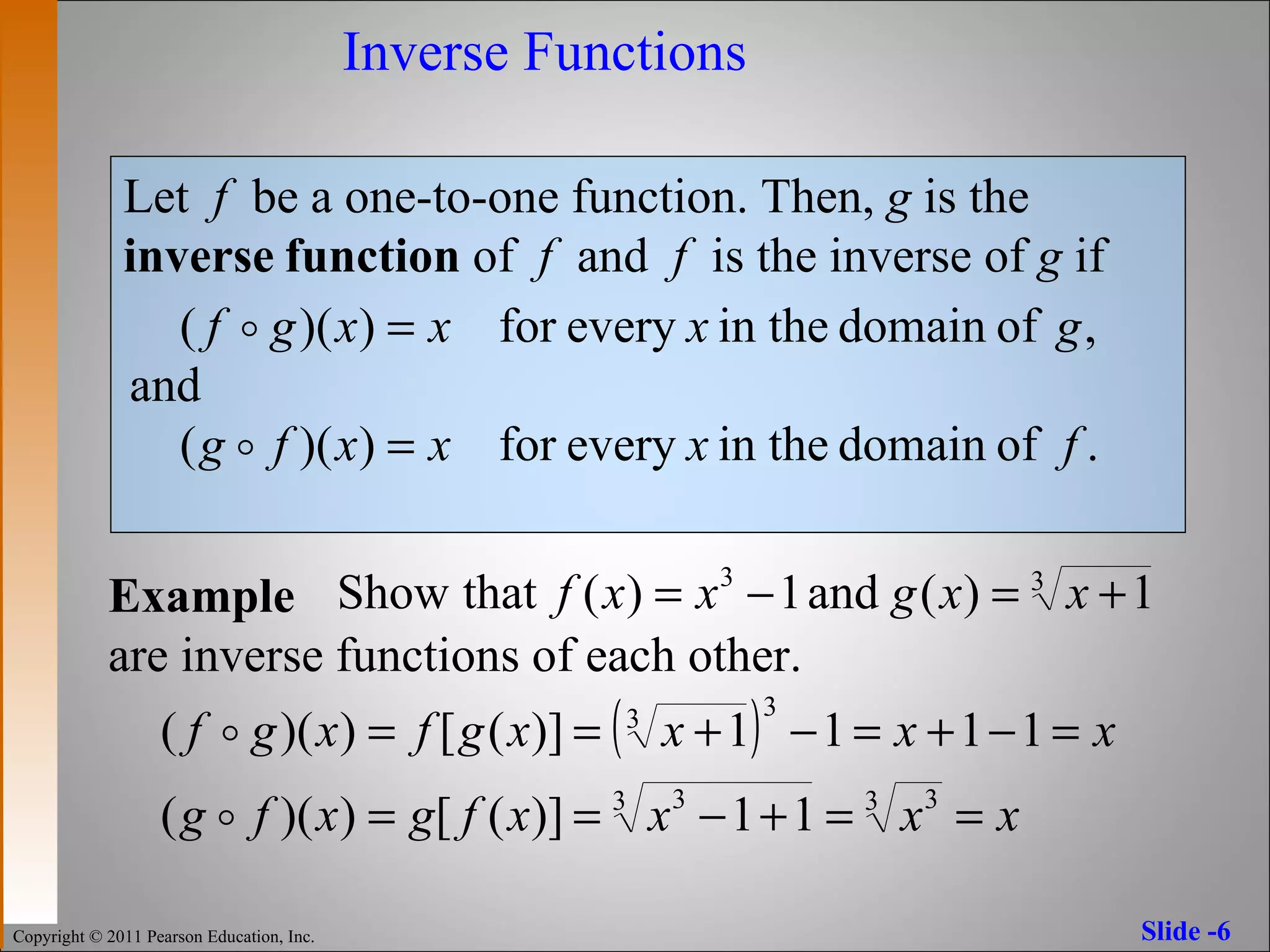
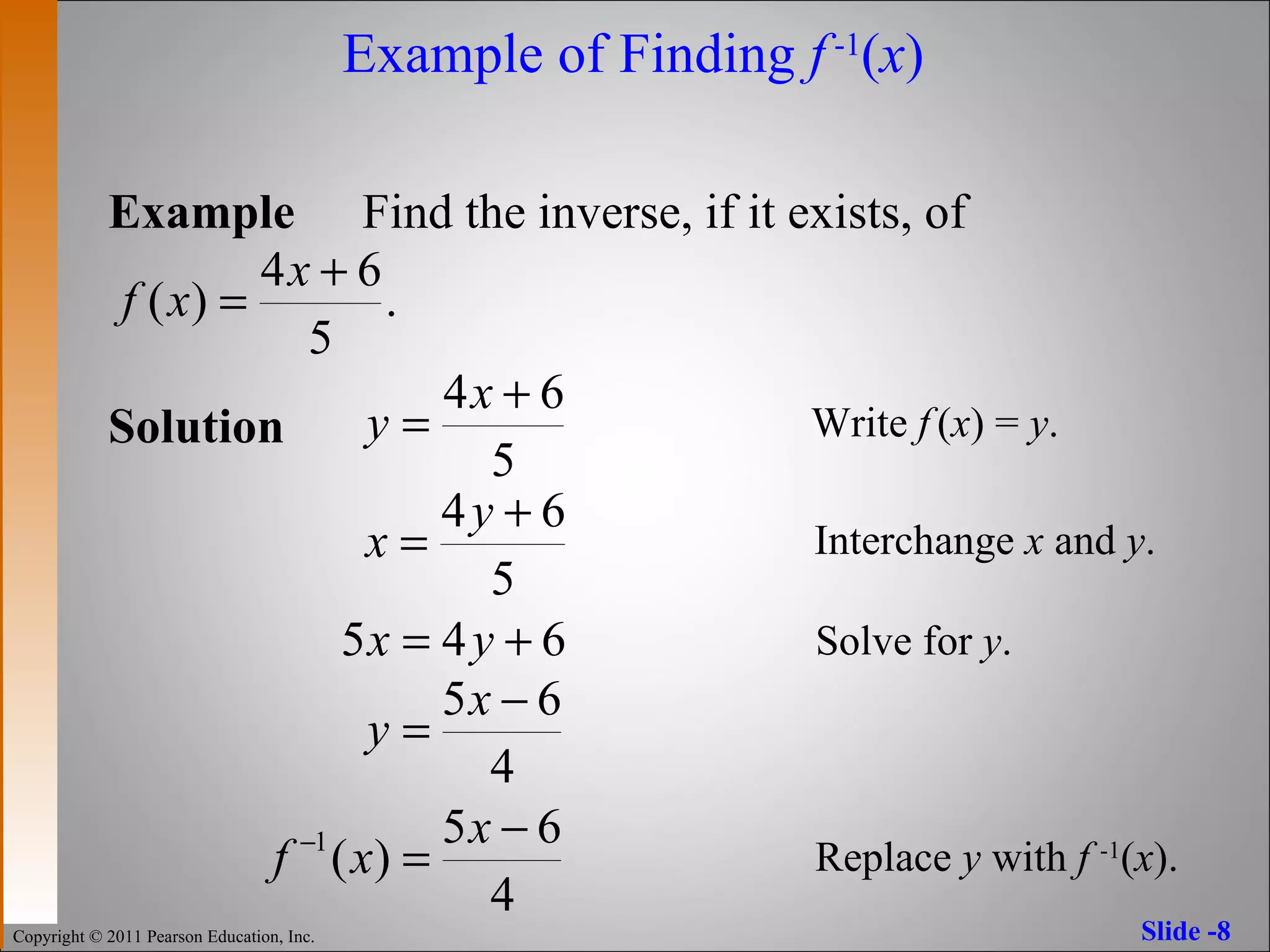
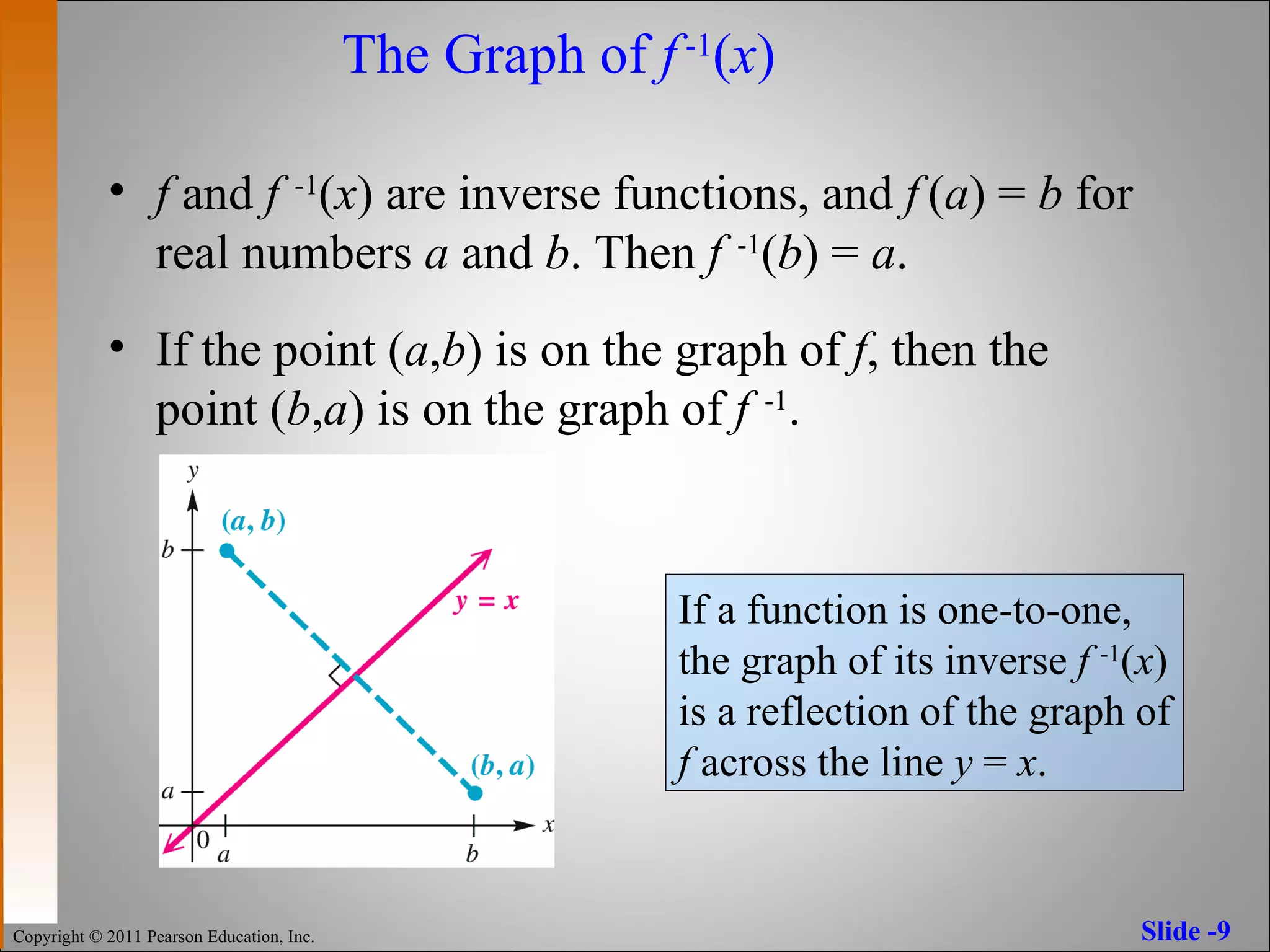
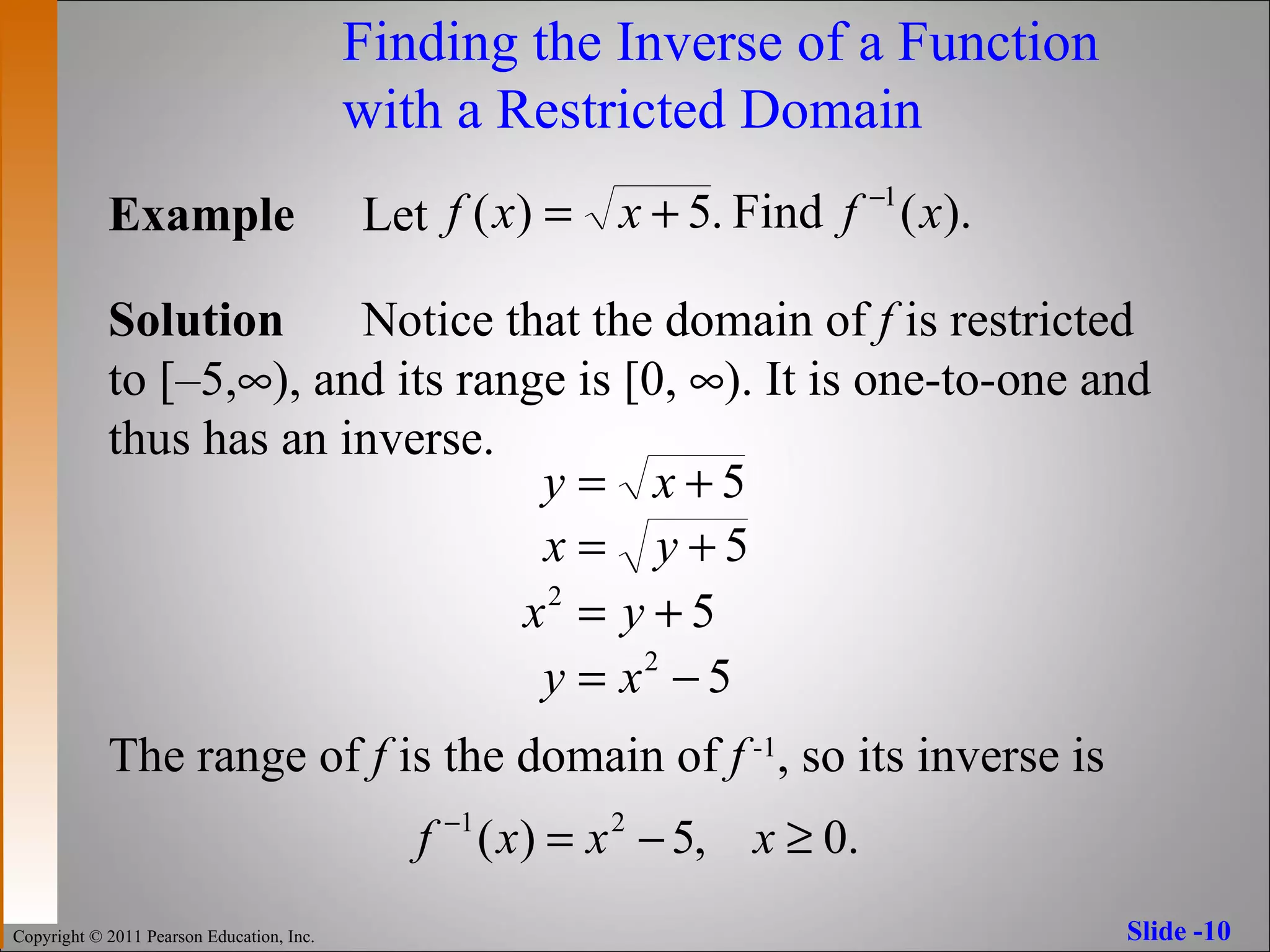
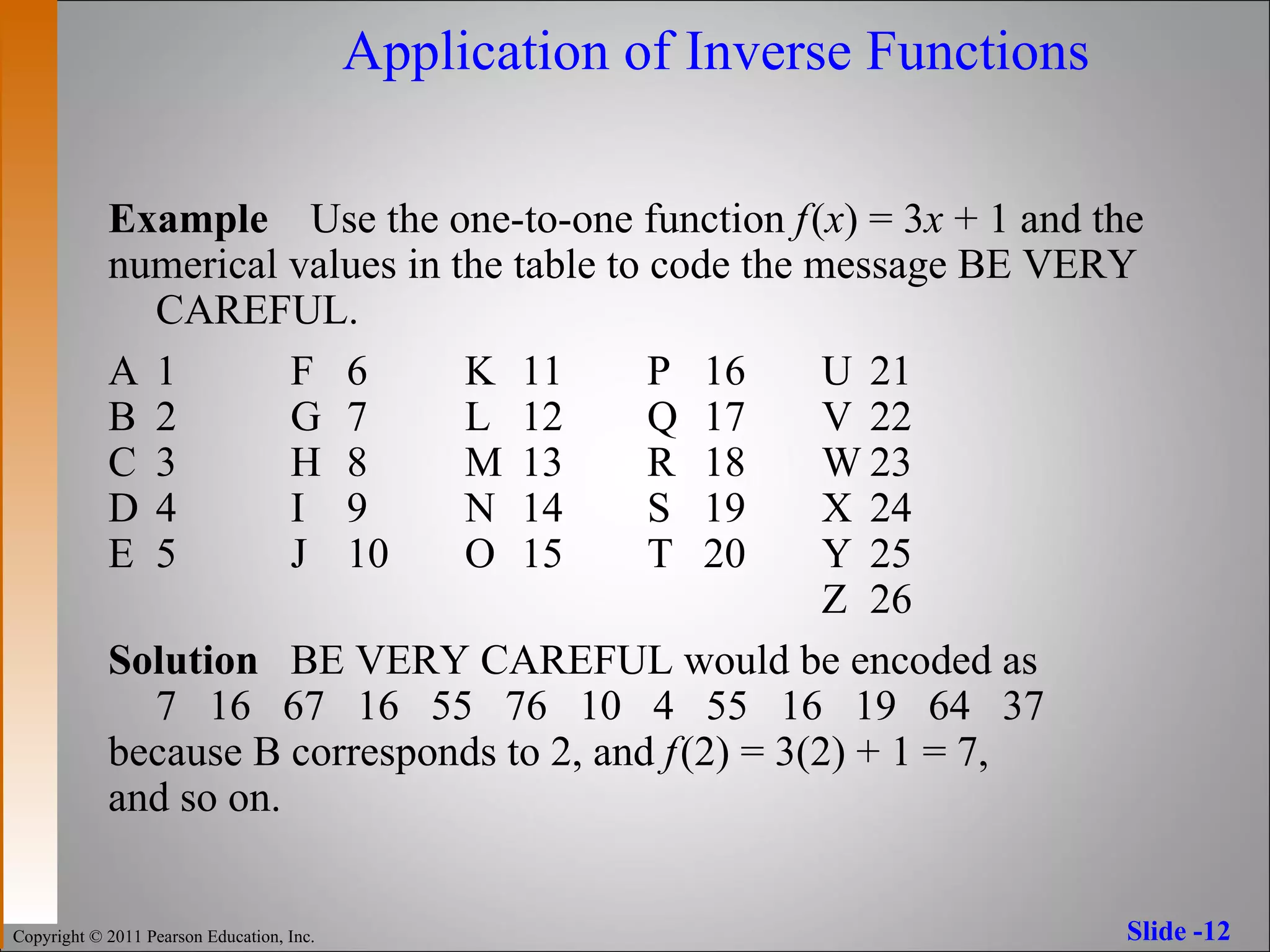
The document discusses inverse functions and one-to-one functions. It provides examples of inverse functions, explains how to determine if a function is one-to-one, and how to find the inverse of a one-to-one function. It also describes properties of inverse functions, including that the domain of a function is the range of its inverse and their graphs are reflections across the line y=x.

![Inverse Functions Example Also, f [ g (12)] = 12. For these functions, it can be shown that for any value of x . These functions are inverse functions of each other.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hat050501-111202170613-phpapp01/75/Inverses-One-to-One-2-2048.jpg)