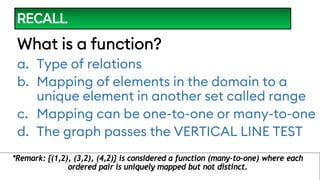
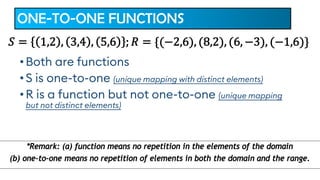
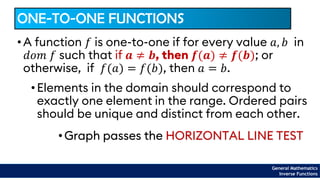
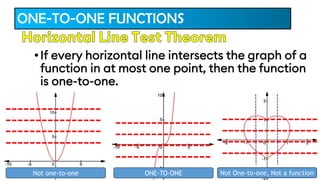
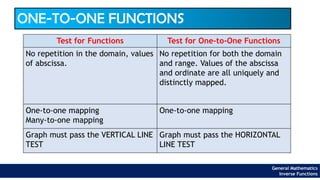
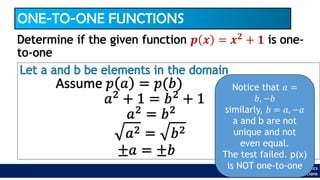
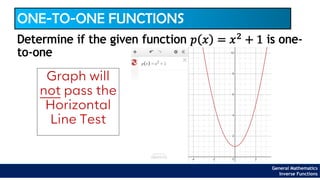
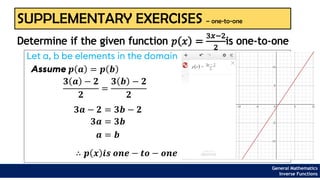
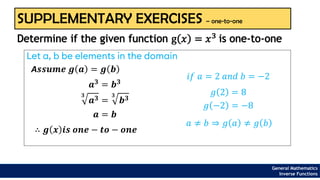
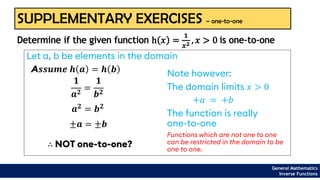
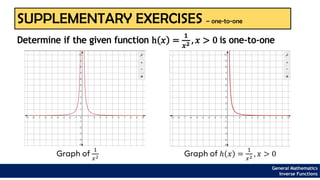
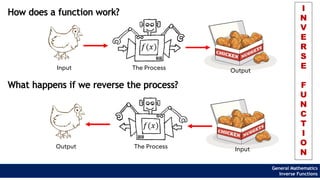
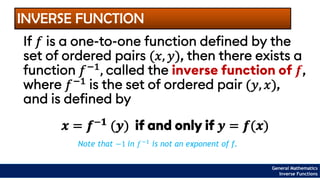
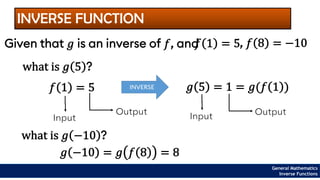
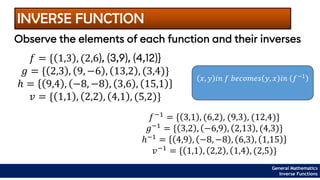
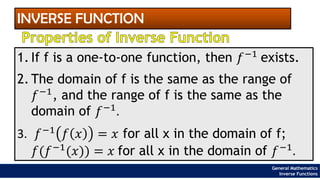
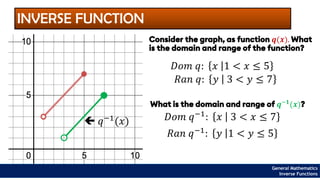
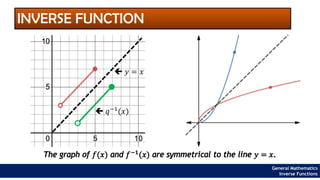
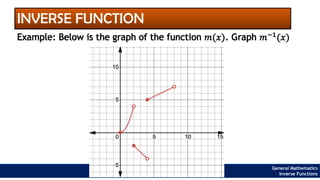
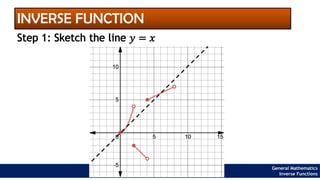
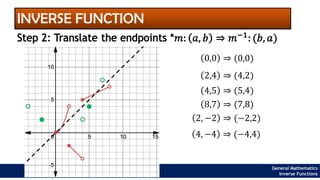
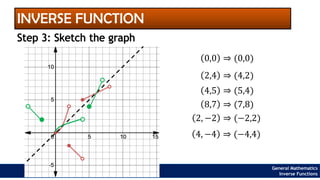
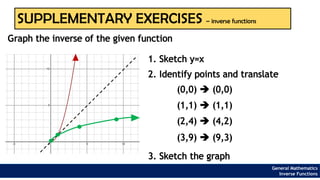
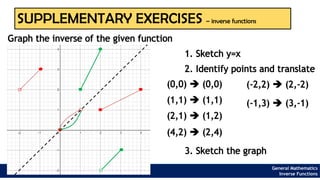
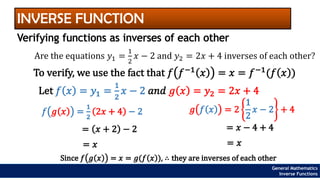
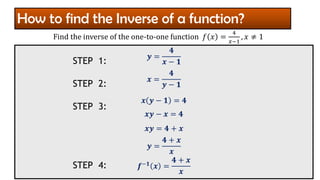
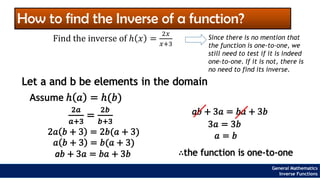
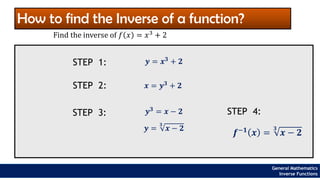
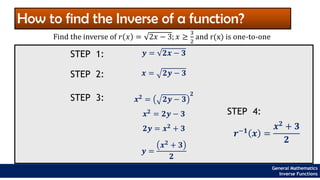
The document provides an overview of inverse functions in mathematics, particularly focusing on one-to-one functions and the criteria for distinguishing them. It explains the concepts of unique mapping, the horizontal line test, and the relationship between a function and its inverse, including the conditions under which an inverse exists. Additionally, supplementary exercises are included to reinforce the understanding of these concepts and verify if functions are inverses of each other.