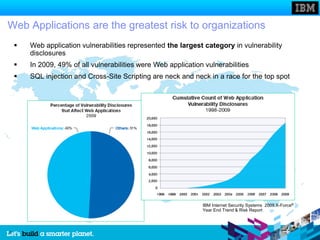
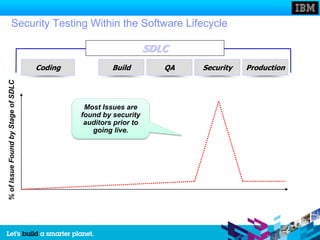
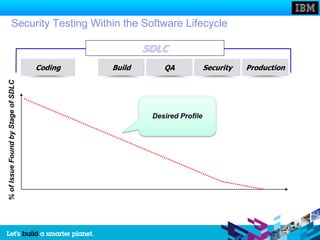
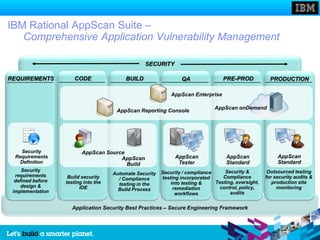
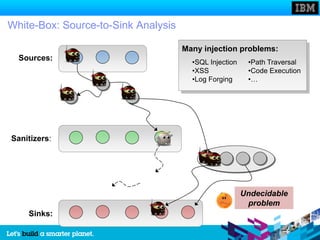
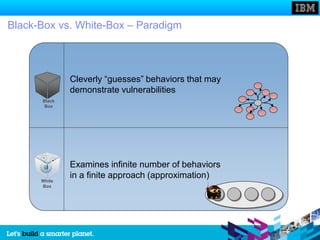
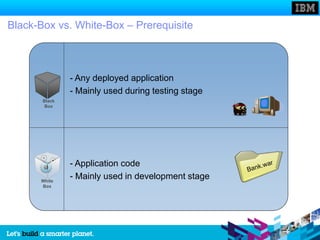
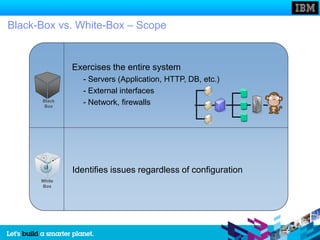
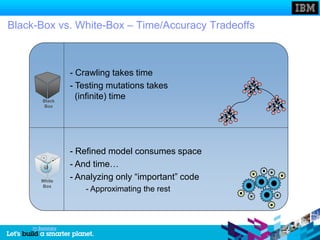
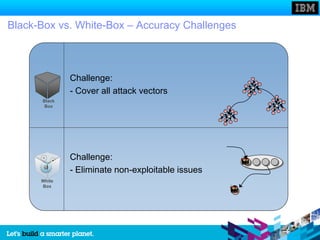
The document discusses static and dynamic technologies for securing web applications. It notes that web application vulnerabilities represented the largest category of disclosed vulnerabilities in 2009. The root causes of these vulnerabilities are identified as lack of security training for developers, underinvestment in security from organizations, and increased complexity of mission critical online applications. Both static (white box) and dynamic (black box) security testing approaches are described, with their respective strengths and weaknesses discussed. The document argues that combining static and dynamic analysis can provide the greatest accuracy in identifying potential security issues.