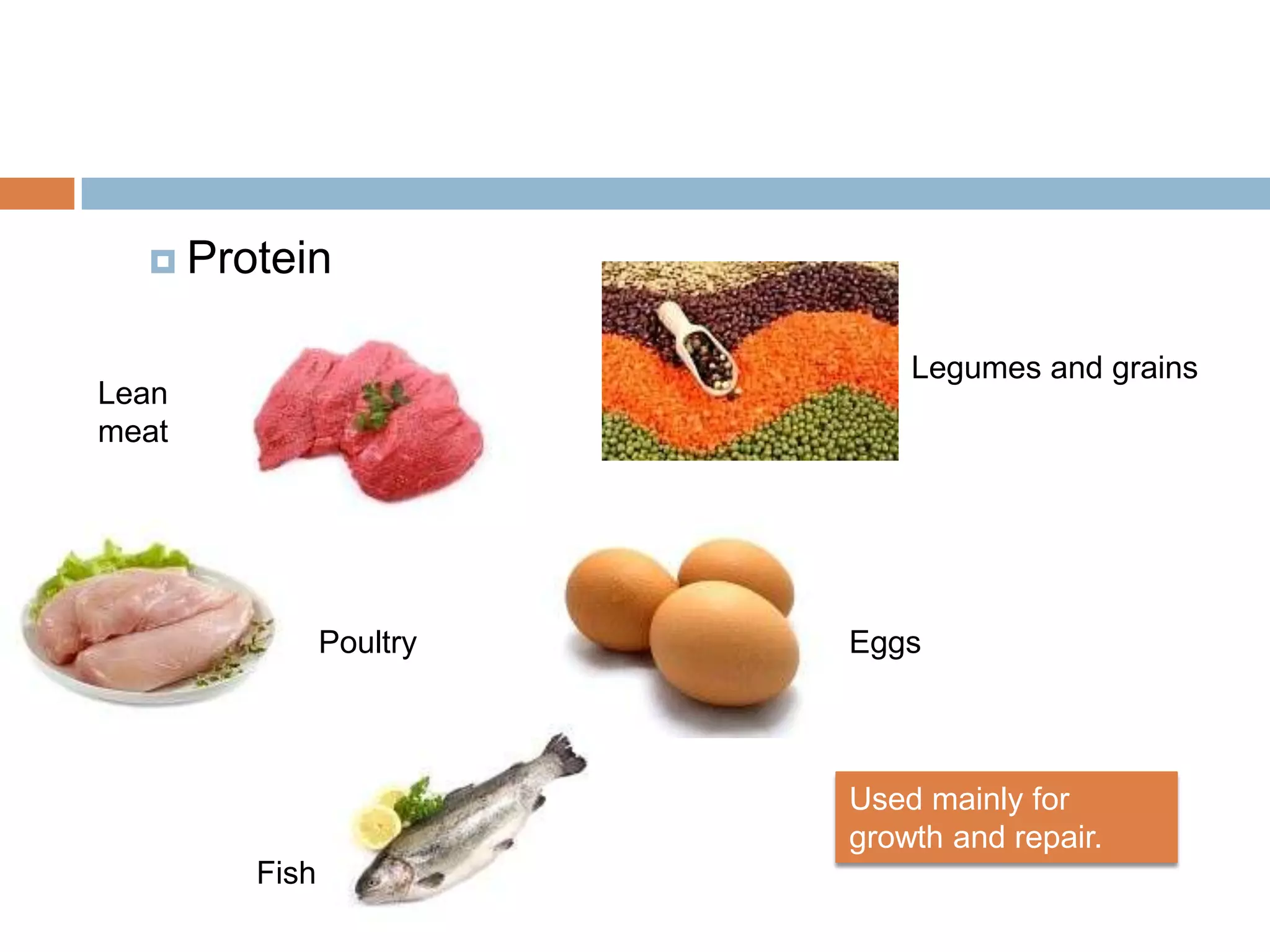
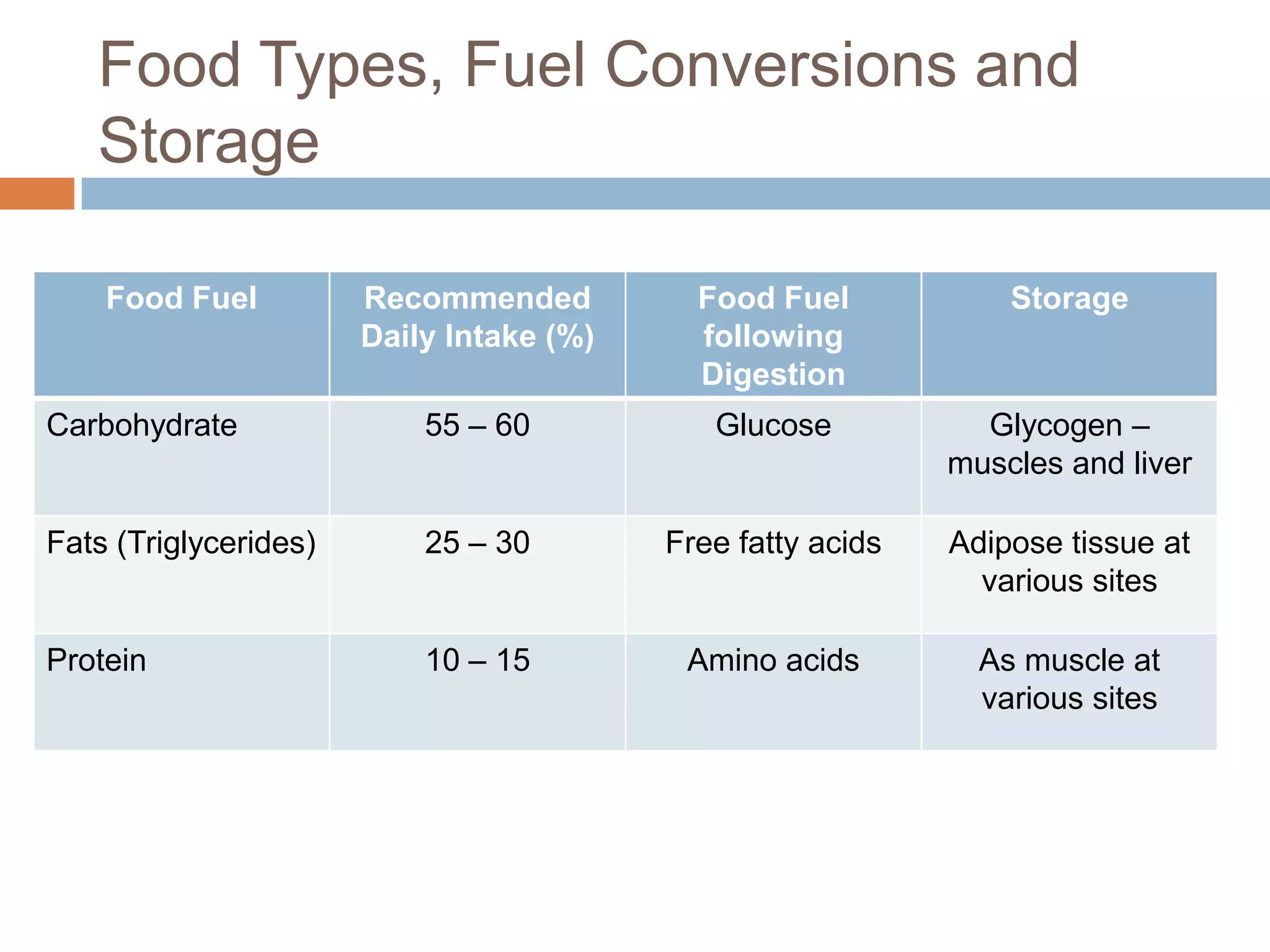
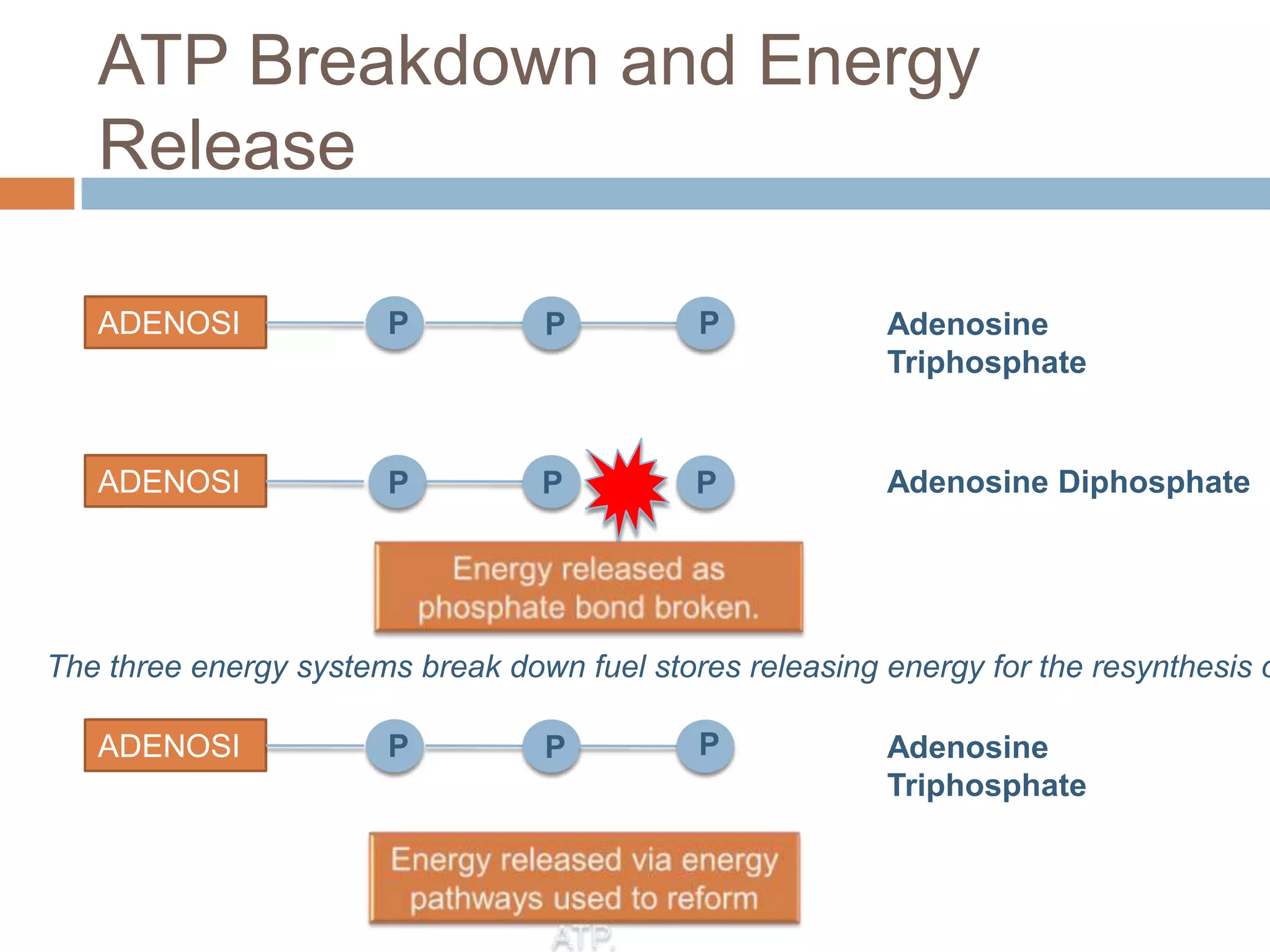
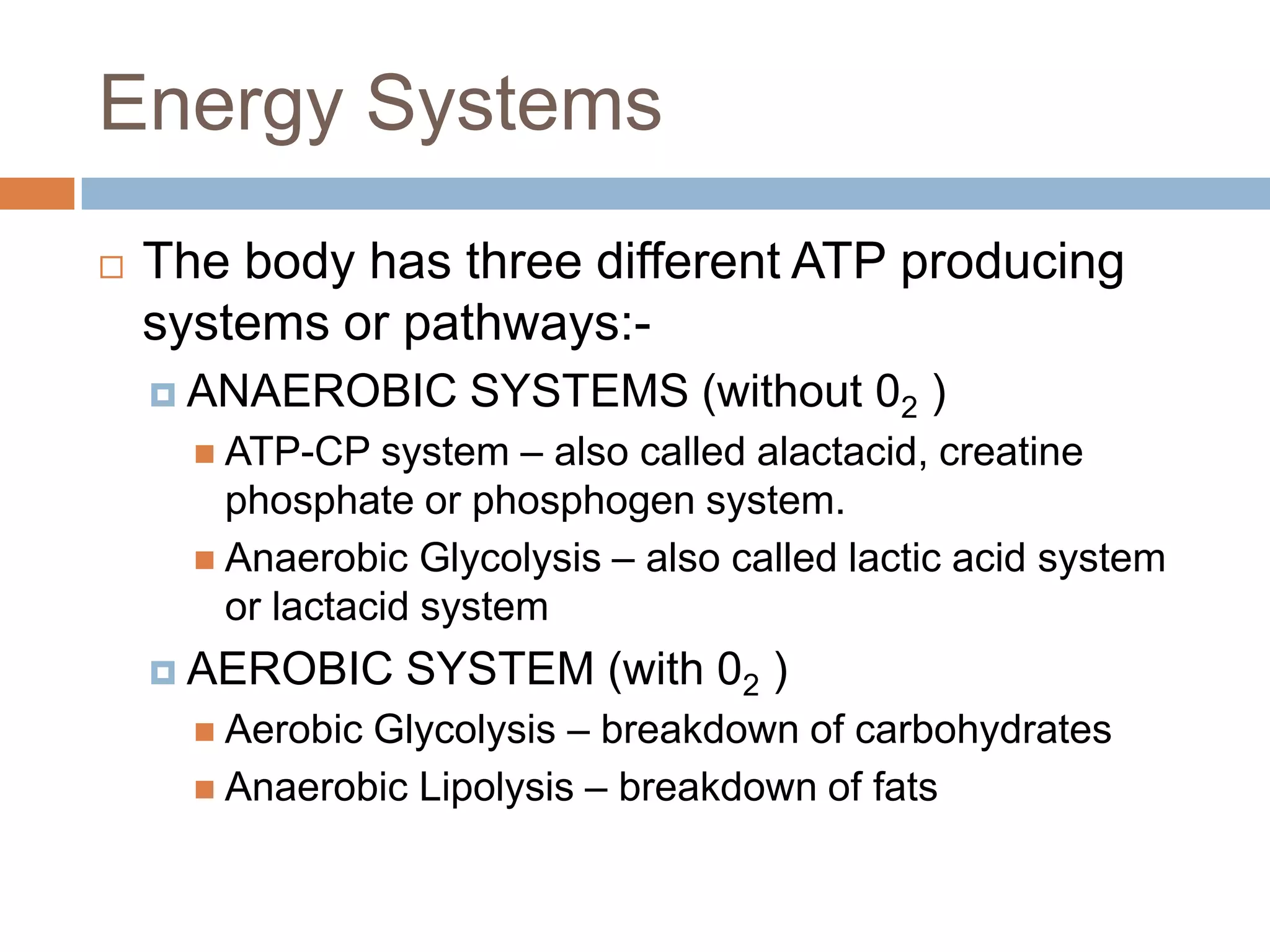
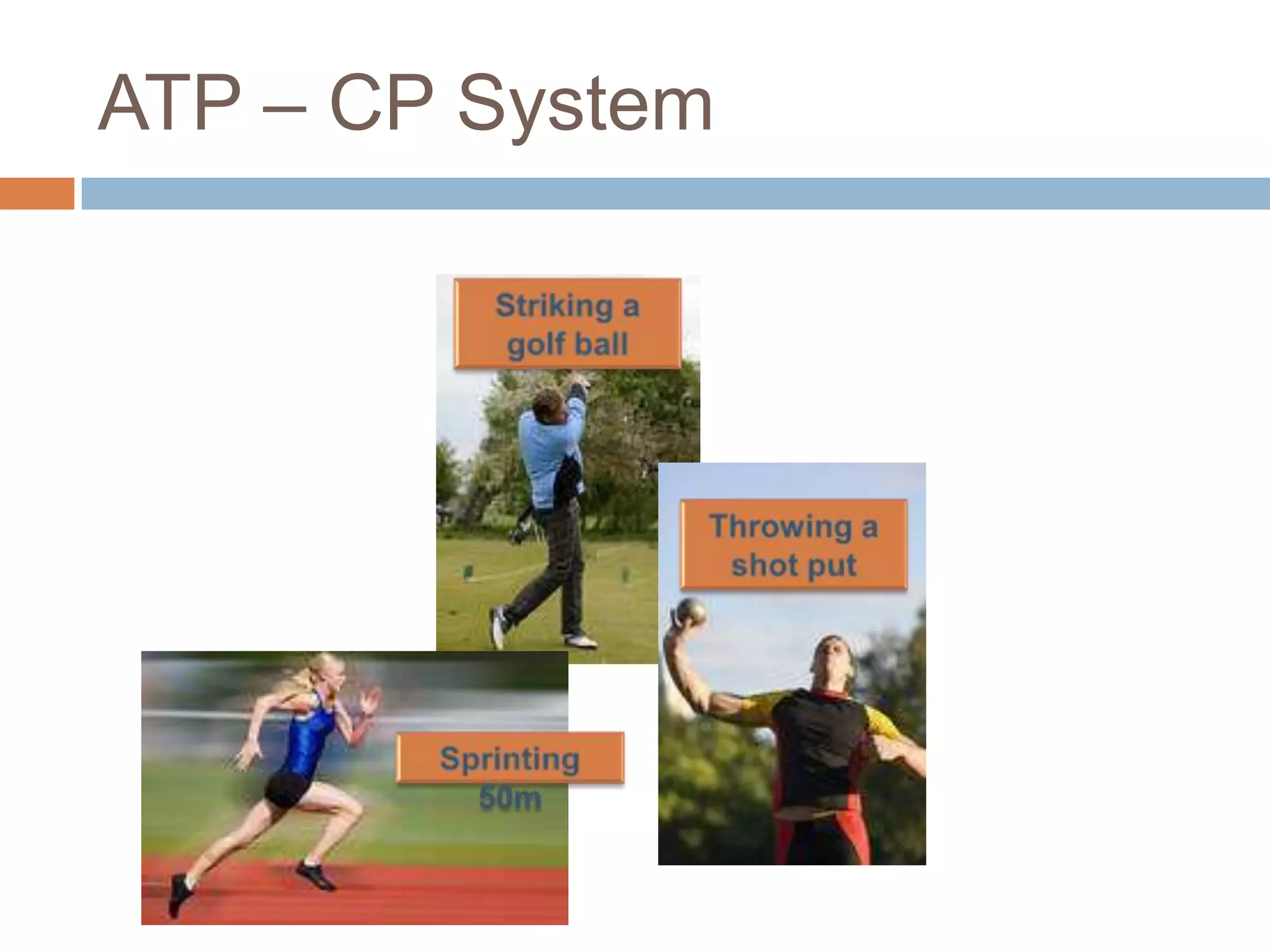
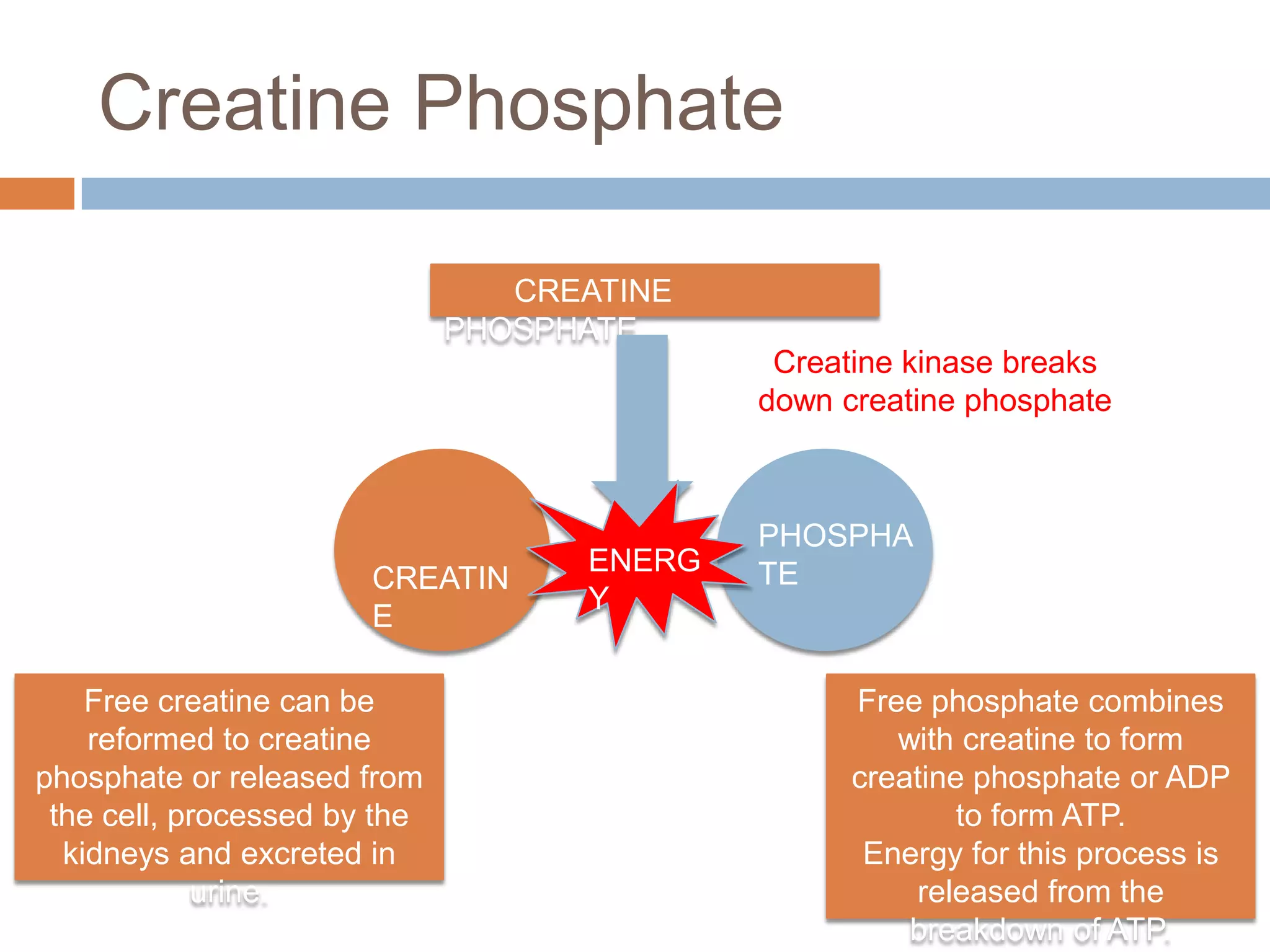
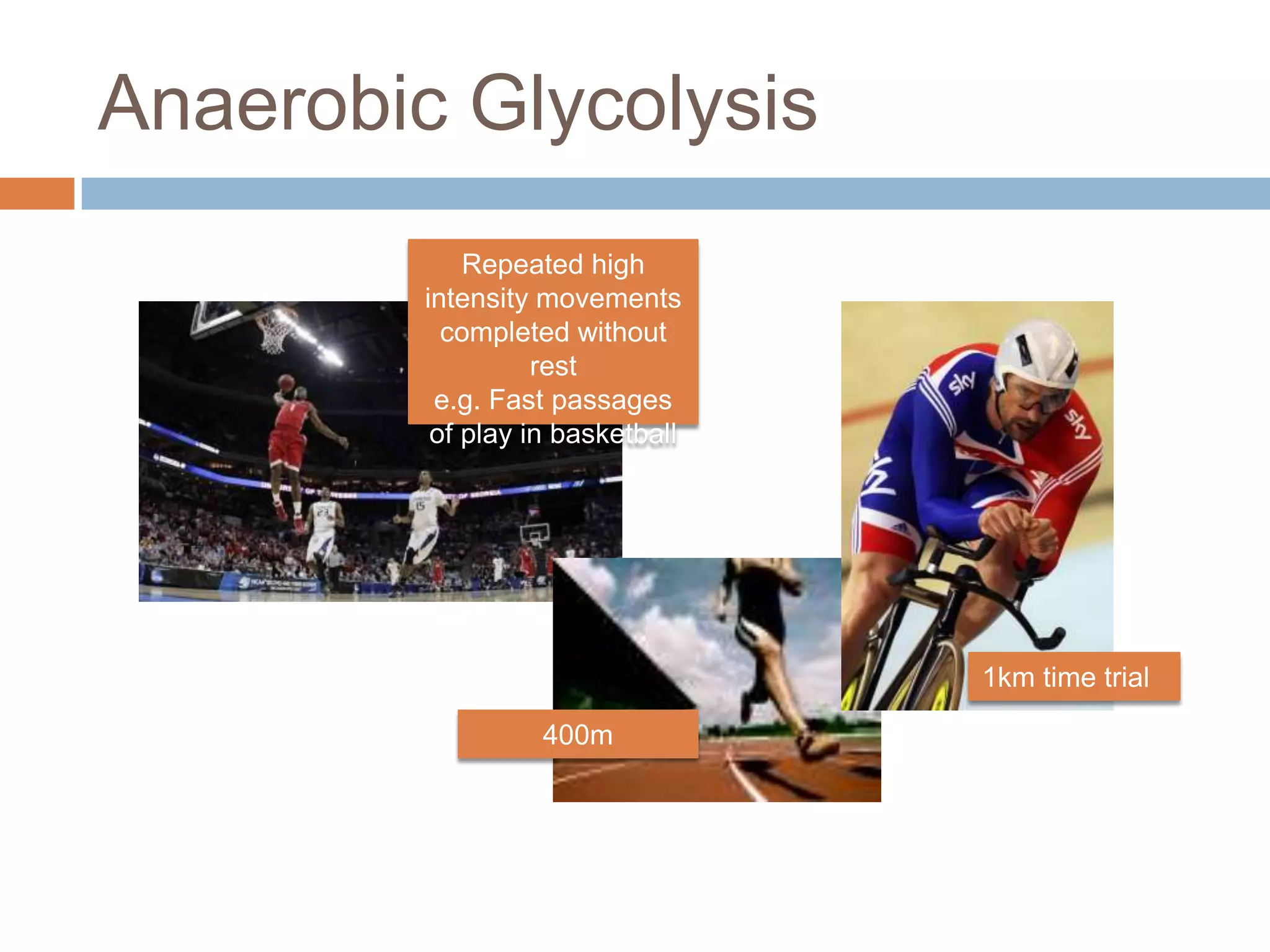
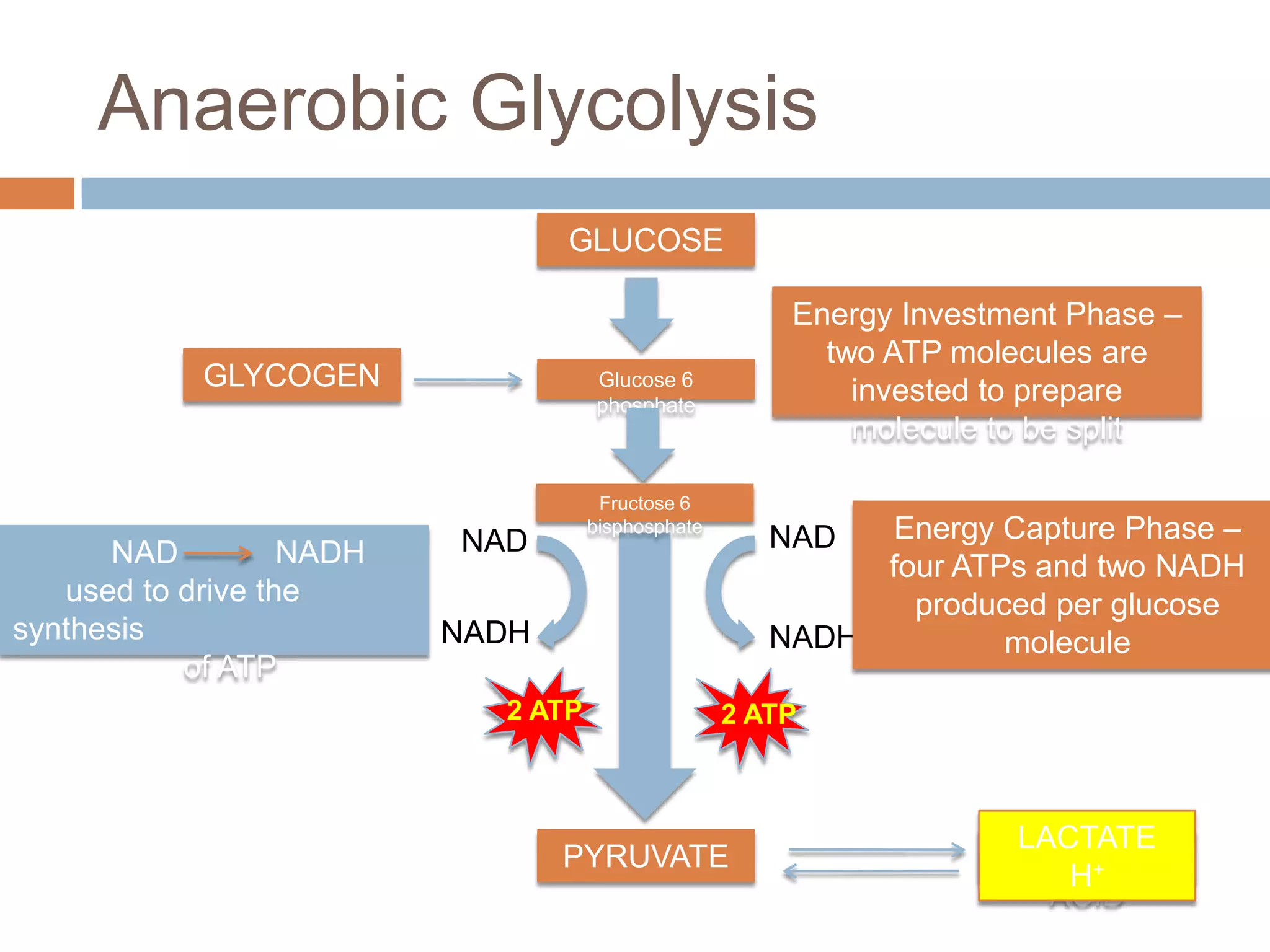
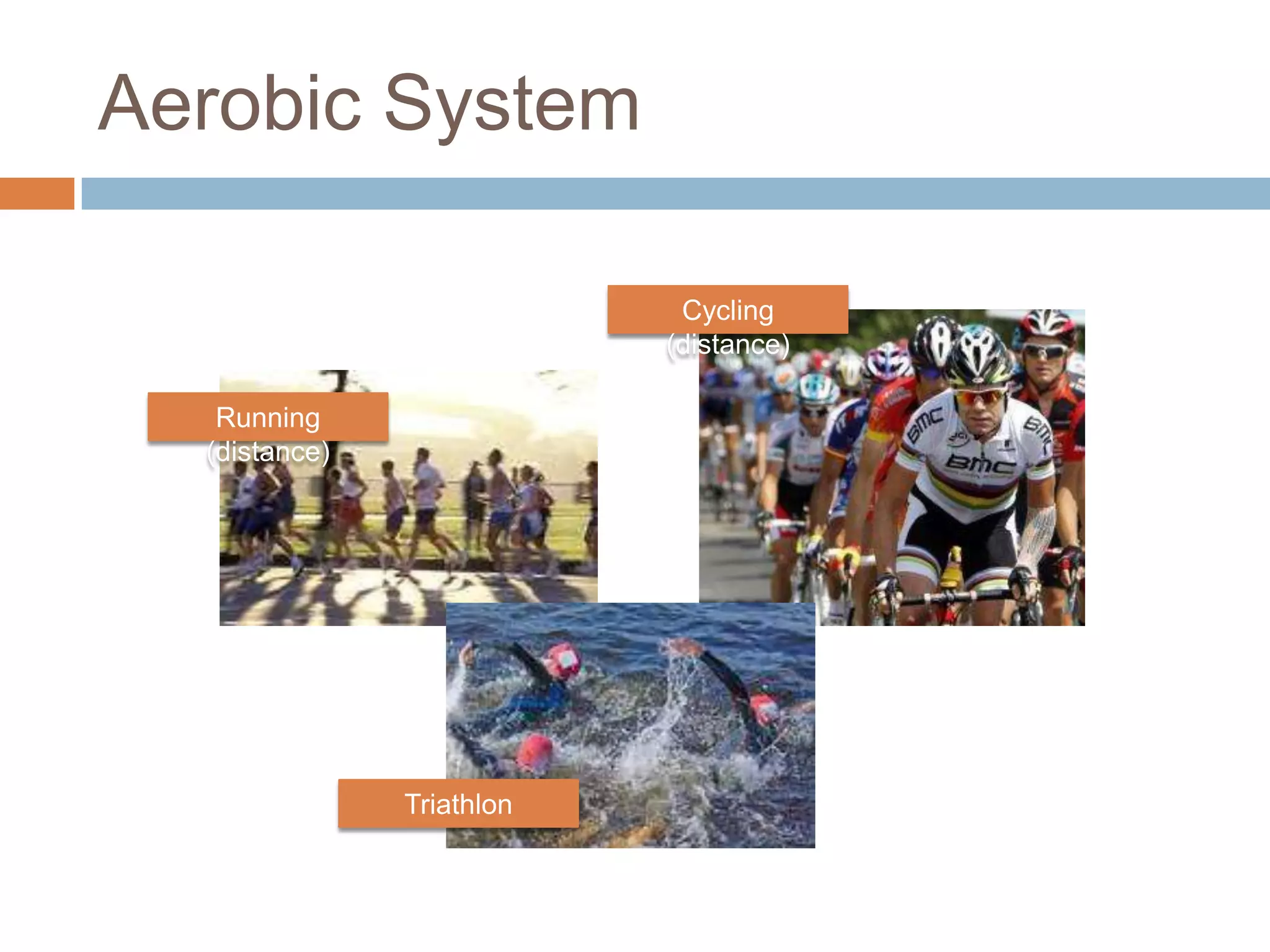
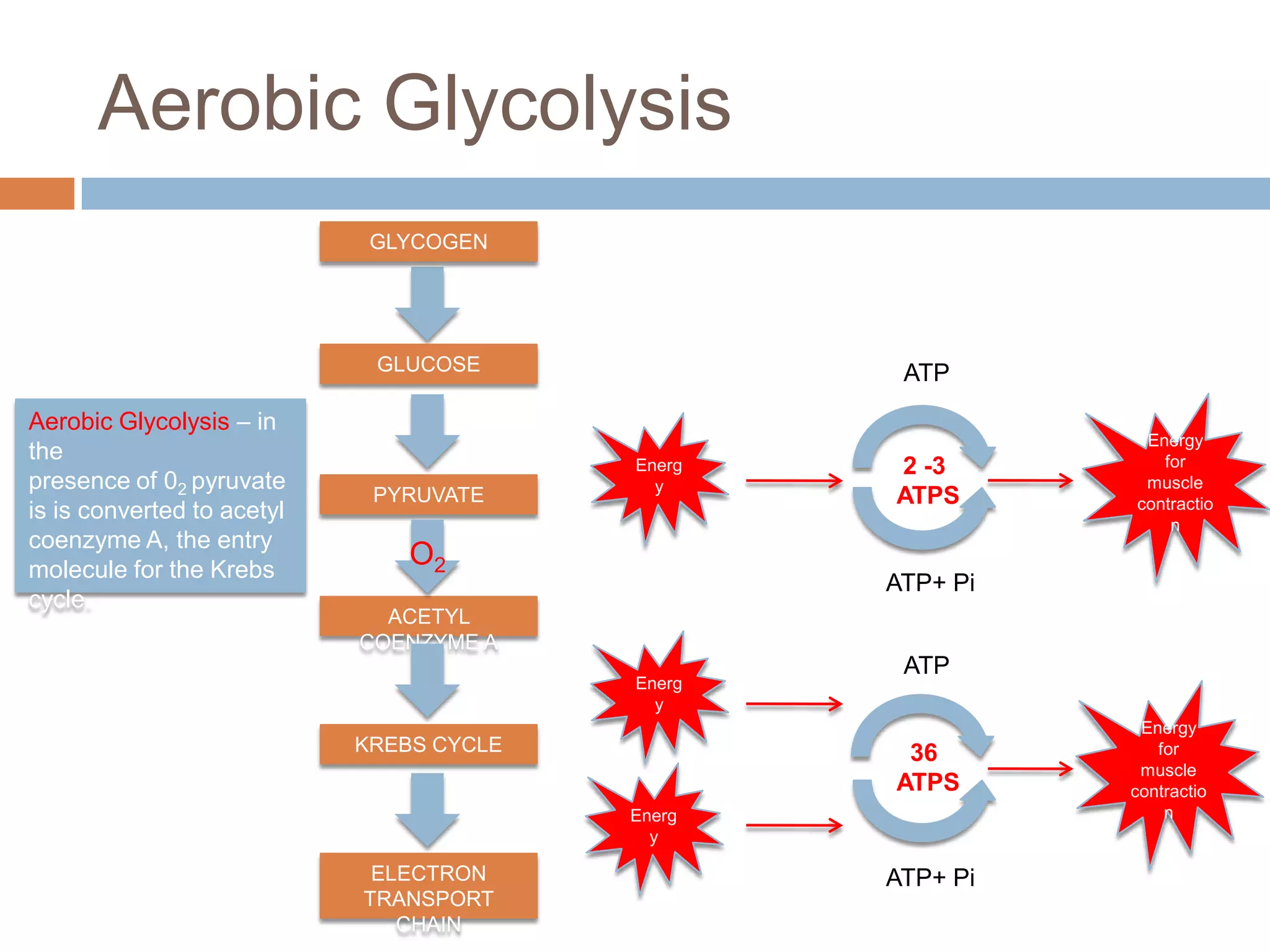
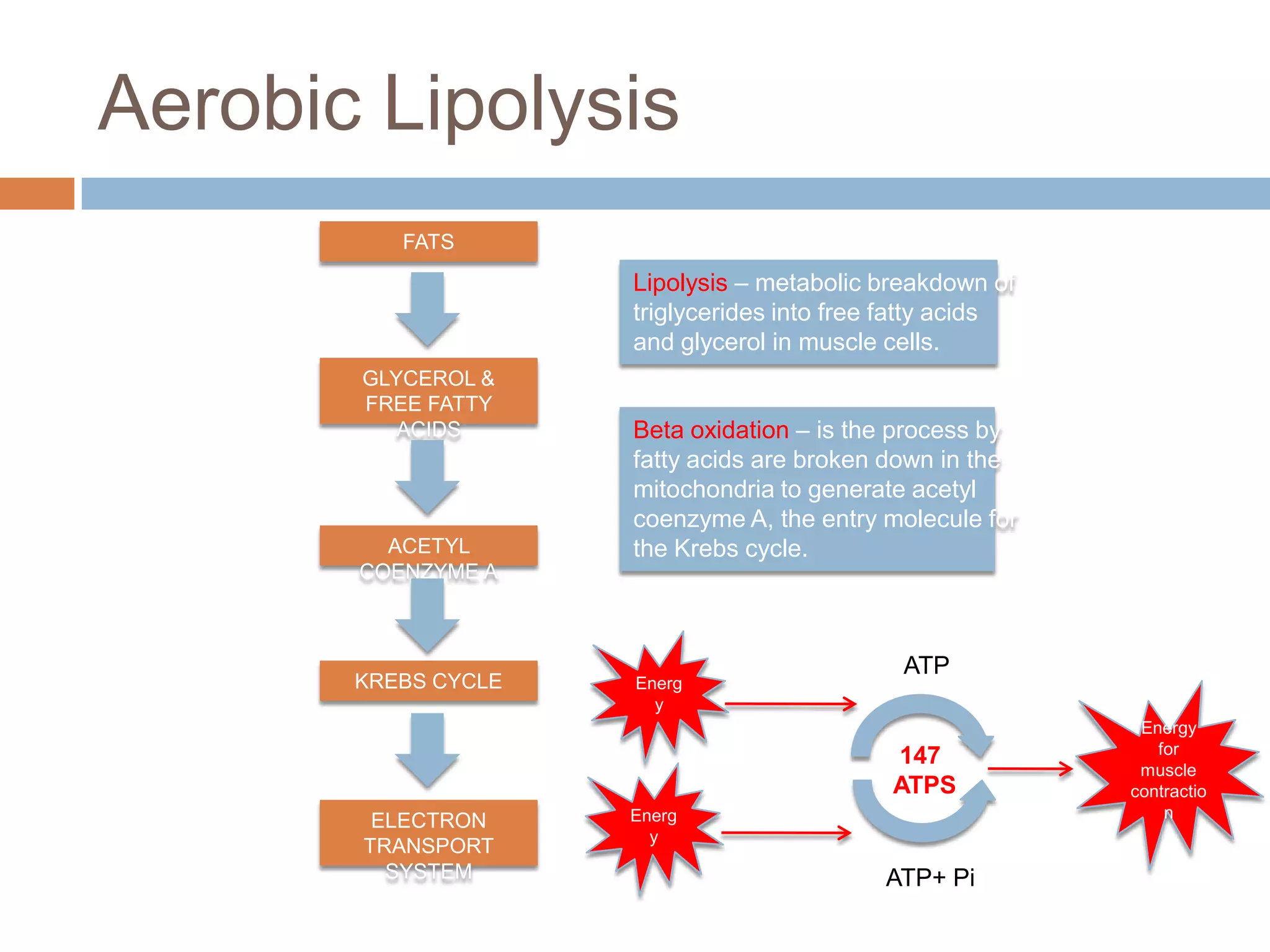
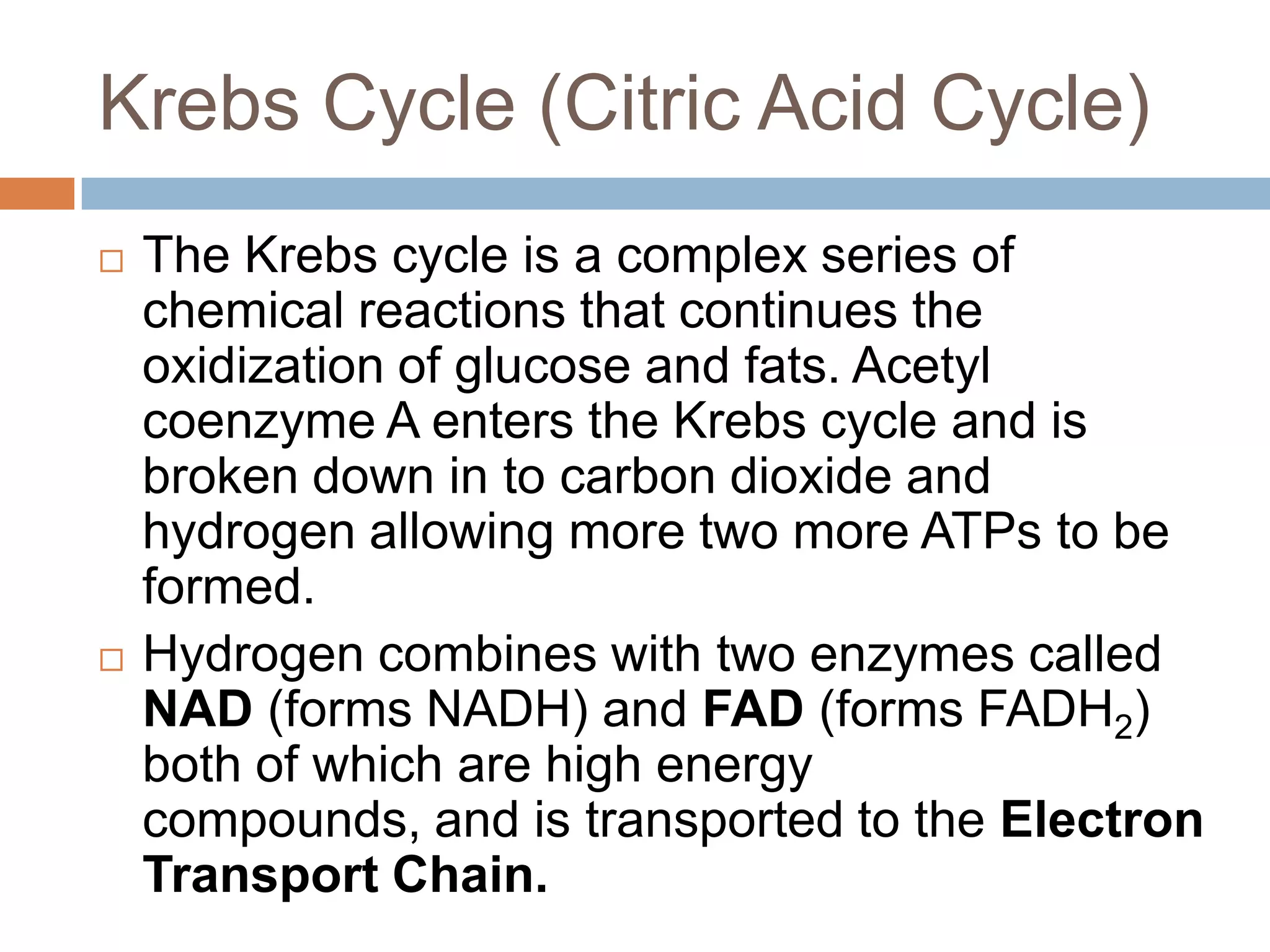
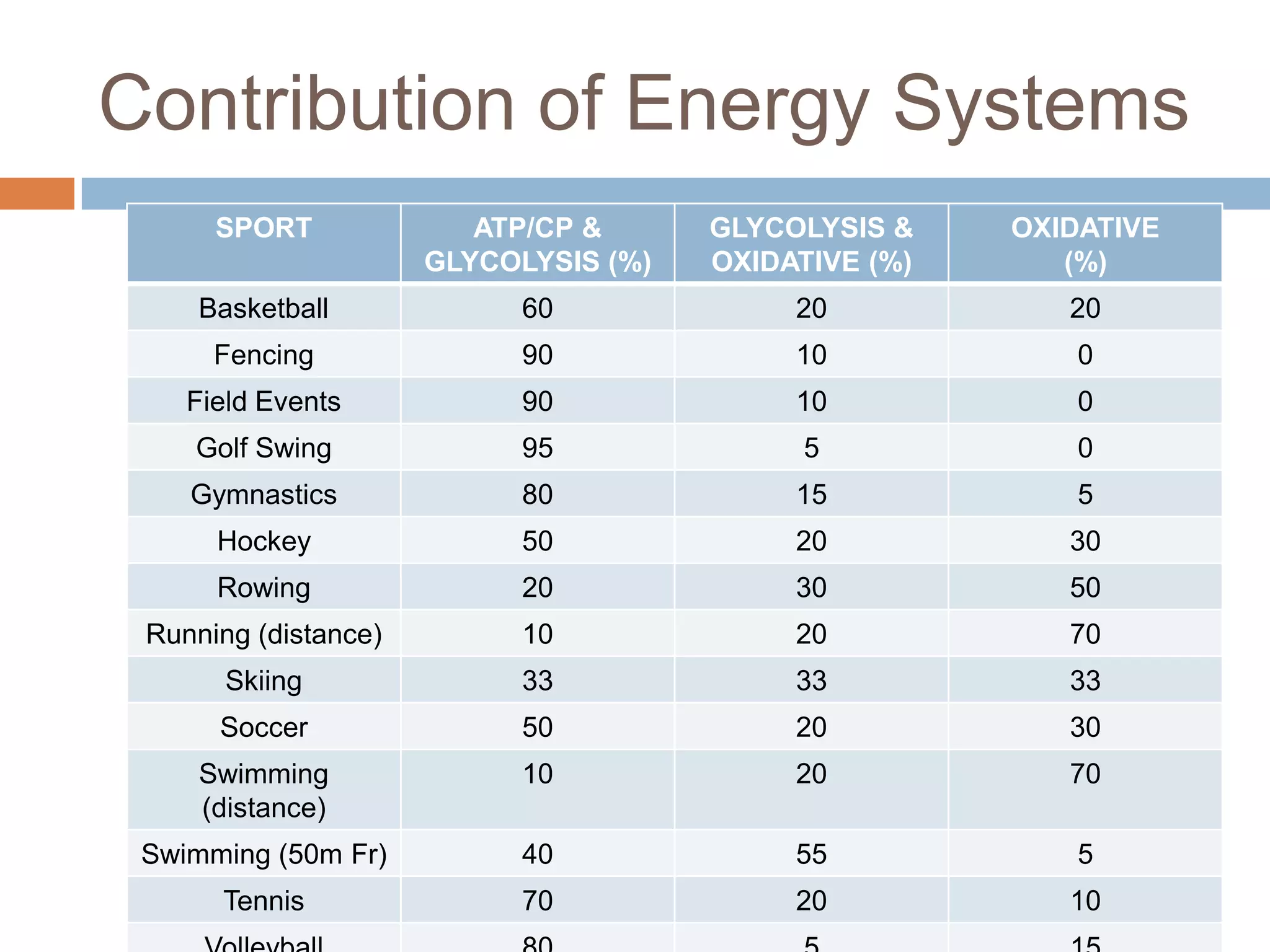
The document discusses the three energy systems - ATP-CP, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic system - that produce ATP to fuel muscle contraction during exercise. The ATP-CP system relies on creatine phosphate and can supply energy for up to 10 seconds. Anaerobic glycolysis breaks down glycogen without oxygen and can fuel exercise for up to 2 minutes, producing lactic acid as a byproduct. The aerobic system breaks down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins with oxygen to slowly produce ATP over longer periods of exercise.