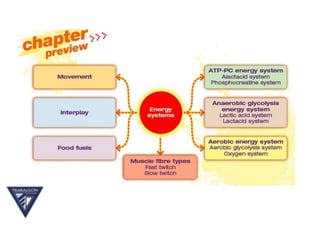
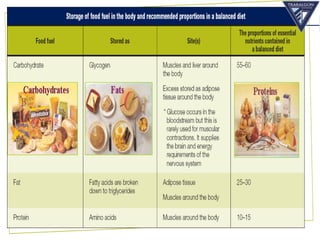
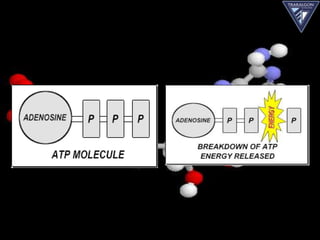
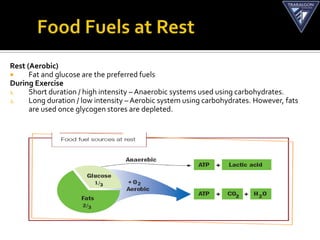
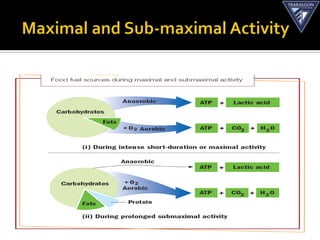
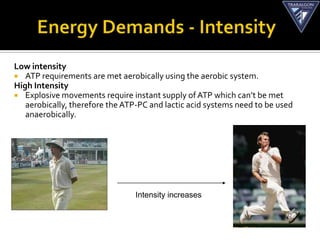
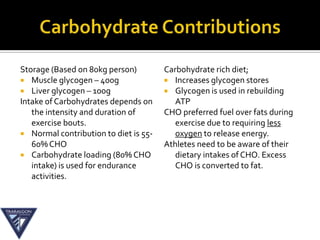
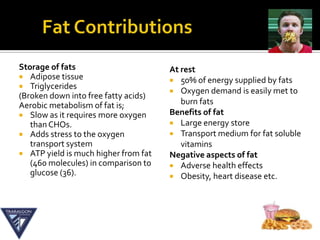
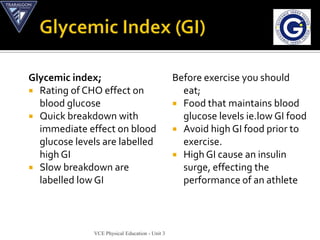
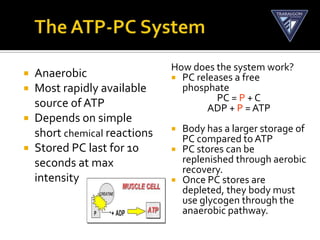
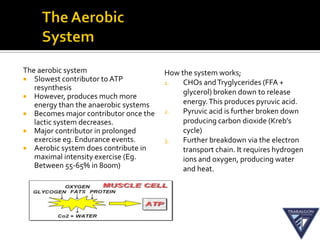
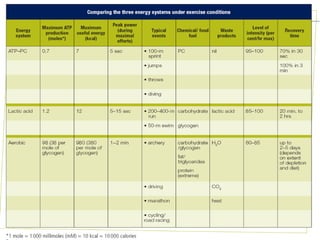
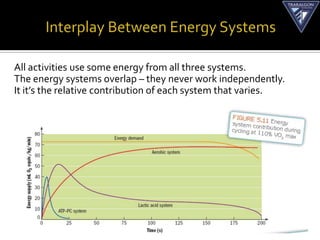
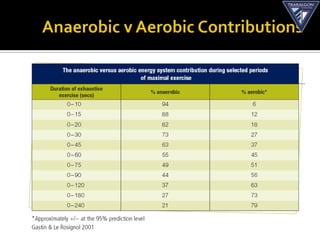
The document discusses the aerobic and anaerobic energy pathways and their contribution to movement. The aerobic pathway uses oxygen to break down fuels for energy over a long duration and low intensity. The anaerobic pathways do not use oxygen, with the ATP-PC system providing a rapid burst of energy lasting 10 seconds and the lactic acid system providing energy for 2-3 minutes during high intensity exercise before fatigue sets in. The document outlines the different fuels, storage sites, and processes of each energy system.