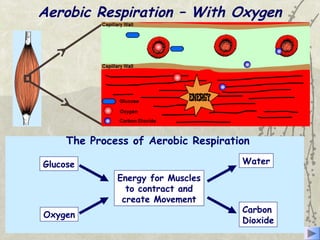
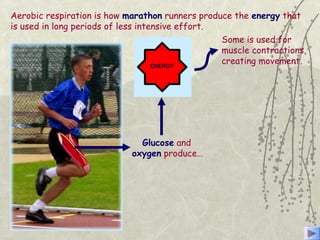
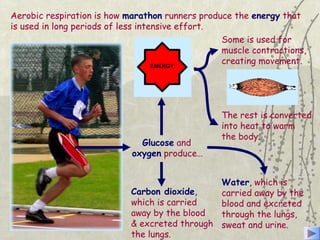
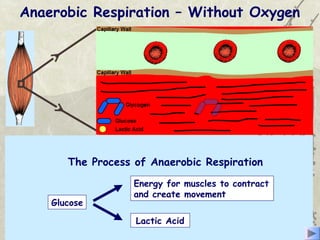
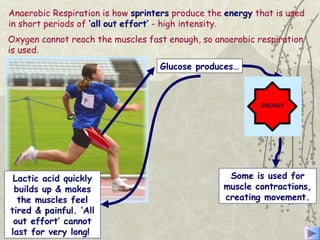
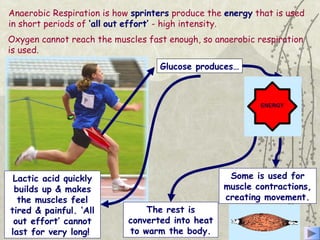
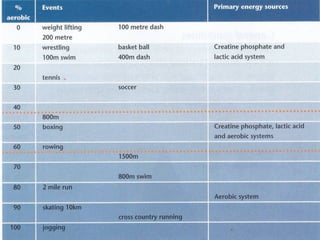
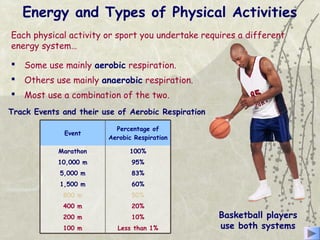
The document discusses three energy systems - the ATP-CP system, anaerobic glycolysis, and aerobic respiration. It provides details on how each system works to produce energy for muscle contraction, including the breakdown of glucose and other fuels as well as the waste products produced. It also discusses how different energy systems are used for various types of exercise depending on intensity and duration, with sprint-based activities relying more on ATP-CP and anaerobic glycolysis while endurance activities utilize more aerobic respiration. Charts are included showing which energy systems various sports predominantly use.