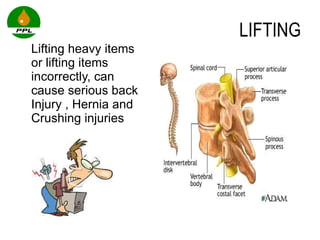
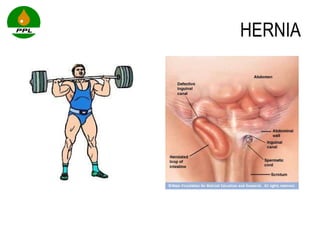
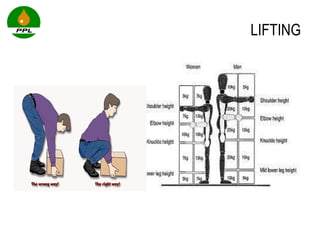
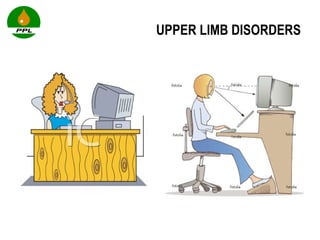
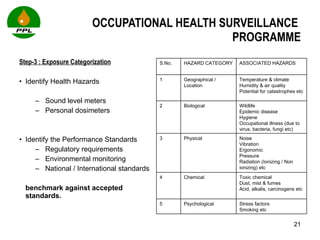
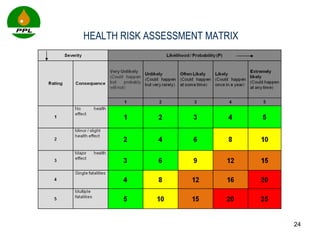
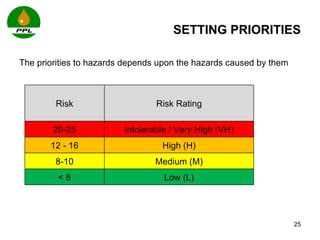
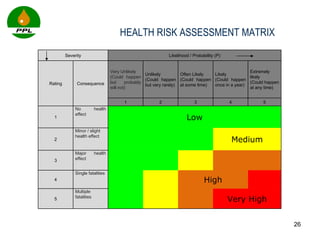
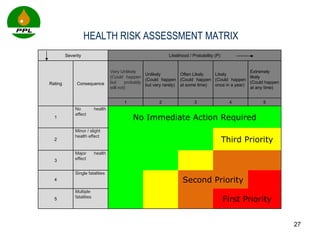
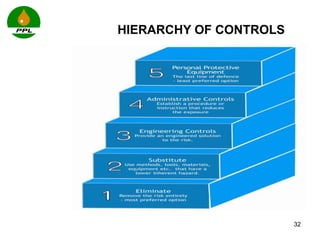
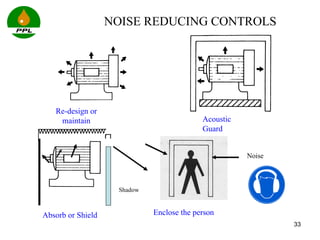
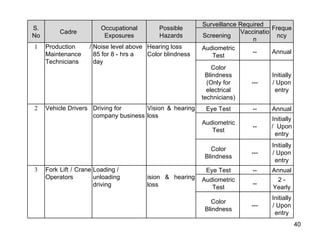
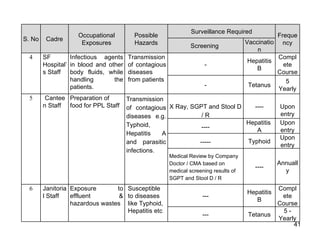
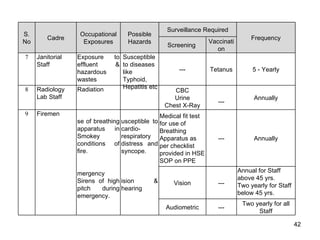
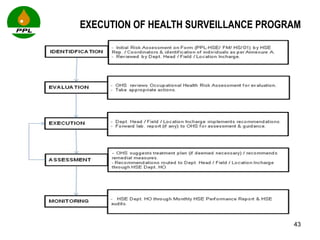
The document discusses occupational health and safety. It outlines the importance of occupational health programs in protecting worker health and safety. Some key risks to worker health mentioned include noise exposure, dermatitis, asthma, musculoskeletal disorders, and injuries from falls, lifting heavy loads, and machinery. The document also discusses international standards and legislation regarding occupational health in Pakistan. An effective occupational health program involves identifying health hazards, assessing and controlling risks, health surveillance of at-risk workers, and measures to ensure compliance with laws and standards.