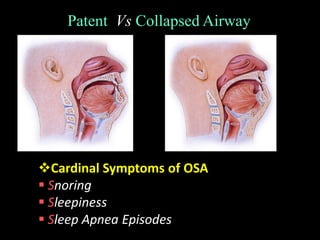
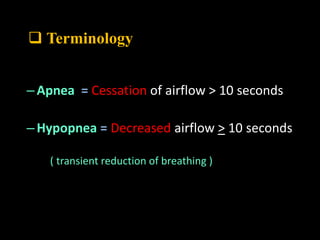
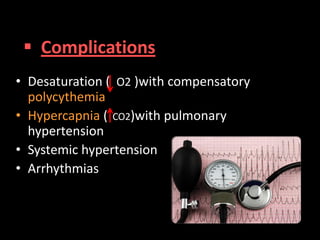
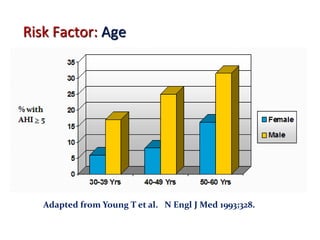
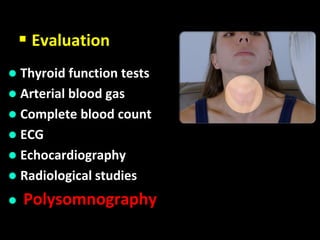
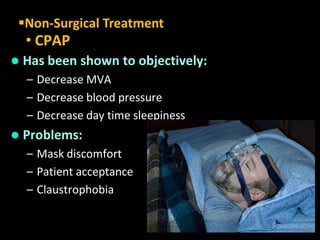
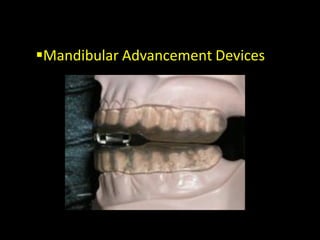
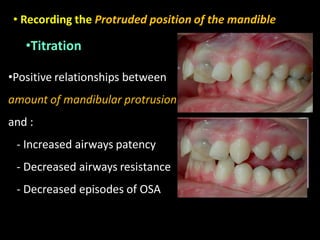
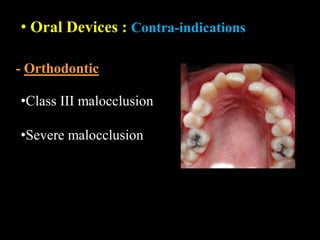
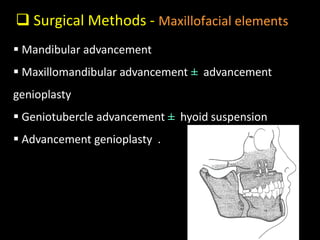
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is a serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated episodes of upper airway obstruction during sleep, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and various health consequences. The condition affects a significant portion of the adult population, particularly those who are obese and over 40 years old, and can be diagnosed through a combination of clinical history, physical examination, and polysomnography. Treatment options include behavioral modifications, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), and oral devices tailored to improve airway patency.




![• 1st description of the disorder in the
medical literature was in 1965 .
Gastaut H, Tassinari CA, Duron B. Polygraphic study of diurnal and nocturnal
(hypnic and respiratory) episodal manifestations of Pickwick syndrome [in
French]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1965; 112:568–579
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a public health
problem and a potentially life-threatening condition .
What Is Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) ?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/obstructivesleepapnea-150916151811-lva1-app6891/85/Obstructive-sleep-apnea-5-320.jpg)