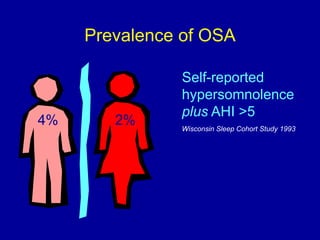
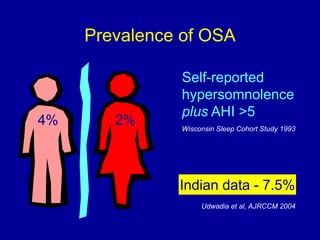
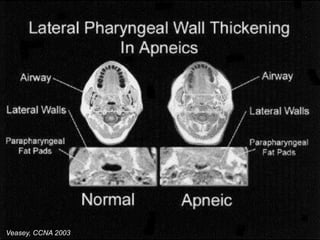
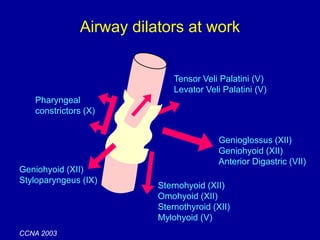
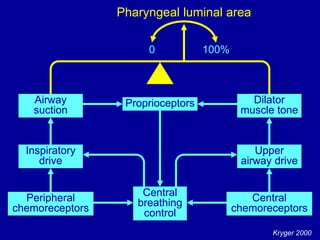
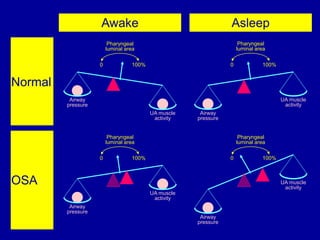
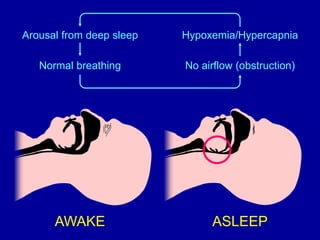
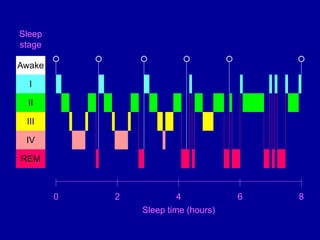
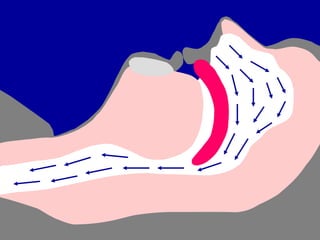
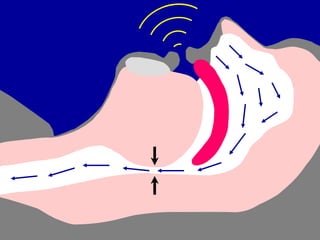
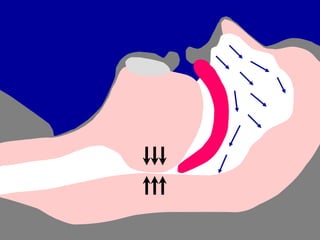
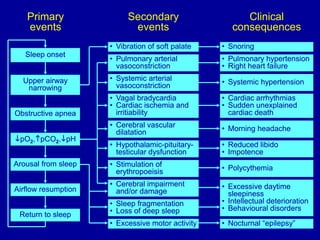
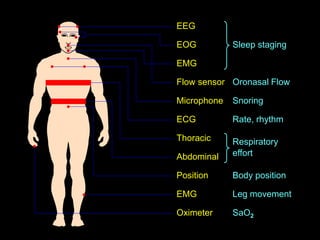
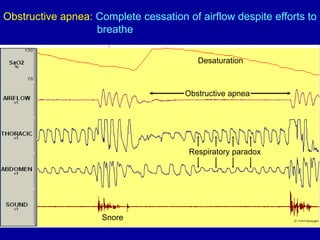
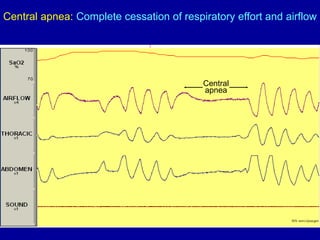
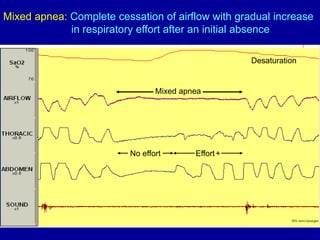
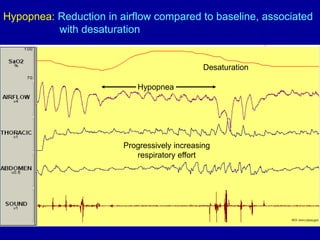
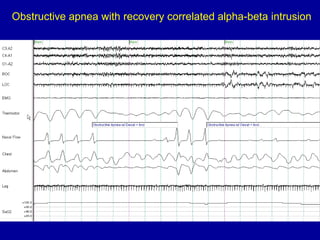
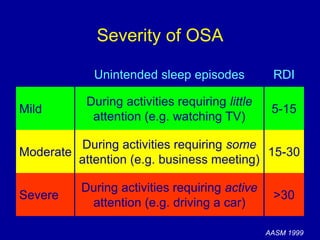
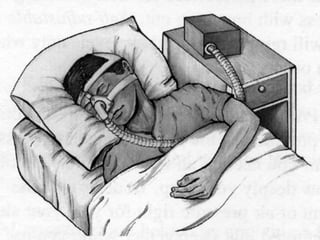
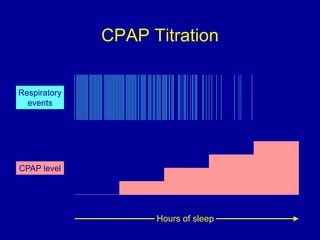
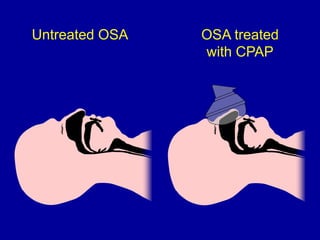
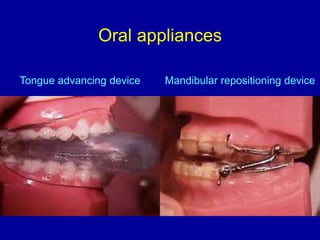
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) is characterized by recurrent upper airway obstruction during sleep, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness and various associated symptoms. Prevalence rates vary, influenced by factors such as obesity and anatomical abnormalities, with diagnosis primarily established through polysomnography to assess apnea-hypopnea index (AHI). Treatment typically involves nasal CPAP therapy, which has been shown to improve neuropsychiatric function and reduce daytime sleepiness.