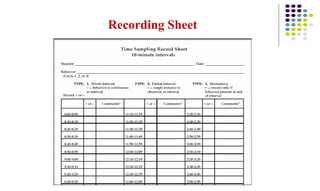
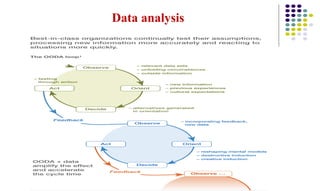
This document discusses observation as a method for business research. It defines observation as a critical analysis that involves carefully watching and immersing oneself in a situation to solve problems. The document outlines the five senses used to observe - sight, hearing, smell, touch, and taste. It also discusses what to observe, including people, physical settings, and environmental features. Reasons for using observation are provided, such as when direct information is needed or when other data collection methods are inappropriate. The document differentiates between unstructured observation, which is unplanned and random, and structured observation, which is quantitative and involves observing specific predefined aspects. It provides examples of each type and discusses how to record observations, including through observation guides, recording sheets