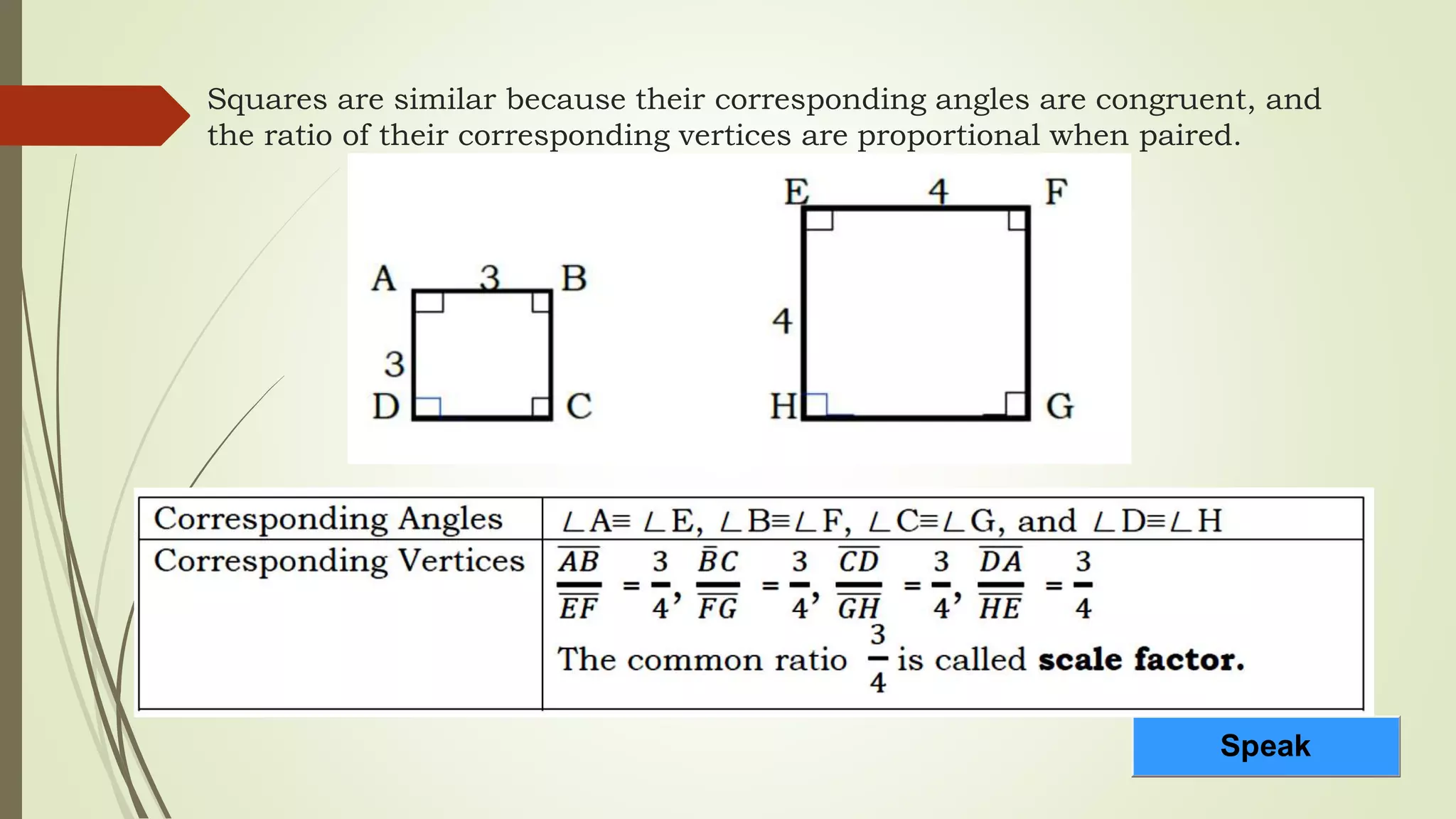
The document discusses similarity of triangles and geometric figures, noting that two figures are similar if they have the same shape but not necessarily the same size, and outlining the AA, SAS, SSS, and right triangle similarity theorems. It also reviews ratios, proportions, and how proportions can be used to show that corresponding segments of similar figures are proportional. The learning objectives are to illustrate similarity of figures and prove the conditions for similarity of triangles using these various theorems.