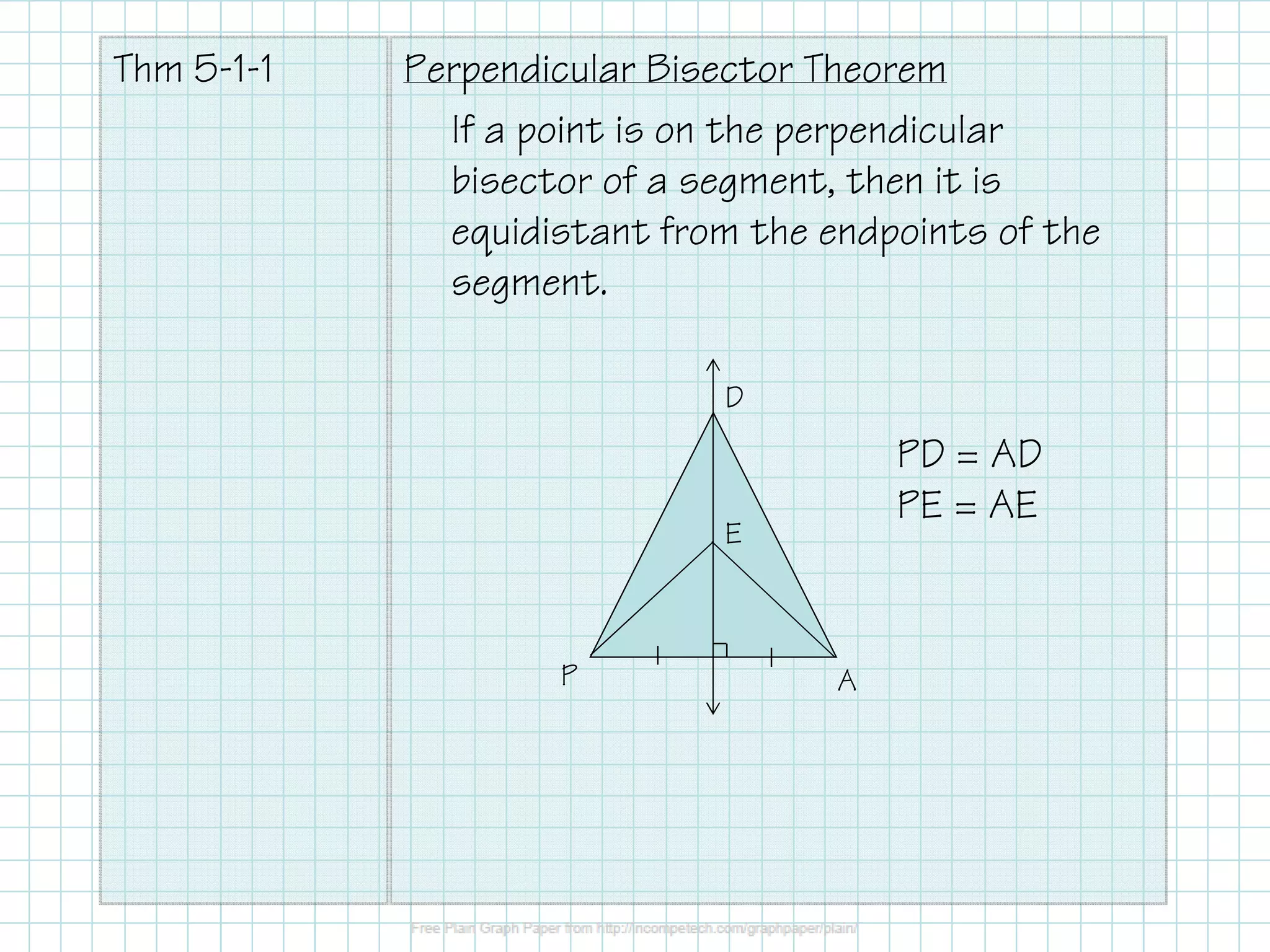
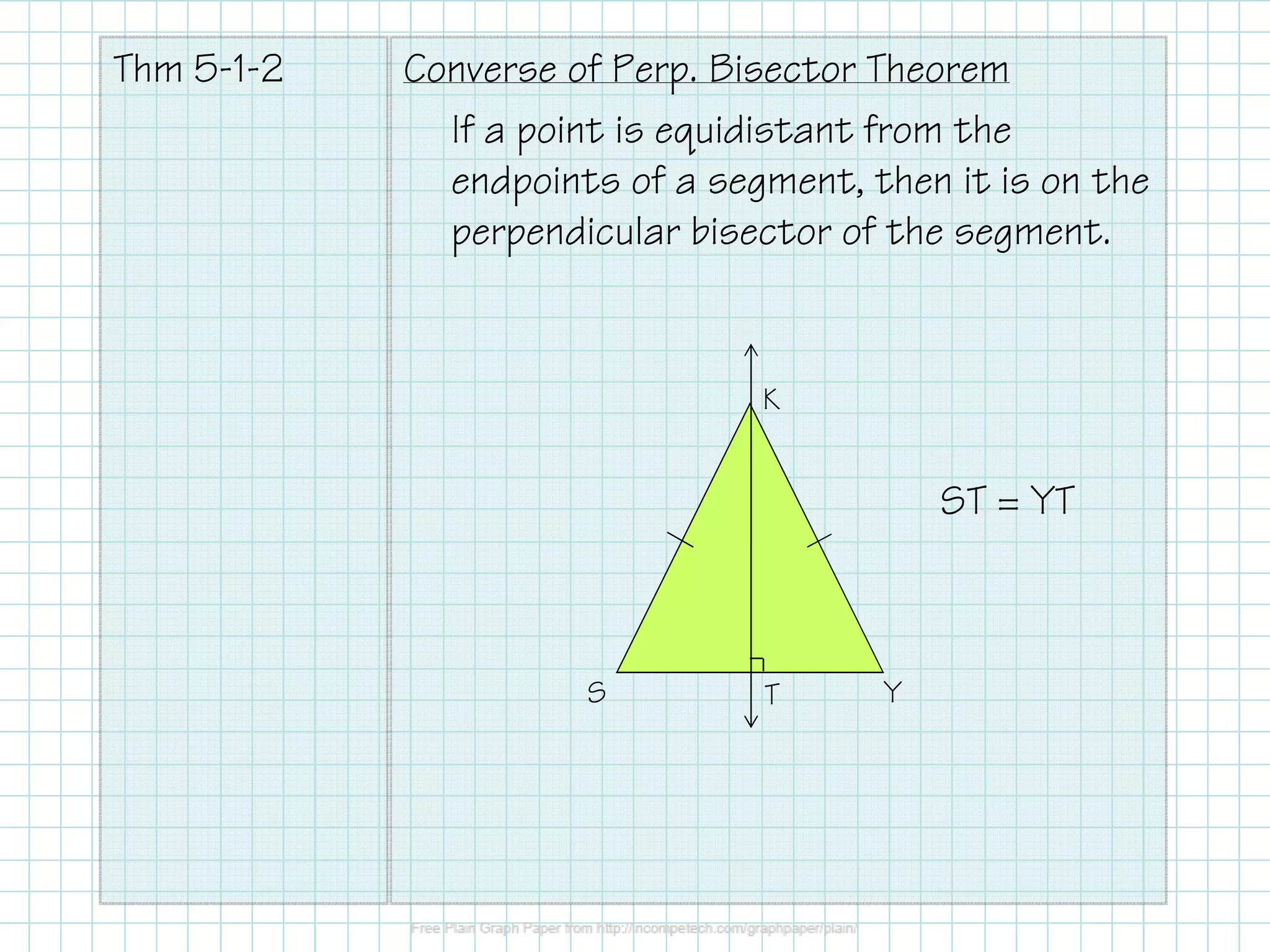
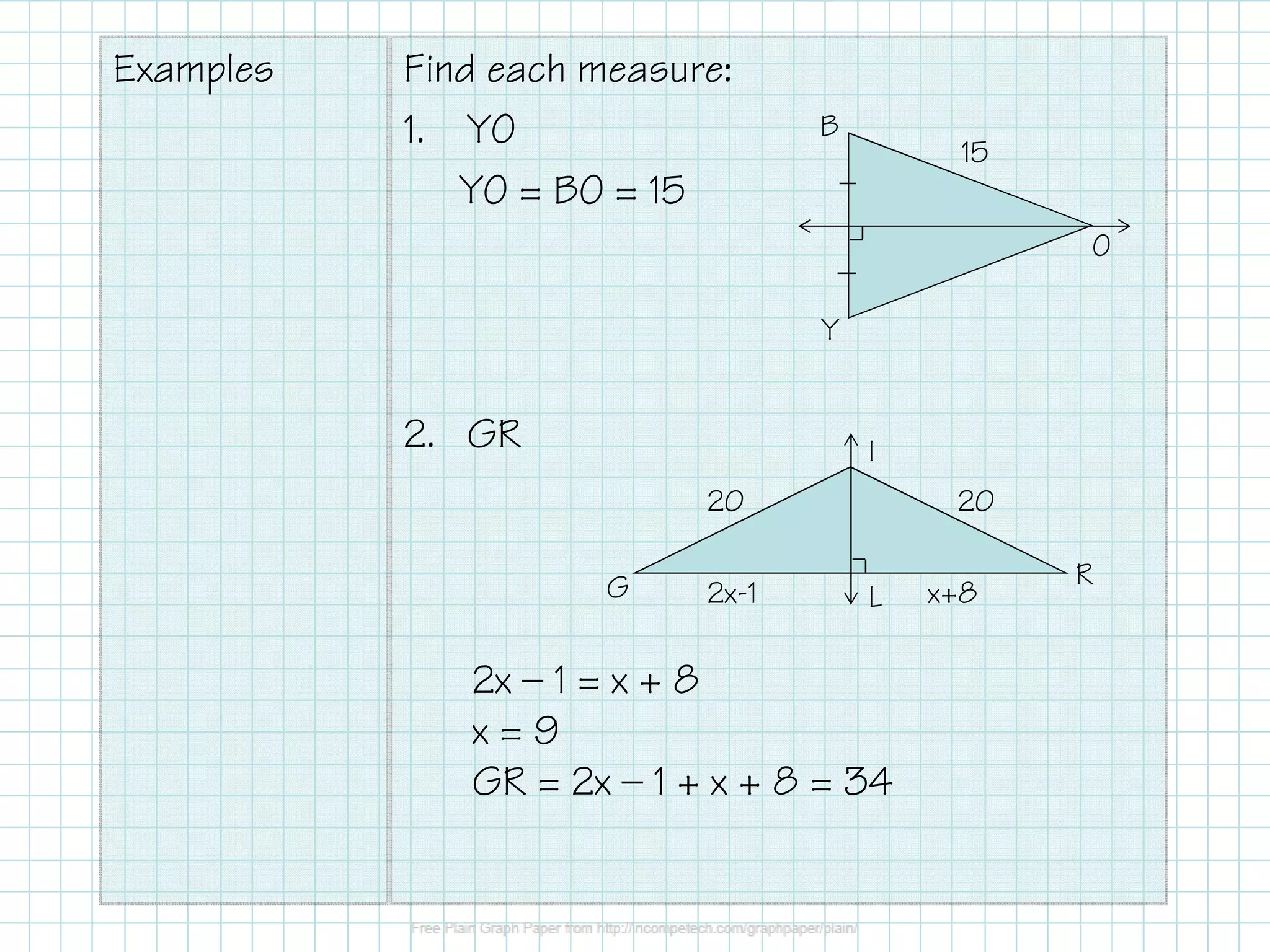
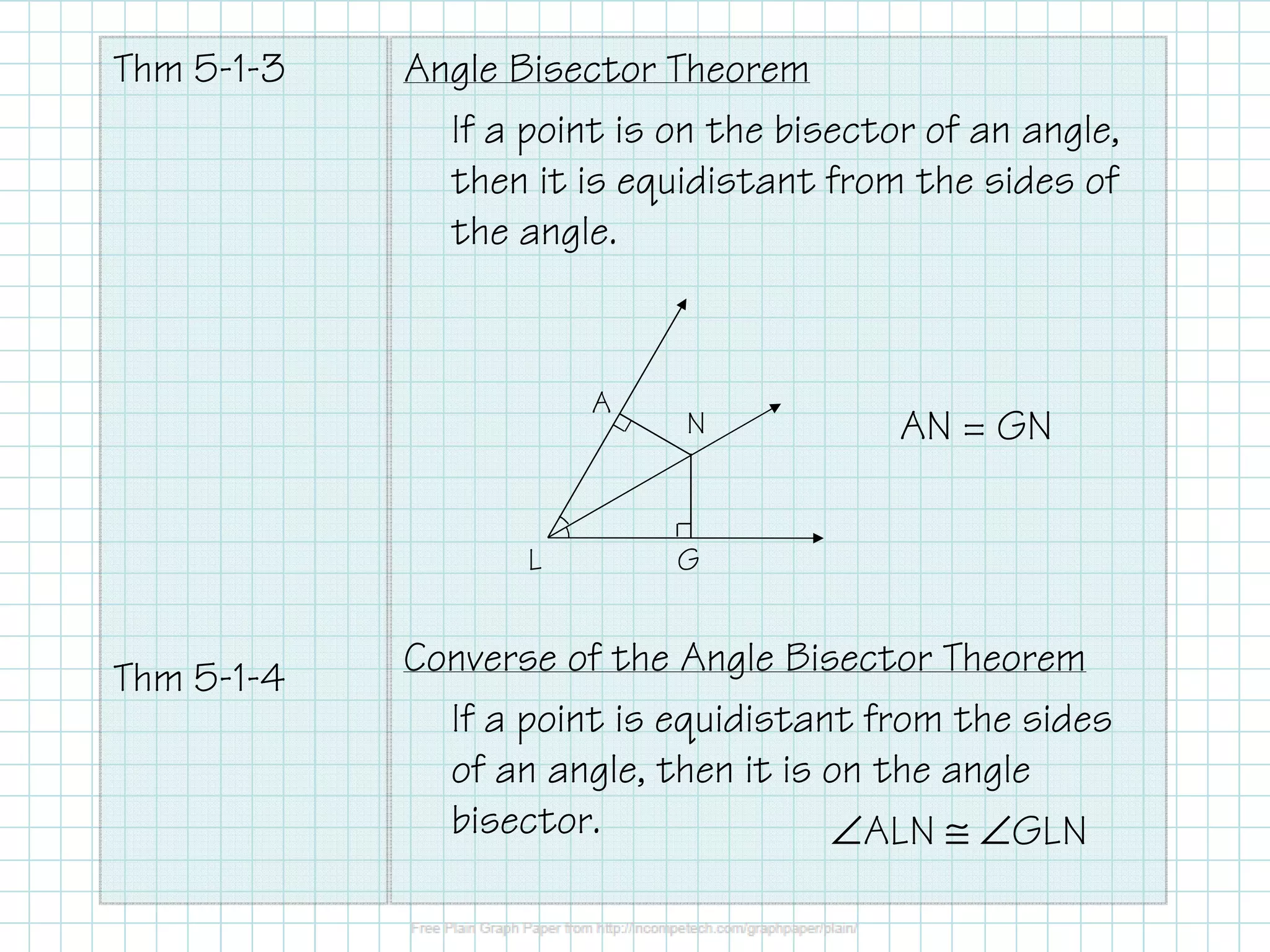
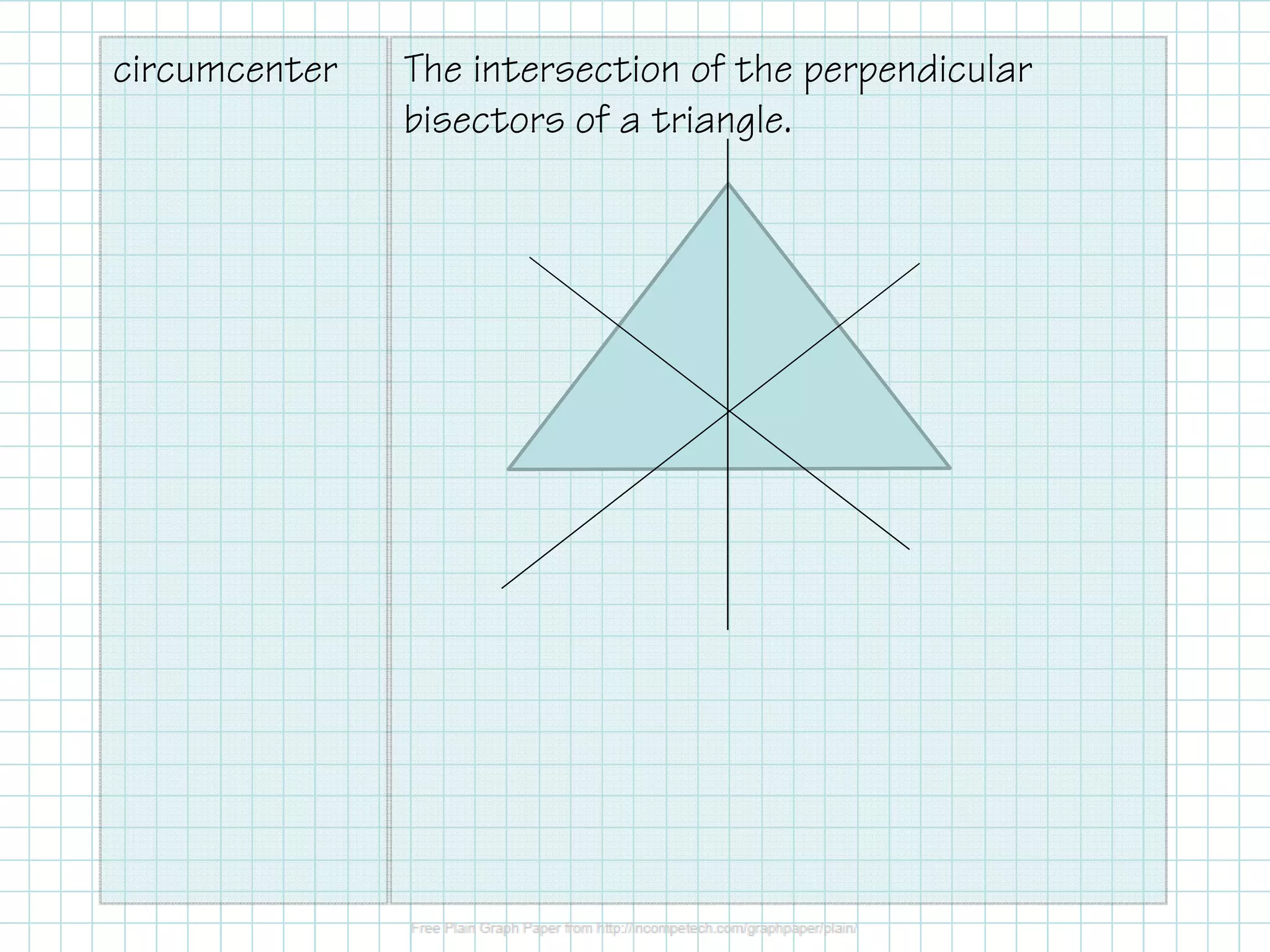
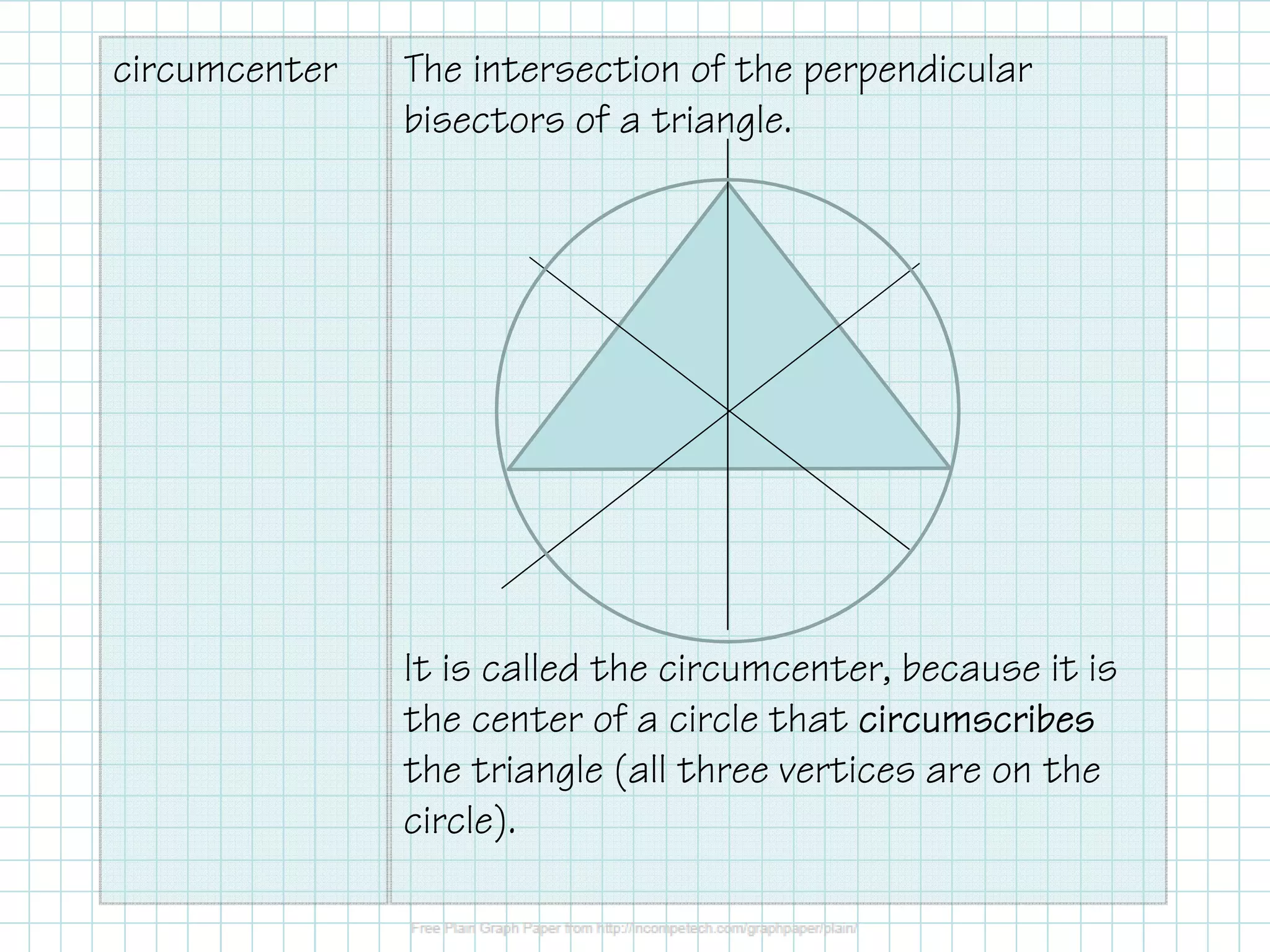
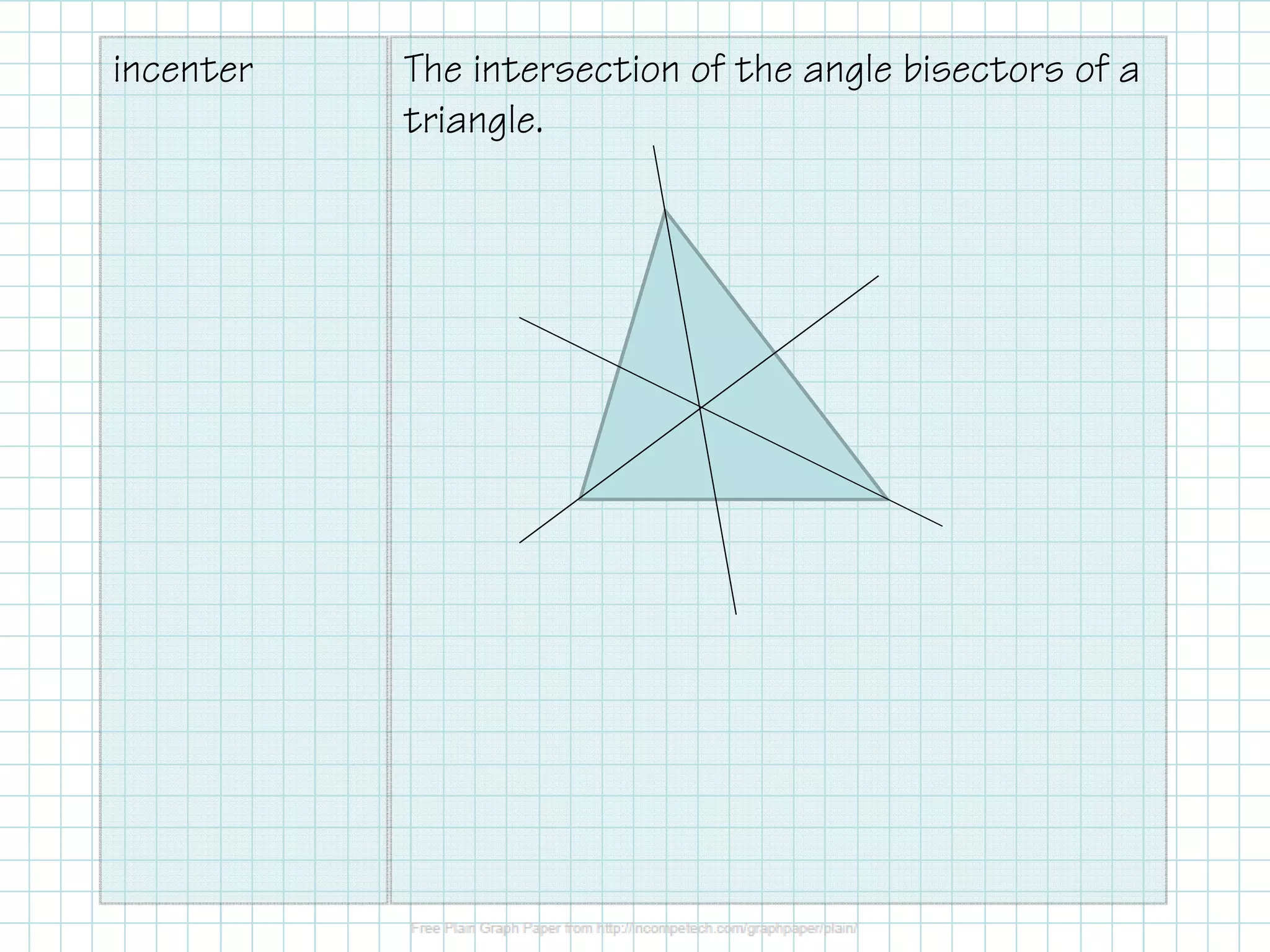
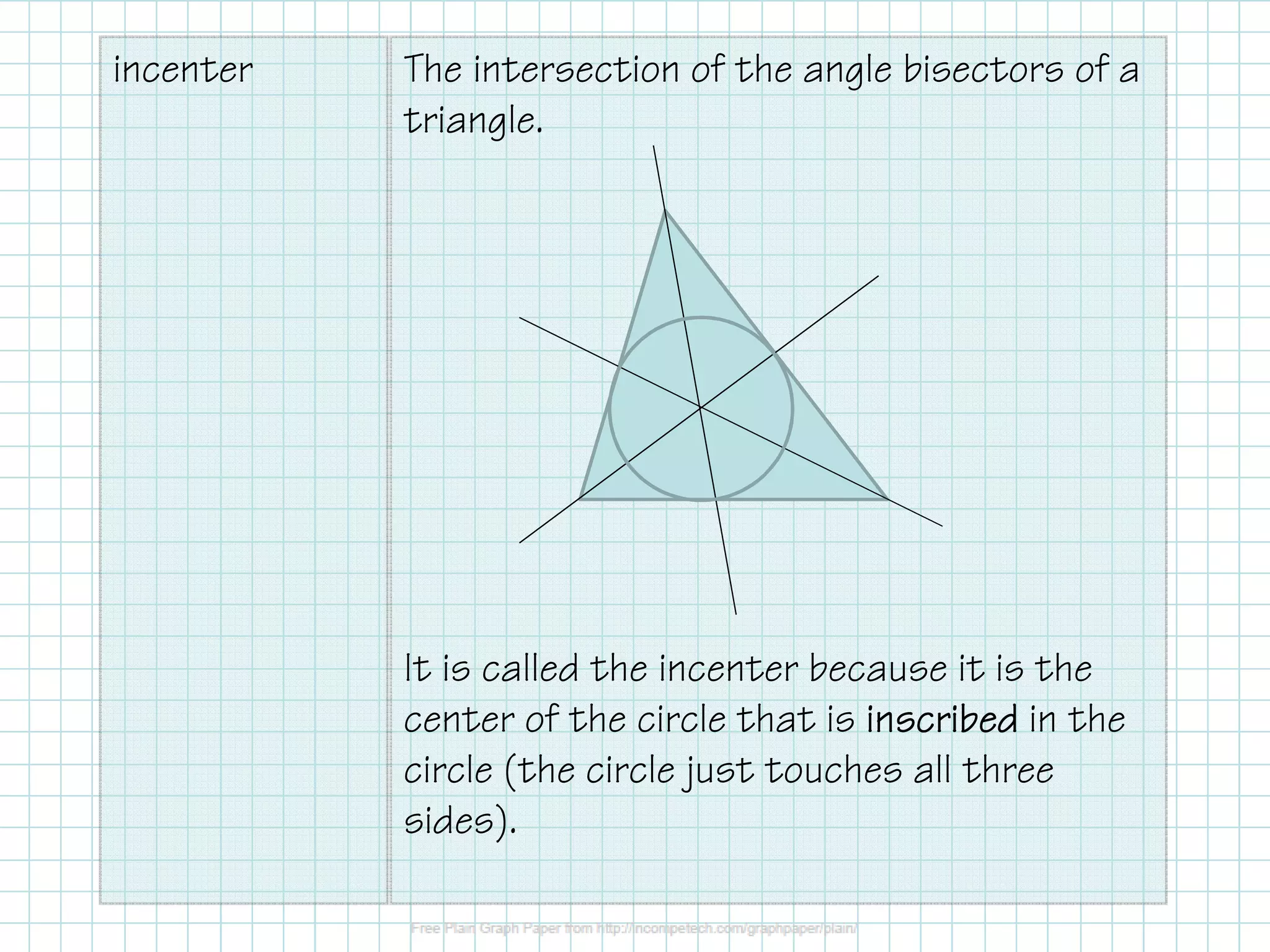
The document covers the construction of perpendicular and angle bisectors, their applications, and properties related to triangles, such as the circumcenter and incenter. It includes theorems regarding the equidistance of points to segment endpoints and angle sides when on a bisector. Examples are provided to illustrate these concepts and calculations.