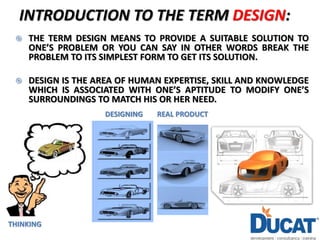
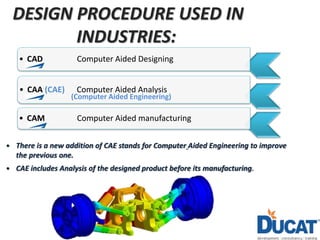
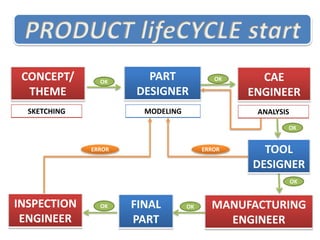
This document provides an introduction to design and the NX 10 software. It defines design as providing suitable solutions to problems by simplifying them. The design process in industries involves CAD, CAE, and CAM. NX 10 is a computer-aided design software first released in 1973 by Siemens that allows for computer-aided design, engineering, and manufacturing. It covers mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and industrial design applications. Skills needed for design jobs include an engineering degree, software skills, and knowledge of topics like tolerancing and design analysis.