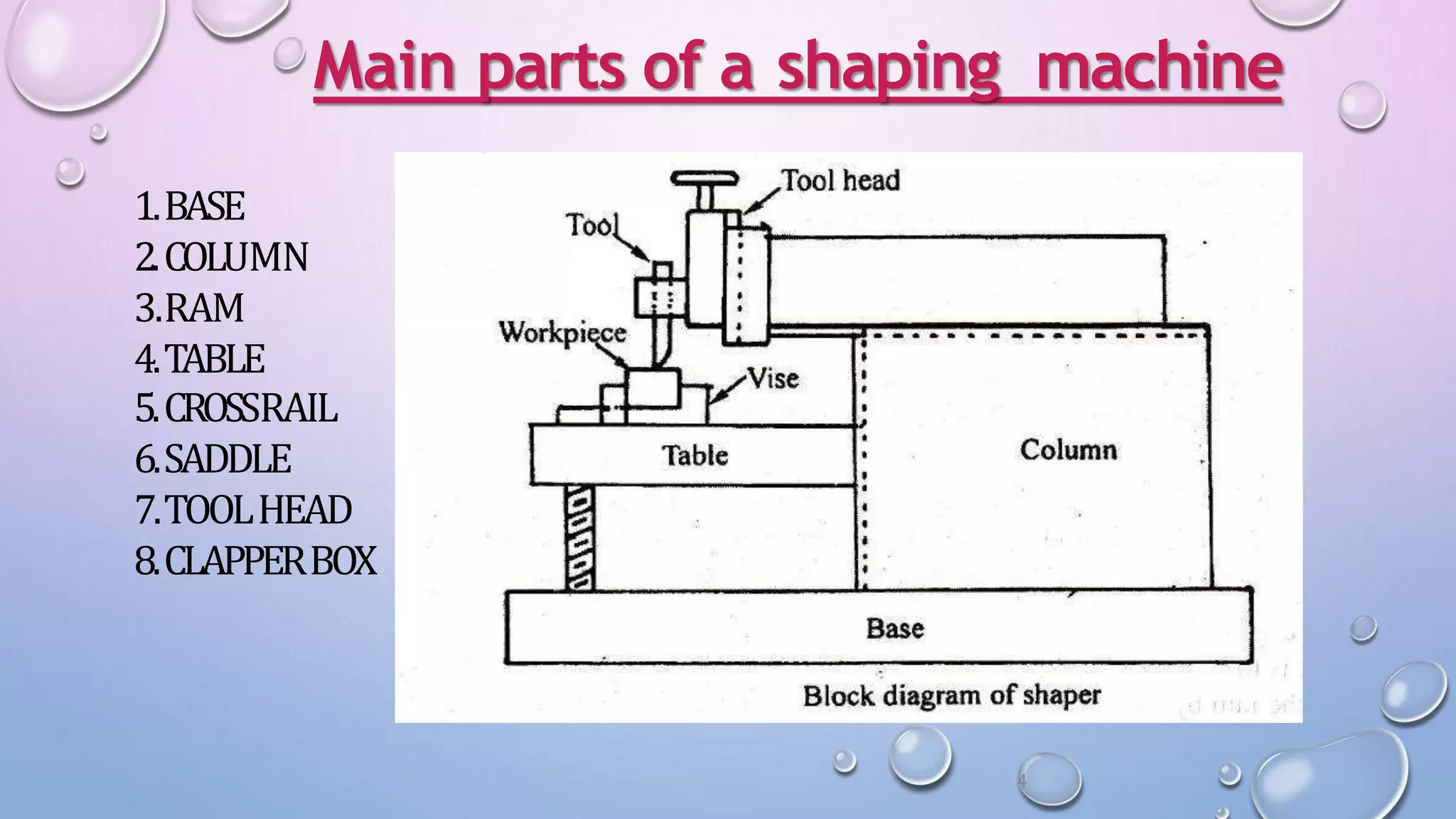
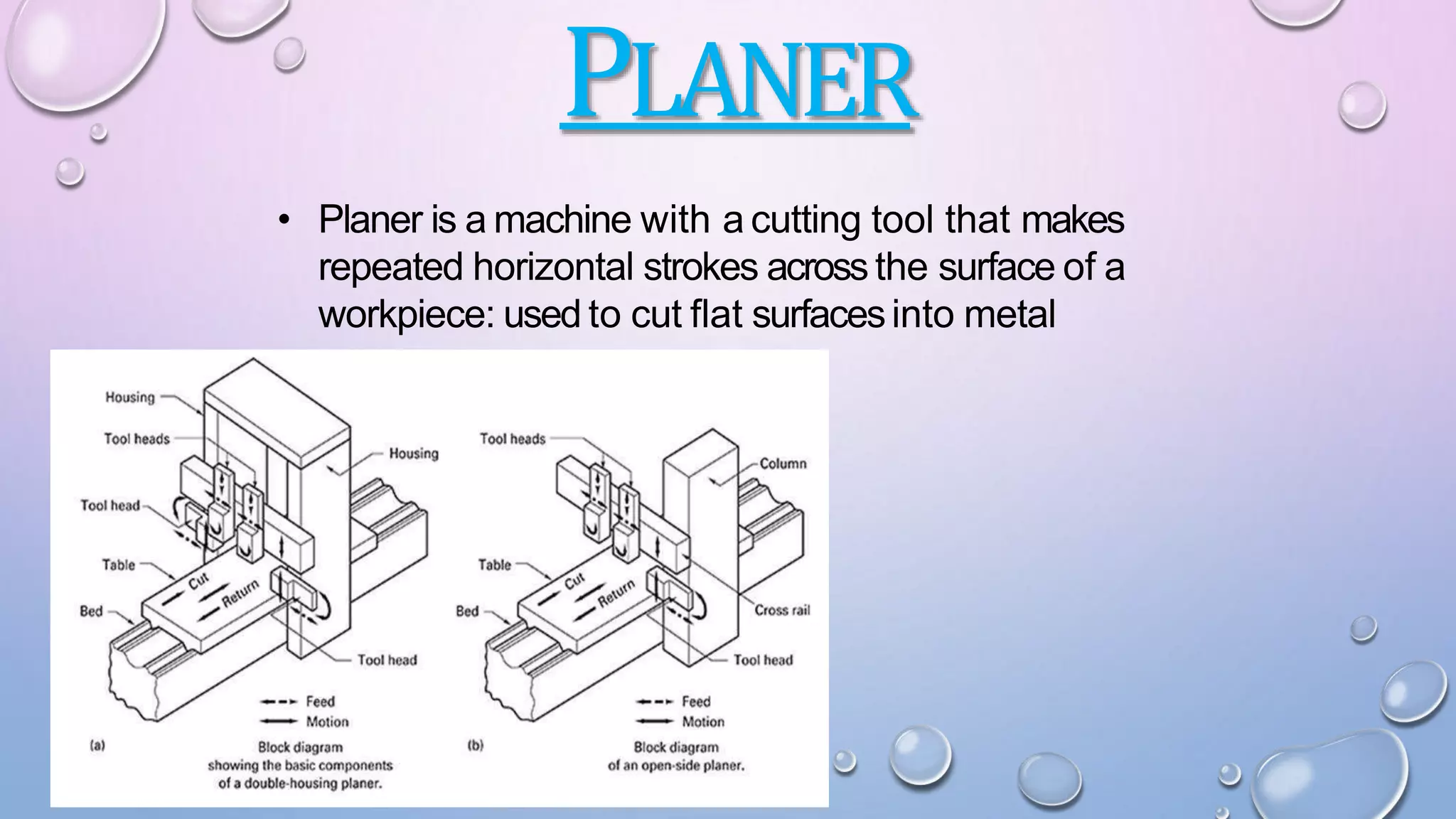
The document outlines a seminar on milling, shaping, and planing machines, detailing their functions and classifications. It describes milling as a rotary cutting process used for precision machining and provides insights into horizontal and vertical milling machines. Additionally, it discusses shaper and planer machines, their mechanisms, features, applications, and types, emphasizing their roles in producing flat and angular surfaces.