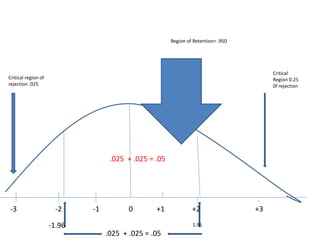
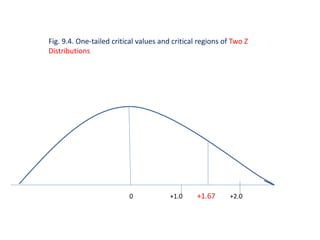
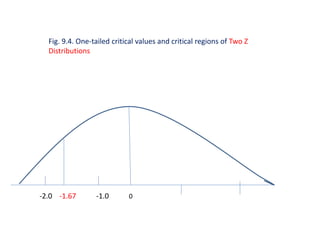
The document discusses key concepts related to p-values and significance testing. It defines a p-value as the likelihood that a difference detected is due to chance rather than a true effect. A difference is considered statistically significant if the p-value is less than 0.05, meaning there is less than a 5% chance the difference is due to random error. The document also discusses critical values, which are numerical cut-offs used to determine whether to reject or retain the null hypothesis, and types I and II errors that can occur in significance testing.