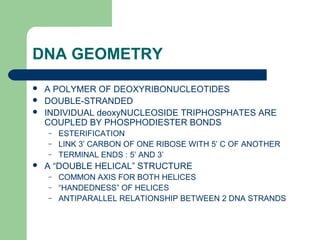
DNA exists in a double-helical structure, with two anti-parallel strands bound together through hydrogen bonding between complementary nucleotide base pairs. The most common form is B-DNA, which is a right-handed double helix with 10 base pairs per turn. DNA structure and stability are maintained through base pairing, base stacking interactions, sugar-phosphate backbone conformations, and ionic interactions with cations like magnesium. The topology and supercoiling of DNA allow for its compact organization in the cell and play important roles in processes like DNA replication and transcription.



















![IONIC INTERACTIONS
THE DOUBLE HELIX IS ANIONIC
– MULTIPLE PHOSPHATE GROUPS
DOUBLE-STRANDED DNA HAS HIGHER ANIONIC
CHARGE DENSITY THAT SS-DNA
THERE IS AN EQUILIBRIUM BETWEEN SS-DNA
AND DS-DNA IN AQUEOUS SOLUTION:
– DS-DNA == SS-DNA
QUESTION: WHAT HAPPENS TO THE Tm OF DS-
DNA AS [CATION] INCREASES? WHY?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnastructure-101120021823-phpapp01/85/Dna-structure-24-320.jpg)






