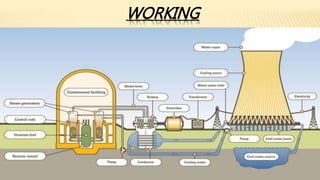
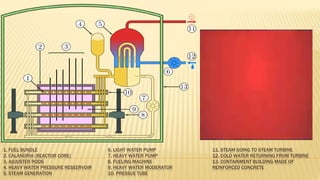
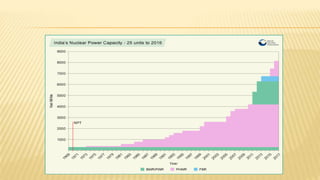
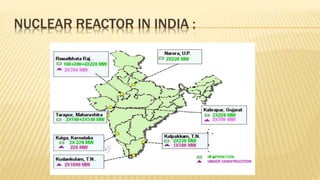
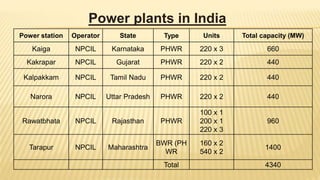
India ranks 6th in the world for nuclear power generation. As of 2010, India has 20 nuclear power plants generating 4,560 MW total. The Kundankulam Nuclear Power Plant is a prominent example, located in Tamil Nadu. It uses a pressurized water reactor with enriched uranium fuel and light water coolant to generate 917 MW. India operates both pressurized heavy water reactors, known as CANDU reactors which can use natural uranium fuel, and light water reactors at various nuclear plants across the country.