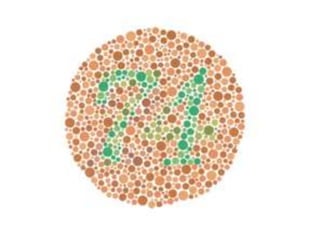
The document discusses sex-linked traits which are traits controlled by genes on the sex chromosomes. It notes that females have two X chromosomes and are denoted XX while males have one X and one Y chromosome and are denoted XY. The X chromosome contains many more genes than the Y chromosome. It describes an experiment by Thomas Hunt Morgan which showed that eye color in fruit flies is sex-linked. It then explains that sex-linked disorders mainly affect males because females need two copies of a recessive gene while males only need one. It gives color blindness as an example and notes that carrier females have one normal and one recessive gene.