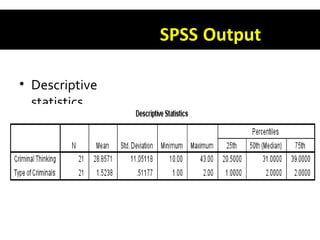
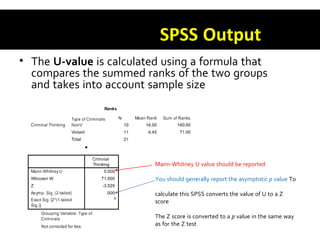
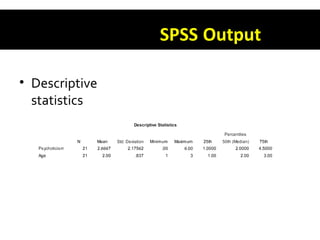
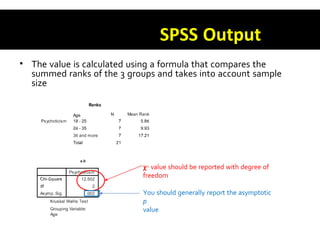
This document discusses non-parametric tests in SPSS, including the Mann-Whitney U test and Kruskal-Wallis H test. The Mann-Whitney U test is used to compare differences between two independent groups on a continuous variable. The Kruskal-Wallis H test is the non-parametric equivalent of a one-way ANOVA and allows comparison of more than two independent groups. Both tests convert raw scores to ranks before comparing groups. The document provides examples of how to report and interpret the results of these tests in SPSS.