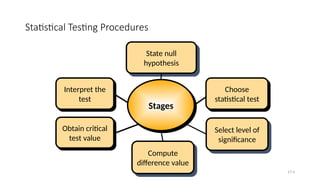
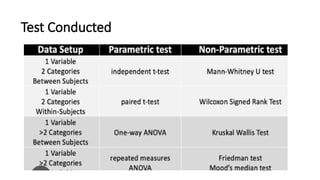
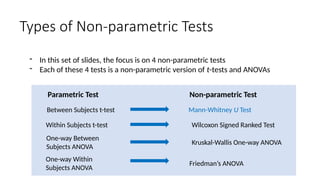
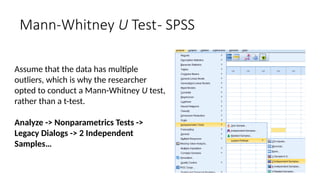
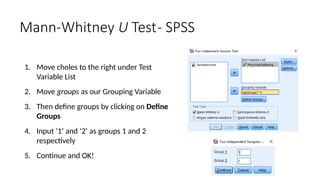
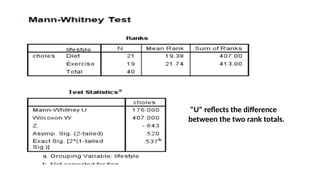
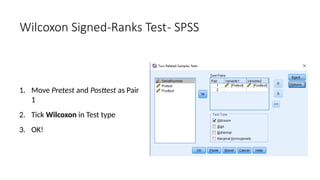
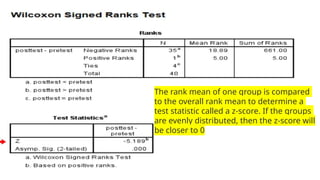
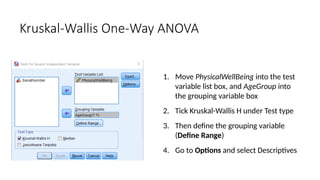
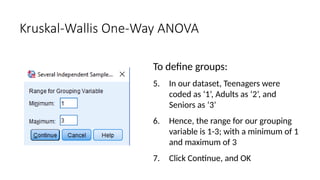
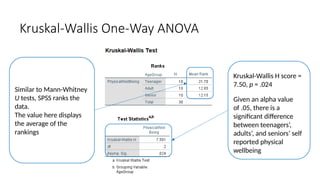
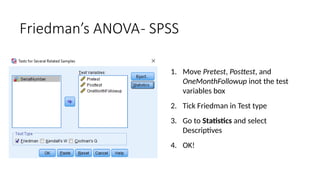
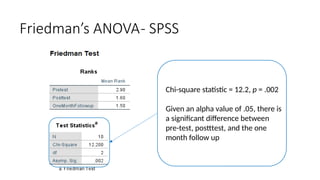
The document outlines the learning objectives and procedures for hypothesis testing, focusing on the use of parametric and nonparametric tests. It describes key nonparametric tests, such as the Mann-Whitney U test, Wilcoxon signed-rank test, Kruskal-Wallis test, and Friedman’s ANOVA, explaining their contexts and applications for statistical analysis. Additionally, it provides practical guidance on using SPSS to conduct these tests effectively.