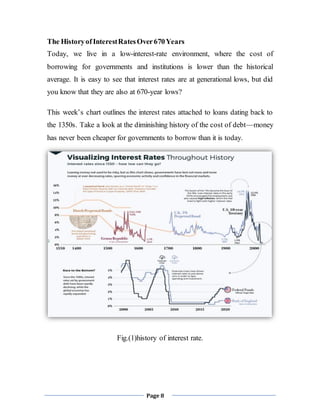
1. The document discusses nominal and effective interest rates, explaining that nominal rates do not account for compounding frequency while effective rates do.
2. It provides an example of a 12% nominal annual interest rate with monthly compounding being equivalent to a 1% interest rate per month.
3. Nominal rates are always lower than equivalent effective annual rates due to differences in compounding frequency, so effective rates provide a better comparison.








![Page 12
Theory
Here we can show some examples about nominal and effective intrest rate :
Example 1.
If a lender charges 12% interest, compounded quarterly, what effective
annual interest rate is the lender charging?
Solution :
A ia = [ 1 + (0.12 / 12) ] 12 - 1 = (1.01)12 - 1 = 1.1268 - 1 = .1268 = 12.68%
B ia = [ 1 + 0.12 ] 12 - 1 = (1.12)12 - 1 = 3.8960 - 1 = 2.8960 = 289.6%
C ia = [ 1 + (0.12 / 12) ] 4 - 1 = (1.01)4 - 1 = 1.0406 - 1 = .0406 = 4.06%
D ia = [ 1 + (0.12 / 4) ] 4 - 1 = (1.03)4 - 1 = 1.1255 - 1 = .1255 = 12.55%
Example 2.
If a lender charges 12% interest, compounded monthly, what is the effective
interest rate per quarter?
Note : m = number of compounding periods per quarter
ie = effective interest rate per quarter.
Solution :
A i = [ 1 + (0.12 / 3) ] 3 - 1 = (1.04)3 - 1 = 0.1249 = 12.49%
B i = [ 1 + 0.03 ] 12 - 1 = (1.03)12 - 1 = 0.4258 = 42.58%
C i = [ 1 + (0.03 / 3) ] 3 - 1 = (1.01)3 - 1 = 0.0303 = 3.03%
D i = [ 1 + (0.03 / 12) ] 3 - 1 = (1.0025)3 - 1 = 0.0075 = 0.75%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engineeringeconomymanagement-200810121847/85/Nominal-effective-Interest-Rates-12-320.jpg)


![Page 15
Solution:
(a) Convert the nominal rates to a semiannual basis, determine m,
(b) calculate the effective semiannual interest rate i. For bid 1,
r _ 9% per year _ 4.5% per 6 months
m _ 2 quarters per 6 months
Effective i% per 6 months = (1+ 0.045/2 )2
– 1 = 1.0455 – 1 = 4.55%
Table(2):Effective simeanuual and anuual intreast rates for three bid rates,example
(b) For the effective annual rate, the time basis in Equation [4.7] is 1 year.
For bid 1,
r = 9% per year m = 4 quarters per year
Effective i% per year = (1+ 0.09/4)4
– 1 = 1.0931 – 1 = 9.31%
The right section of Table 4–4 includes a summary of the effective annual
rates.
(c) Bid 3 includes the lowest effective annual rate of 9.16%, which is
equivalent to an effective semiannual rate of 4.48% when interest is
compounded monthly.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/engineeringeconomymanagement-200810121847/85/Nominal-effective-Interest-Rates-15-320.jpg)

