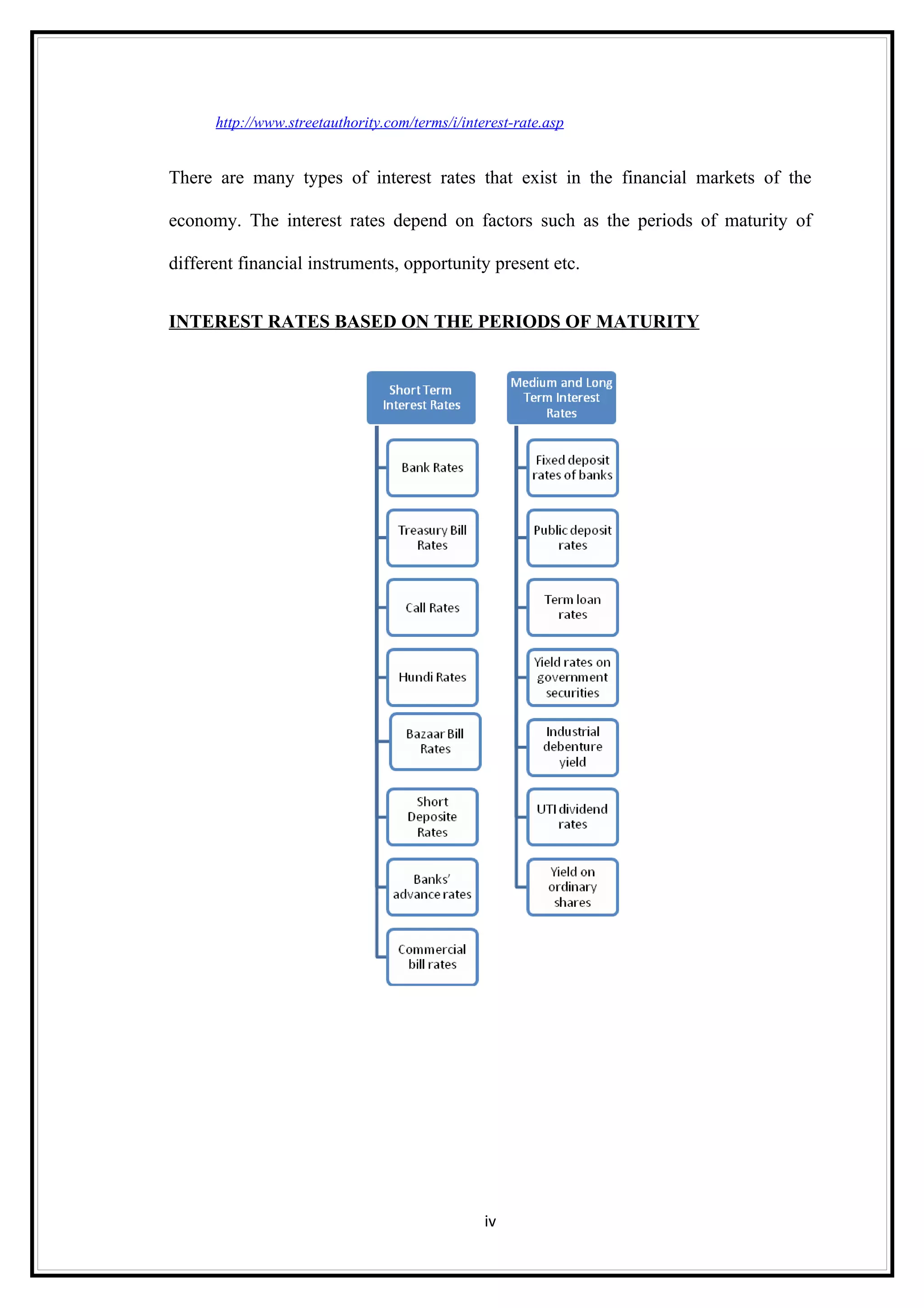
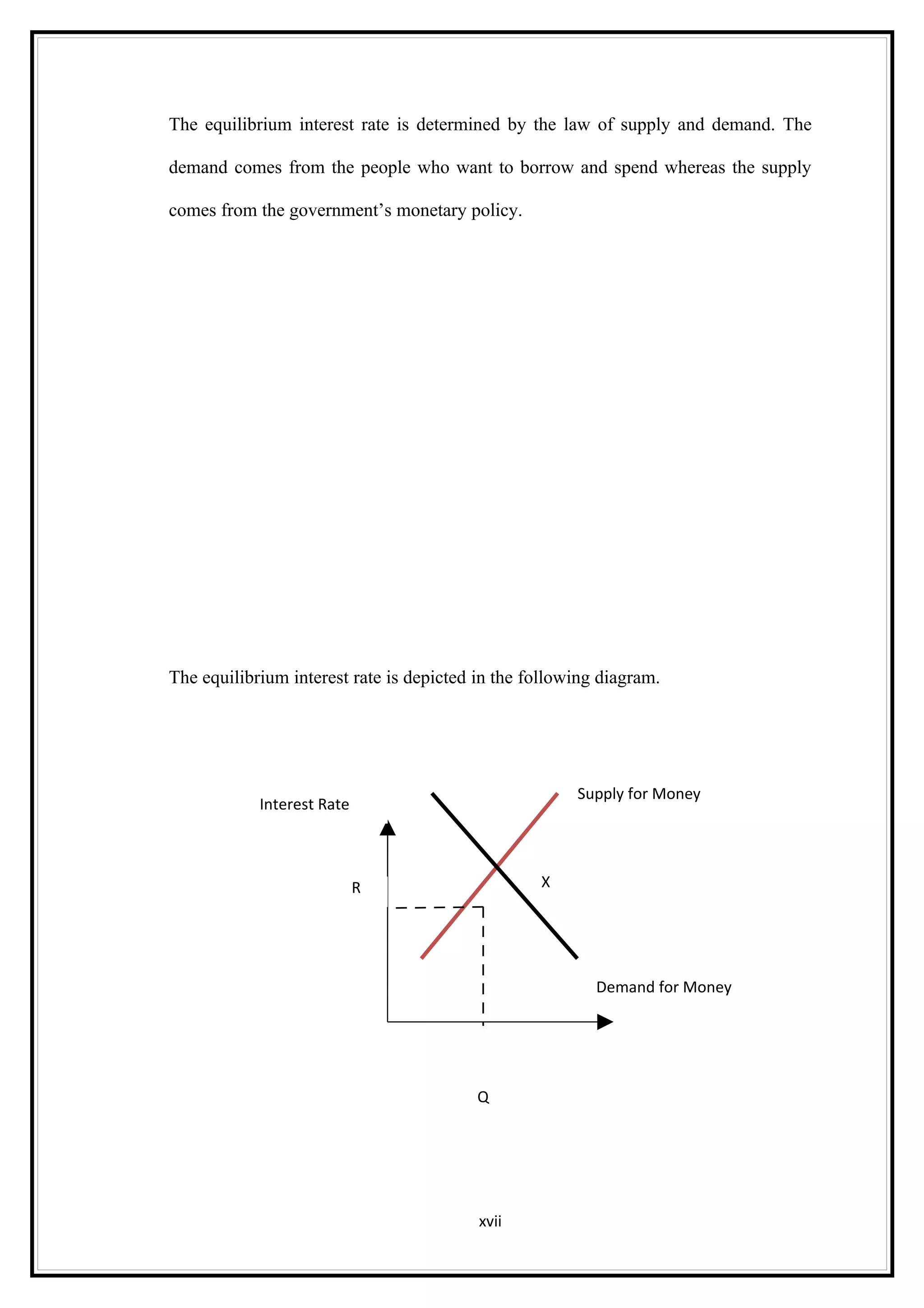
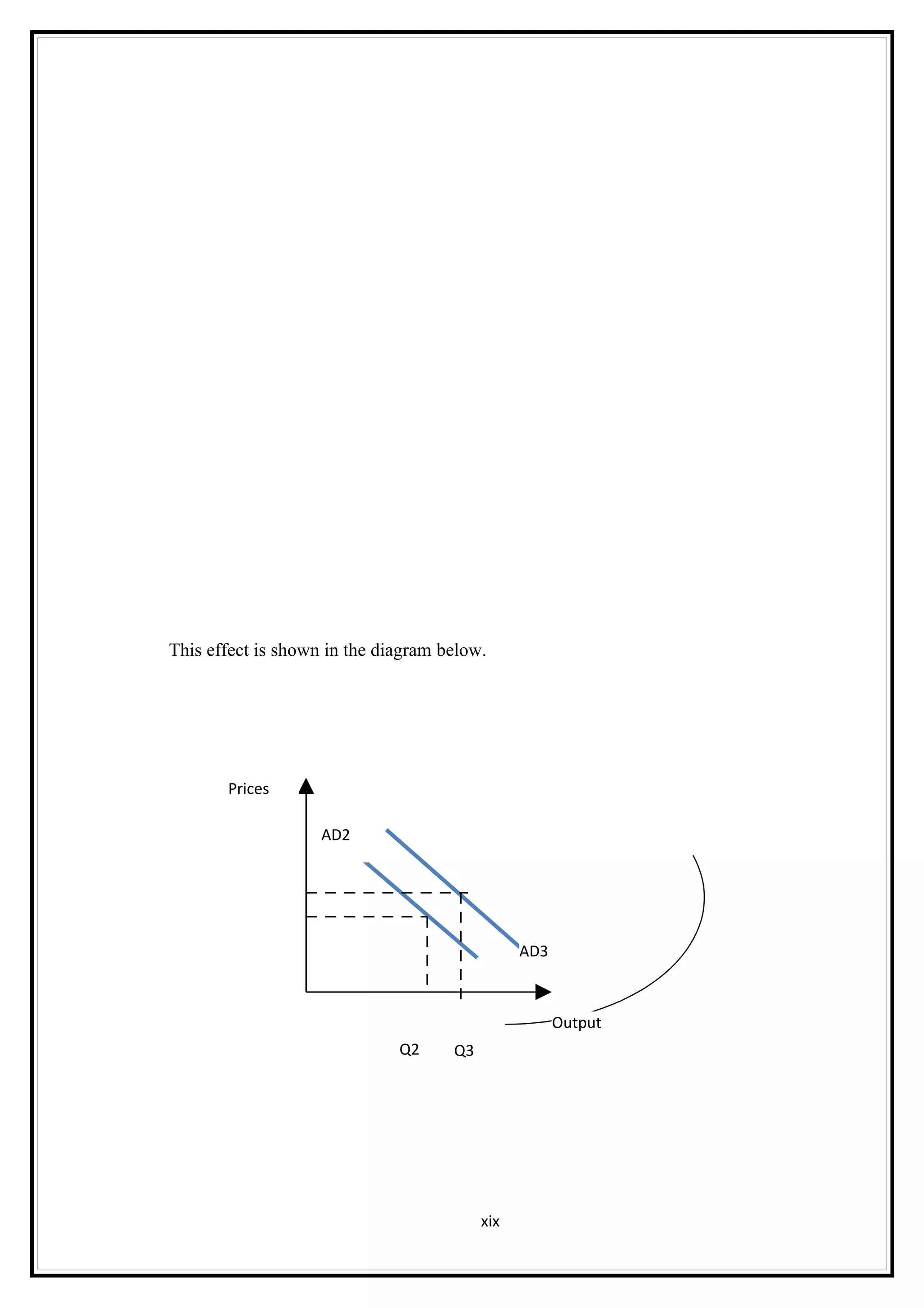
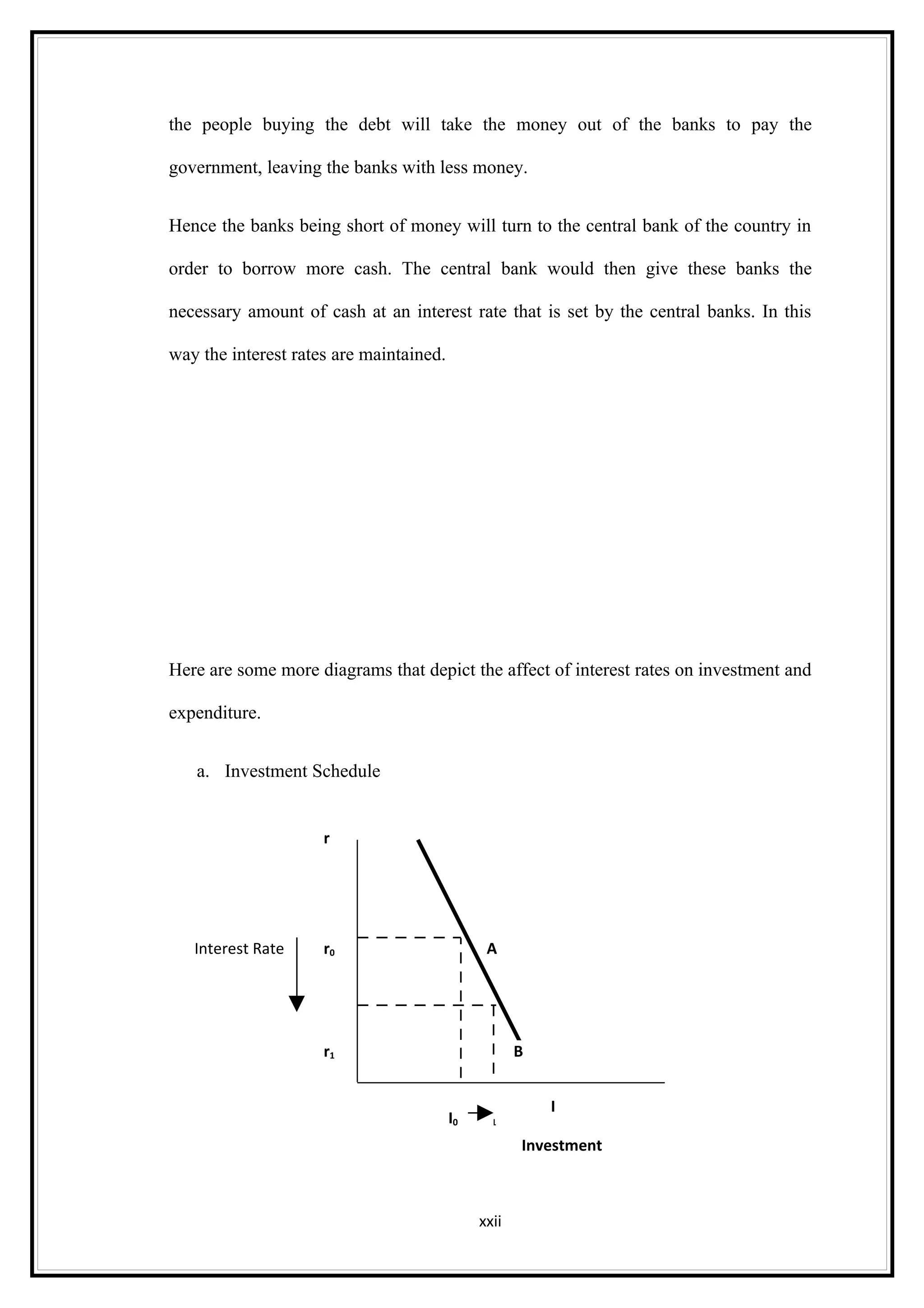
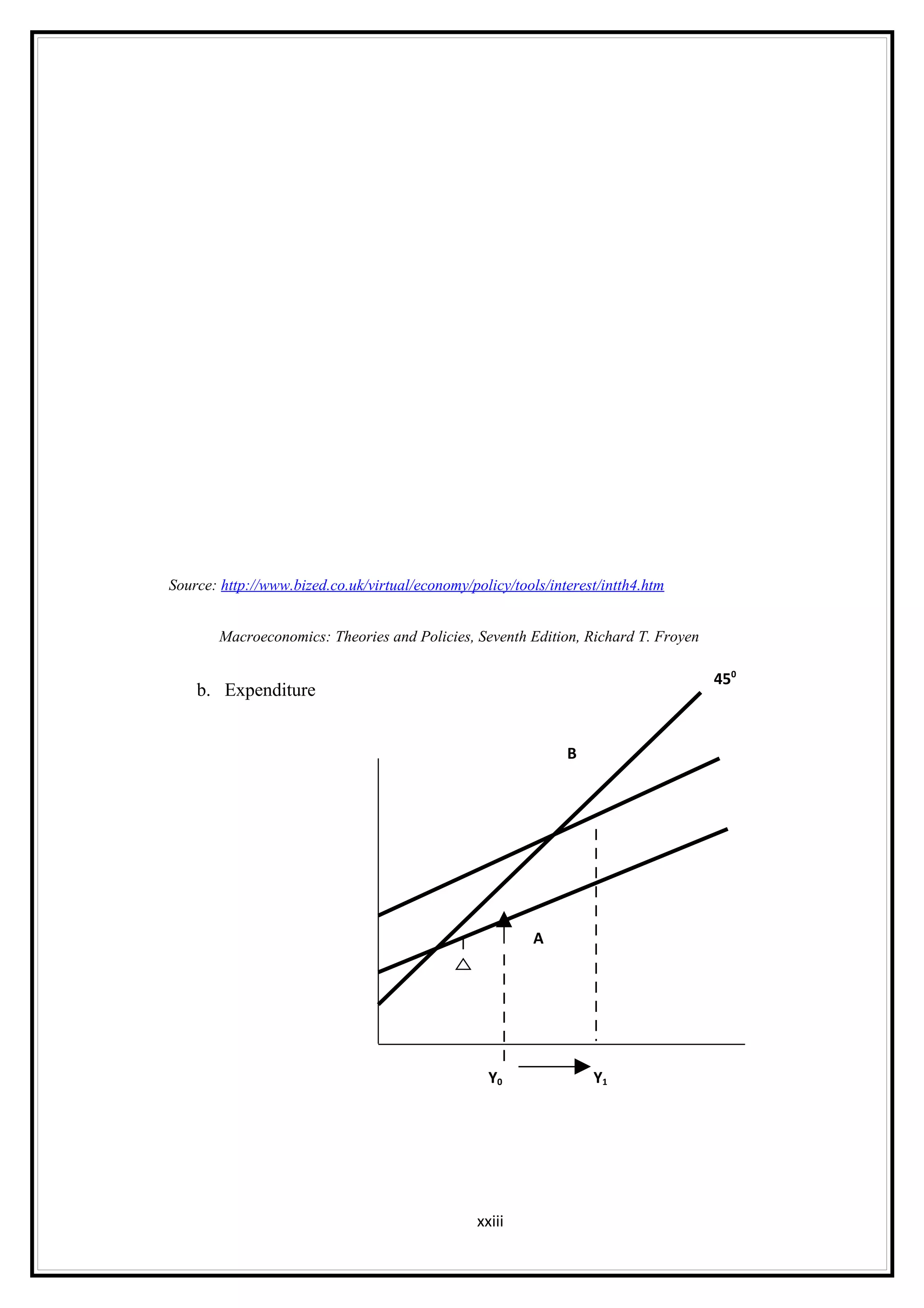
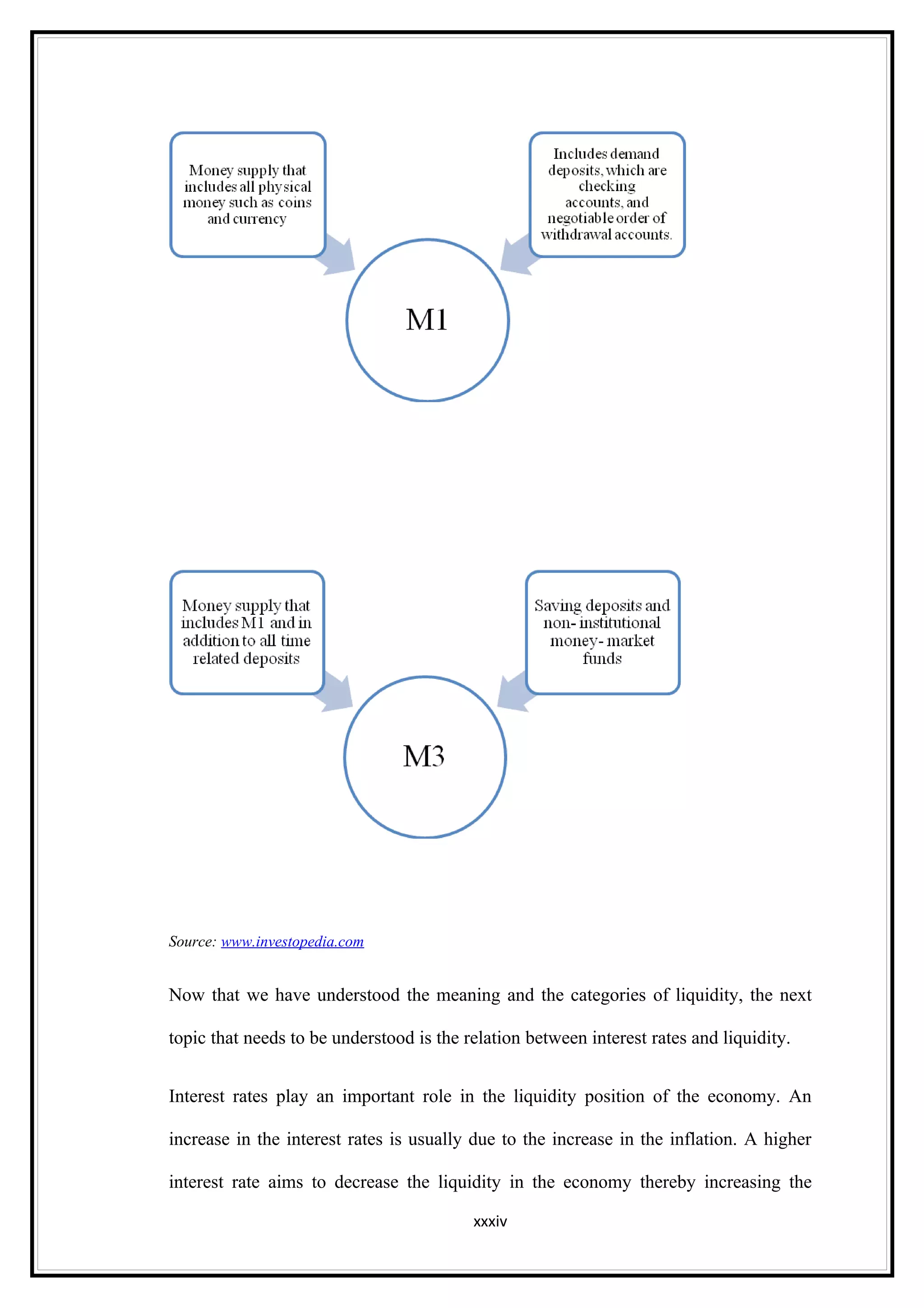
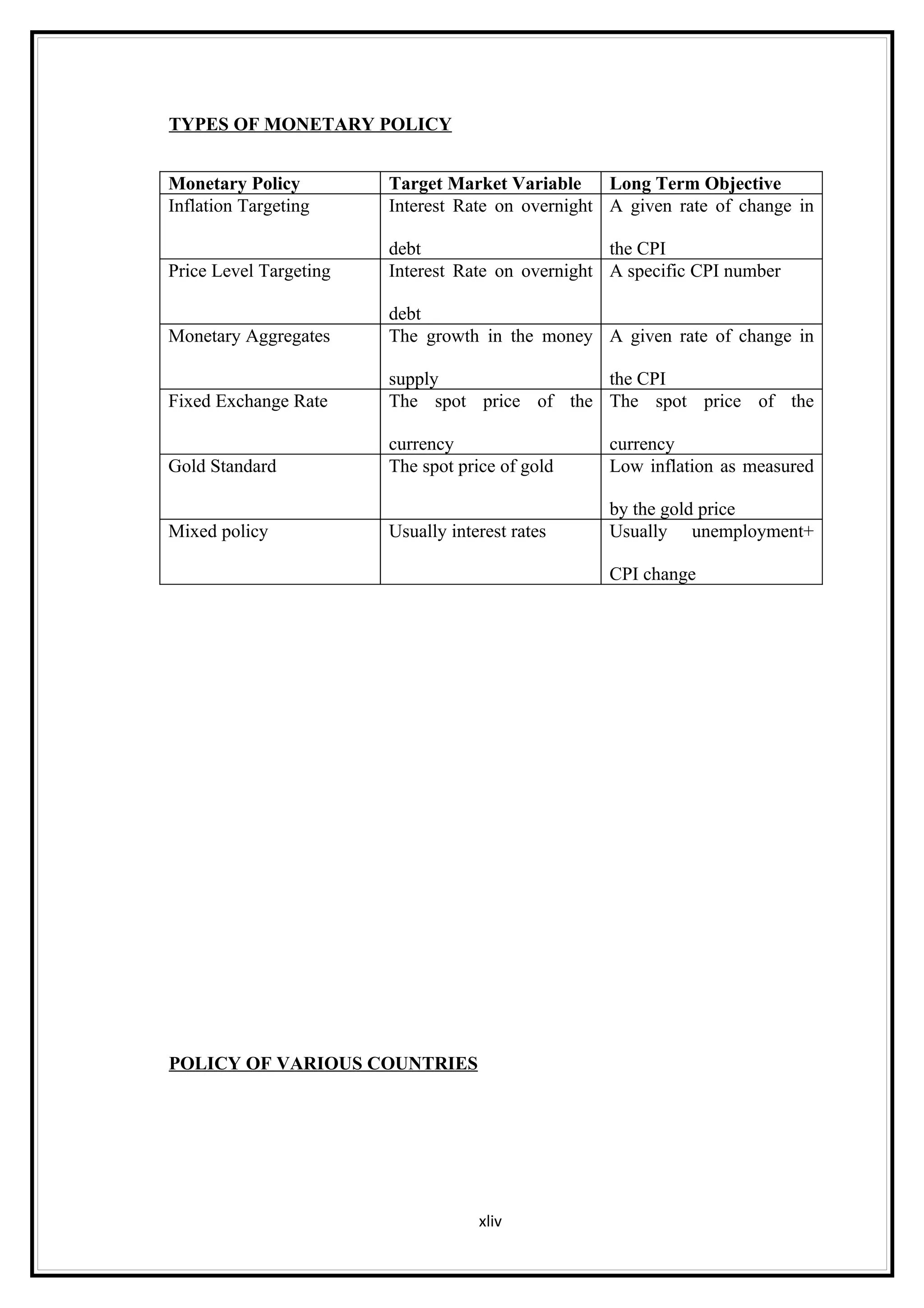
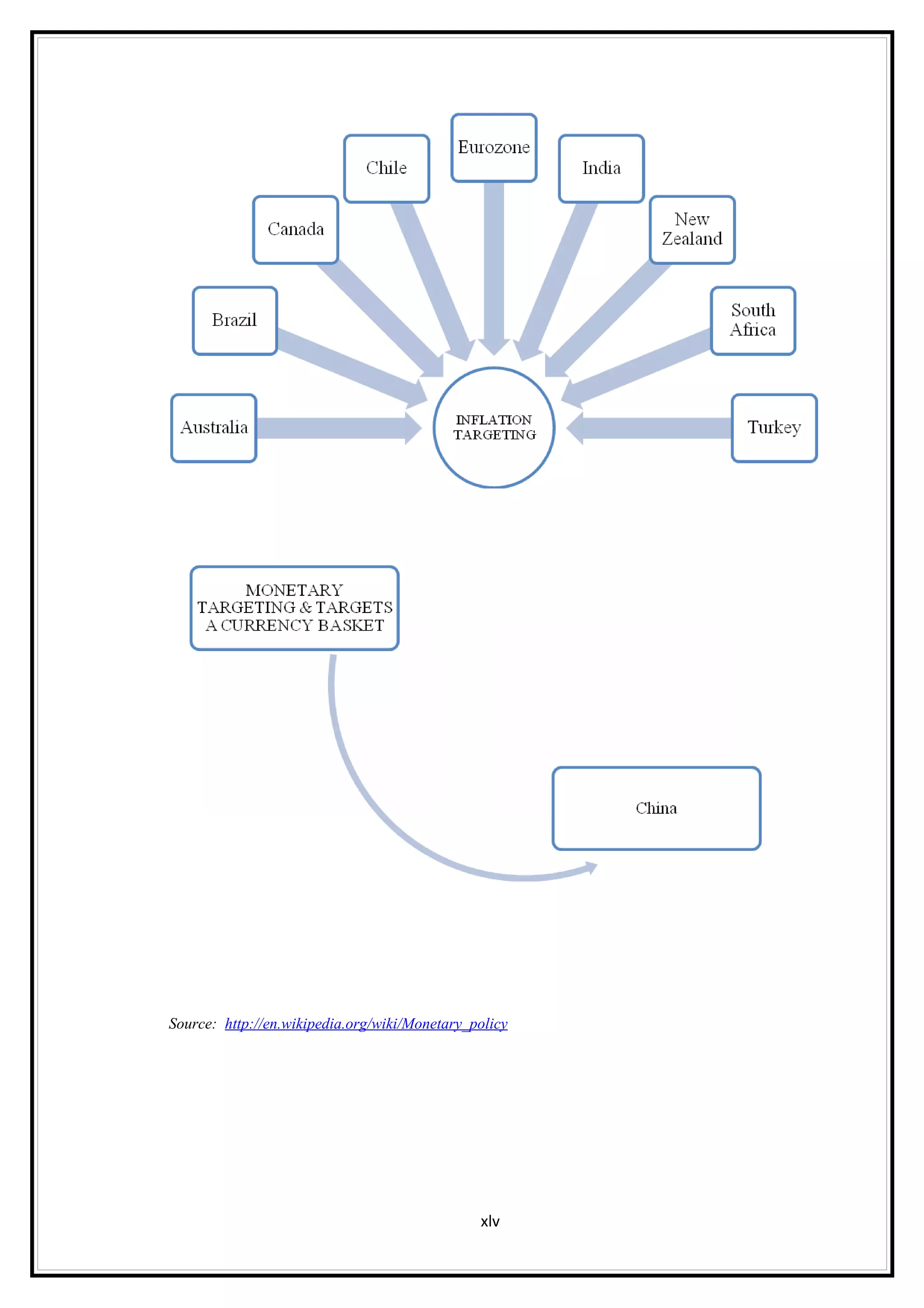
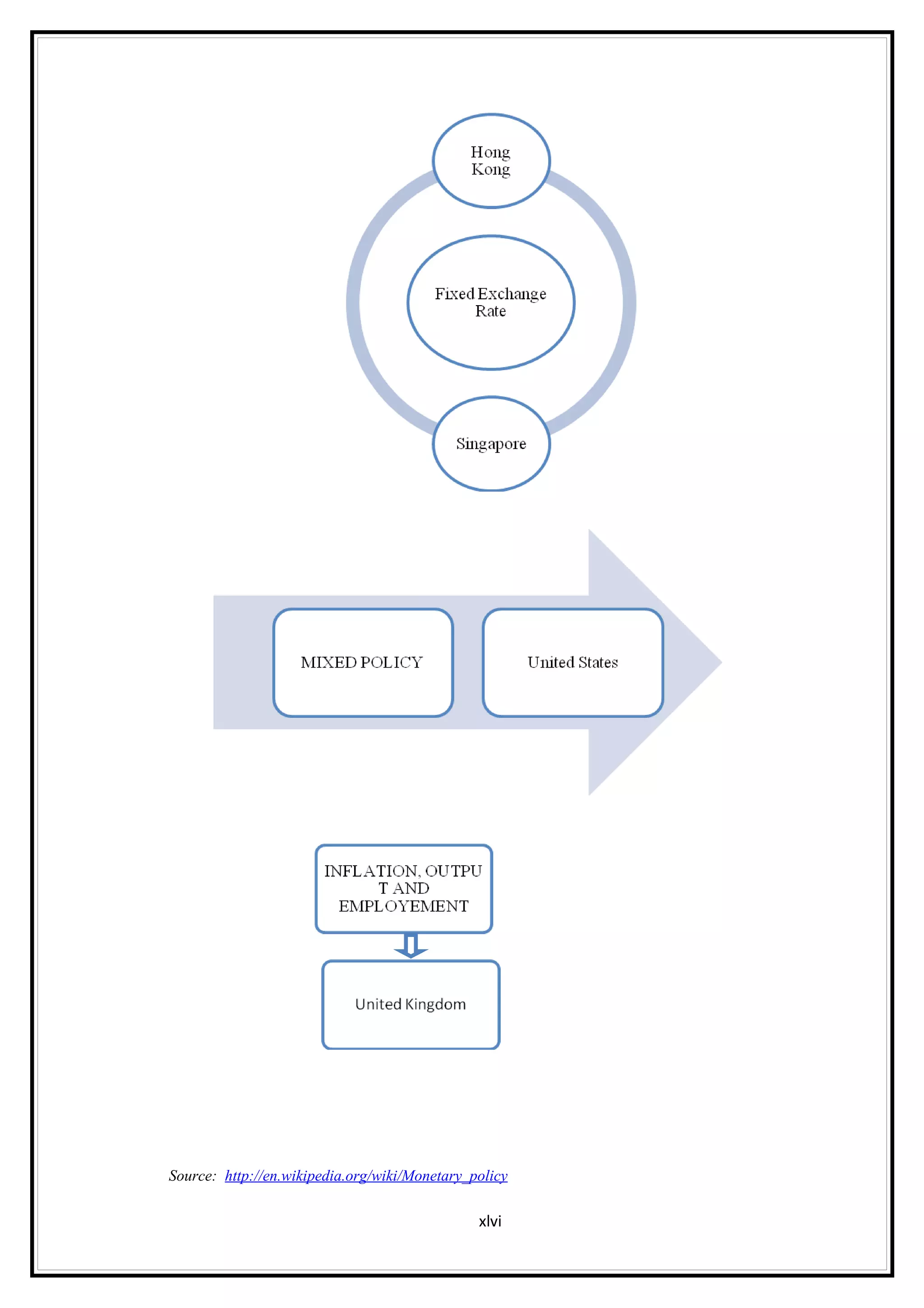
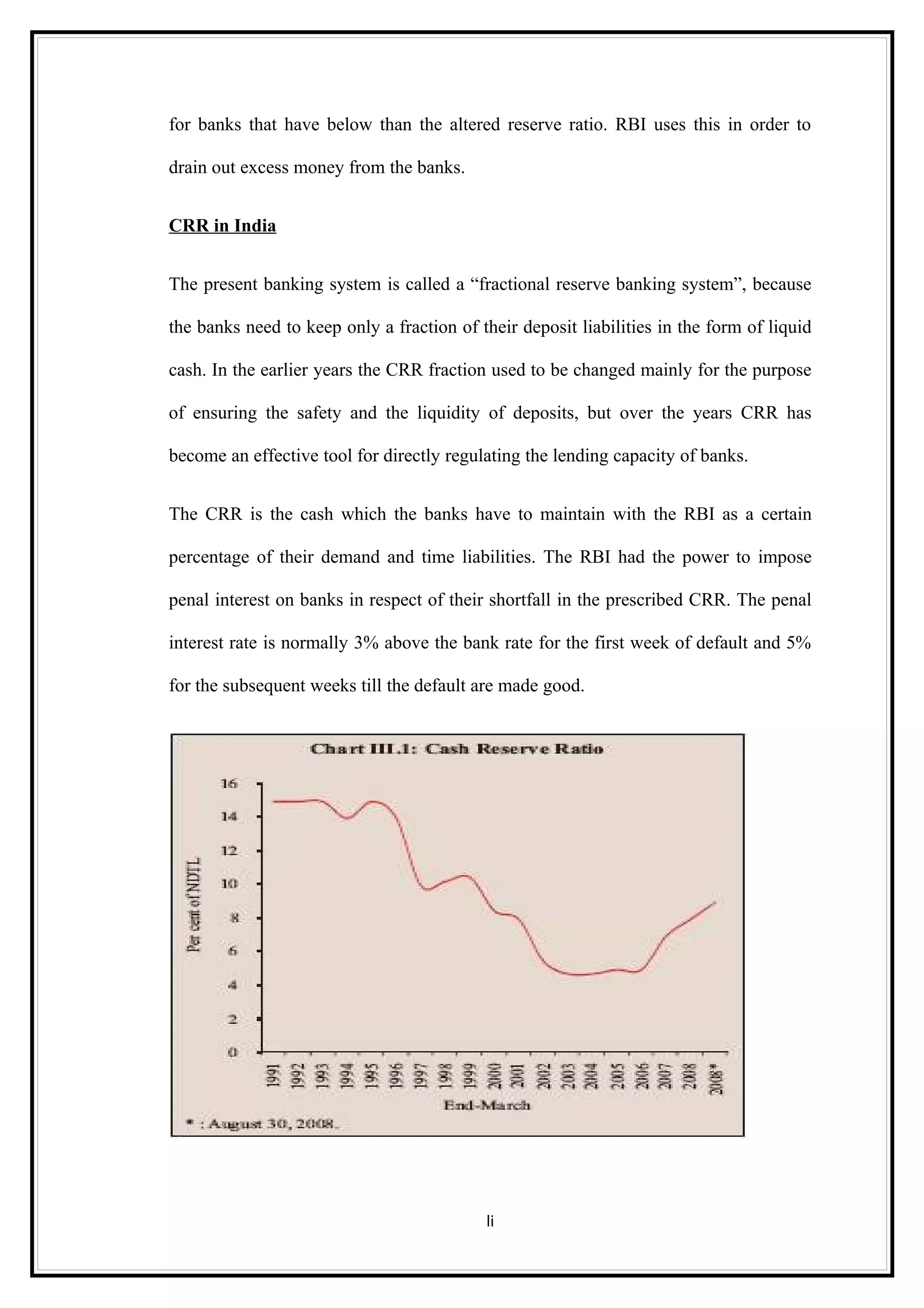
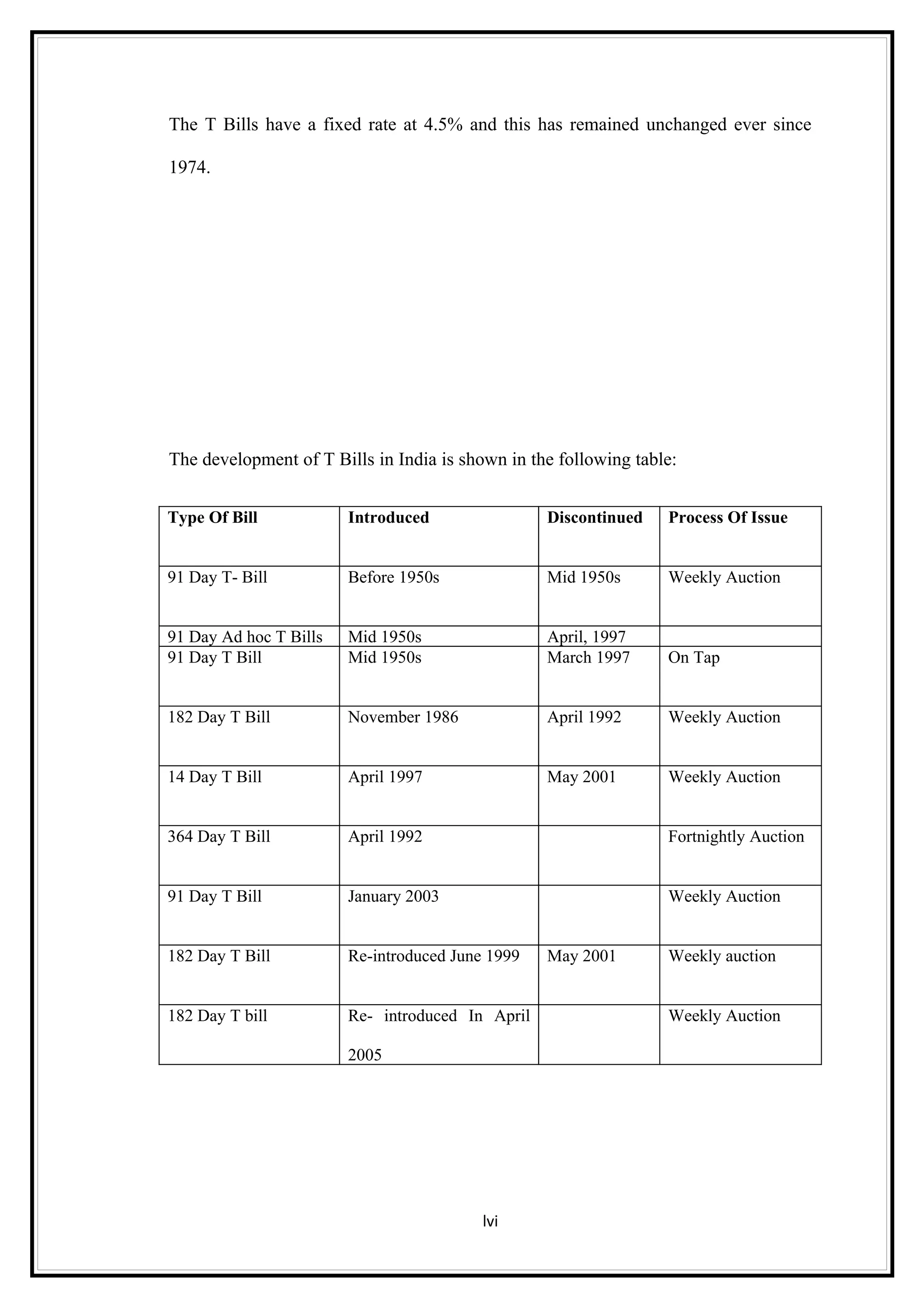
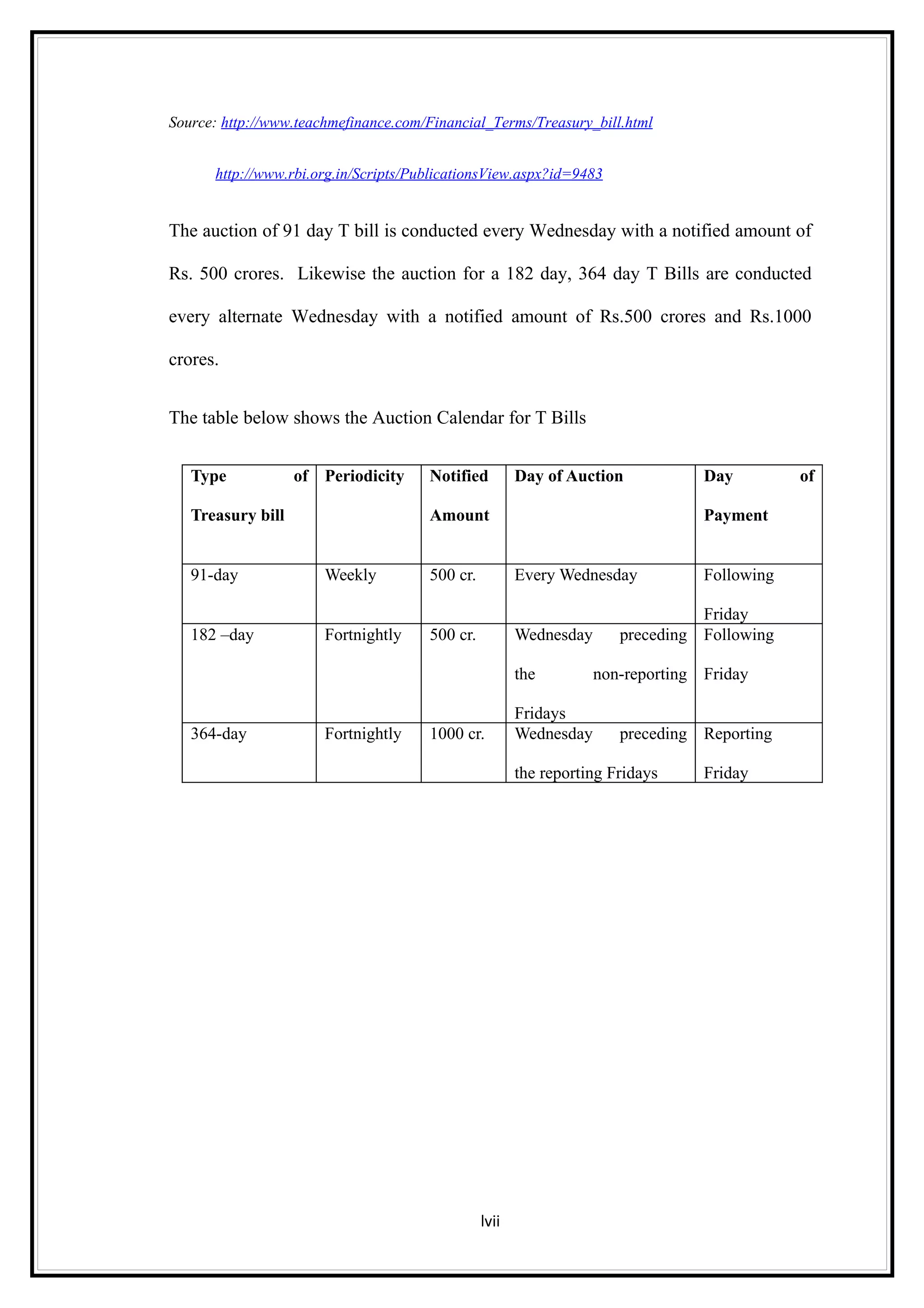
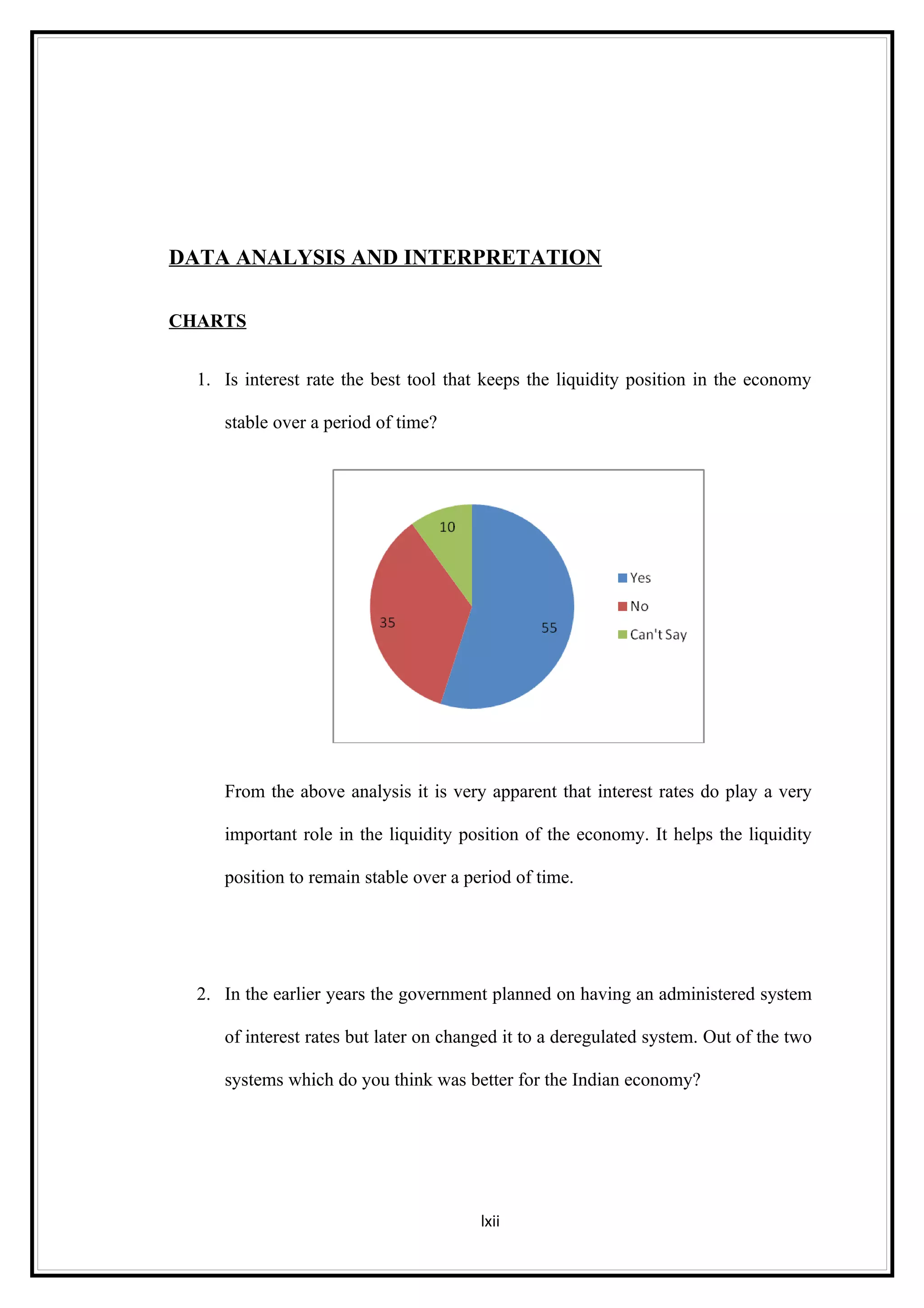
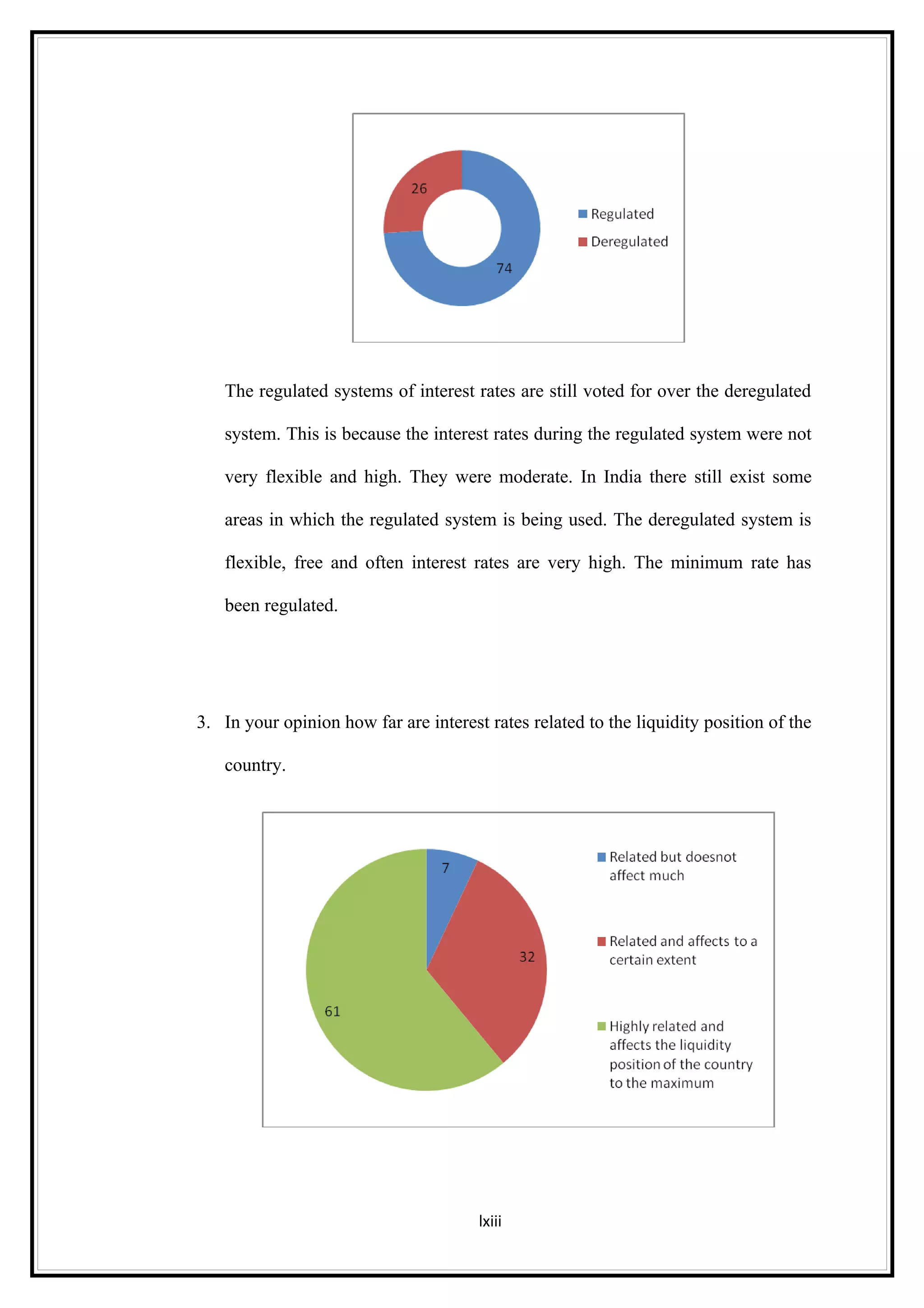
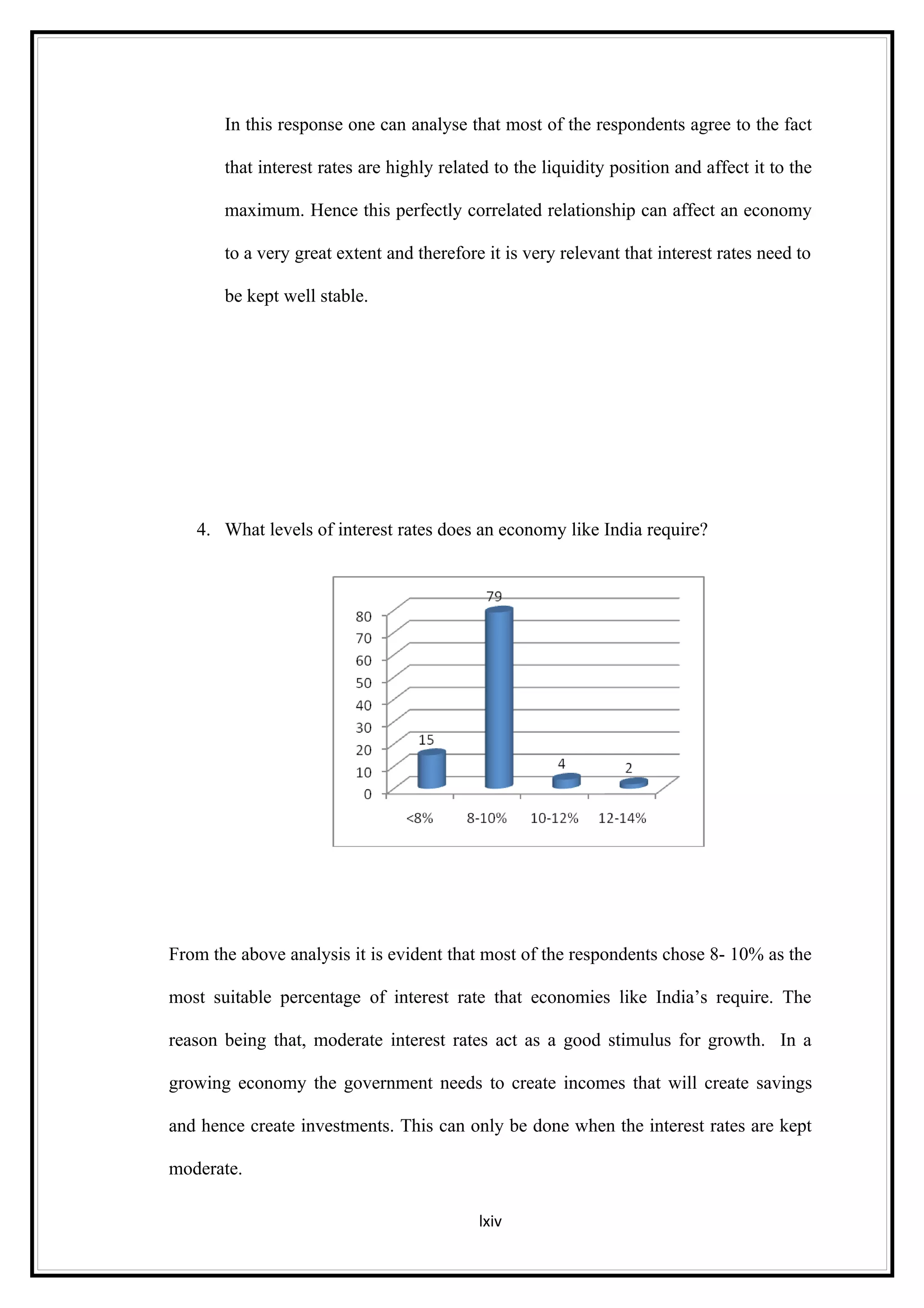
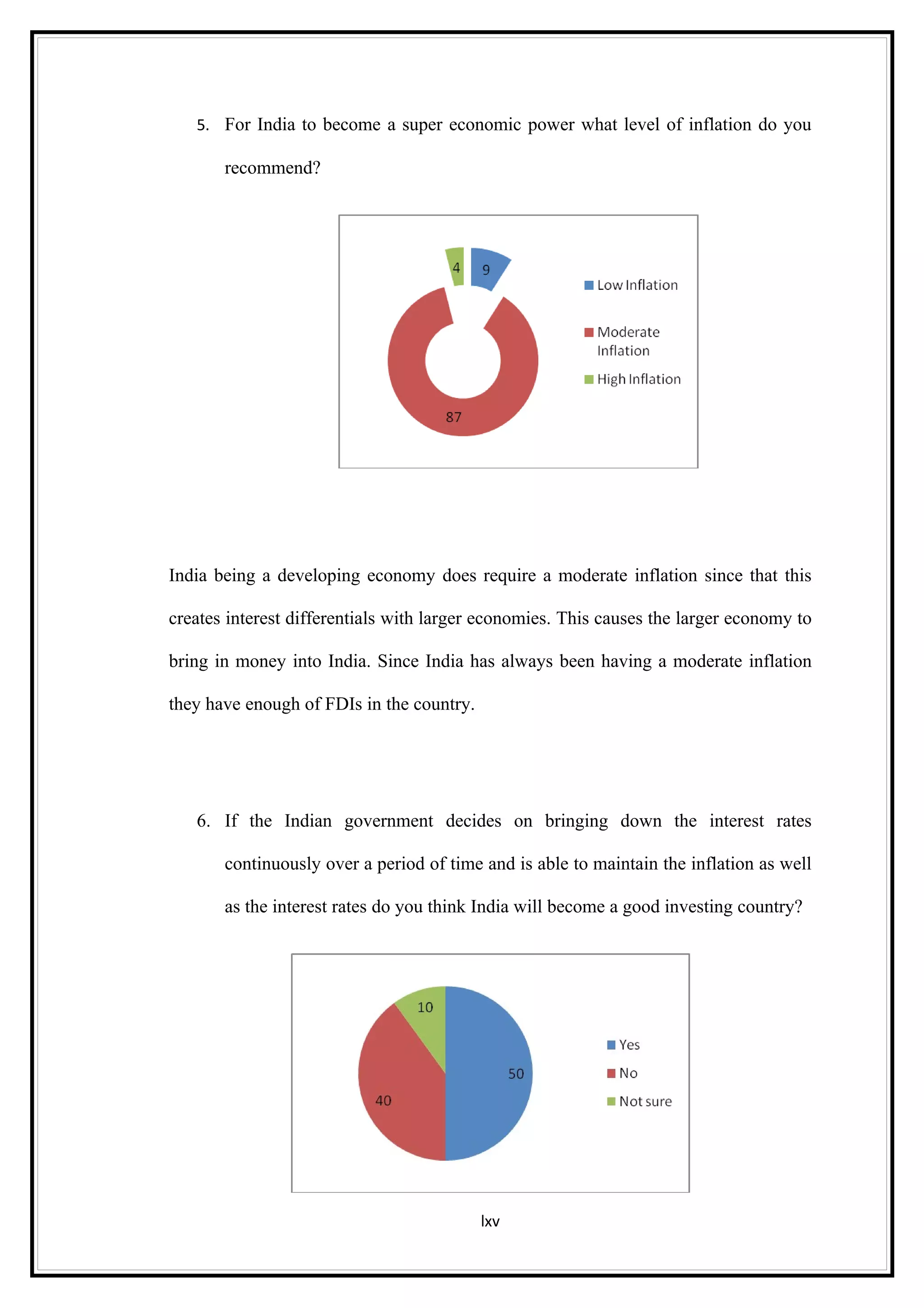
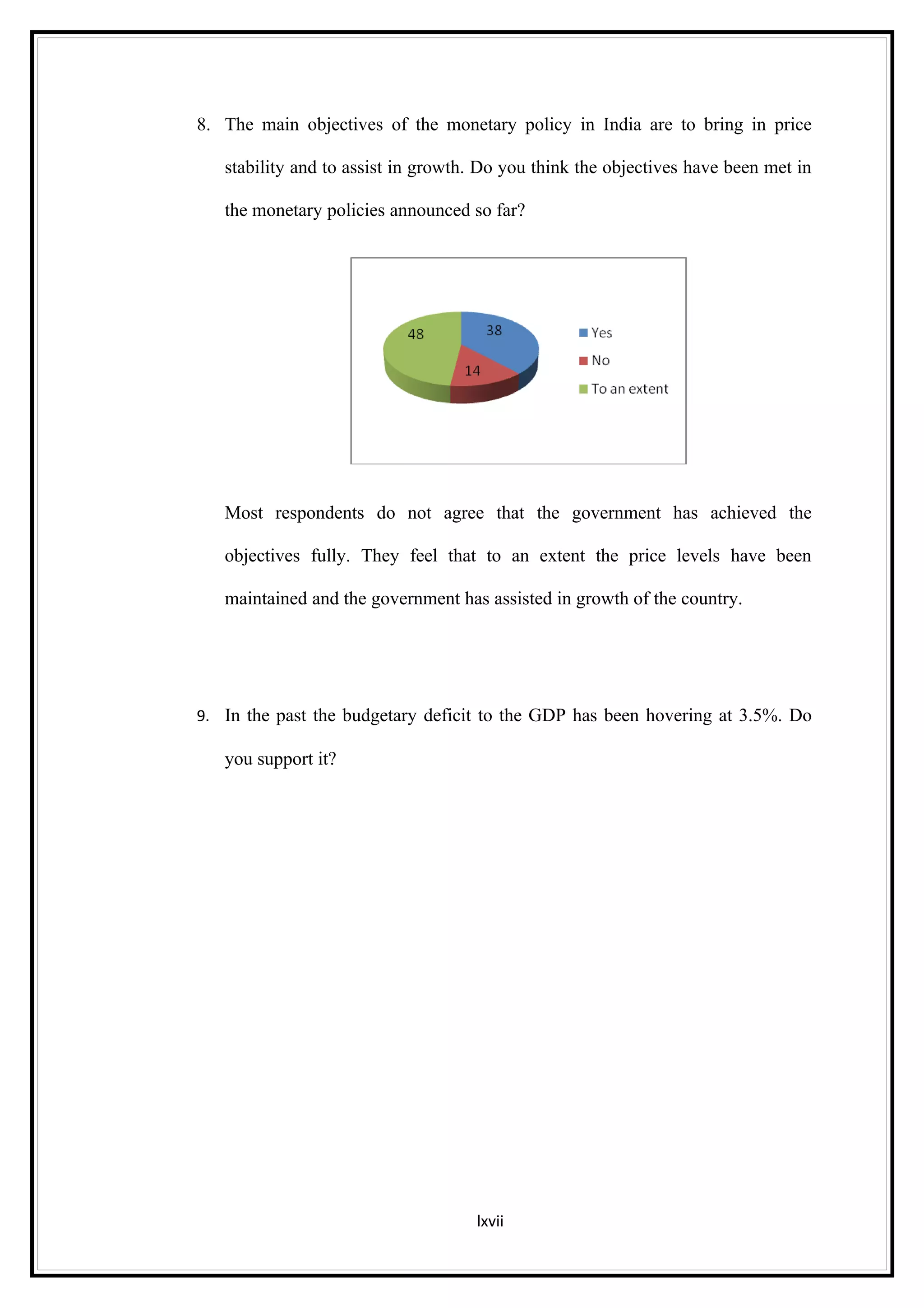
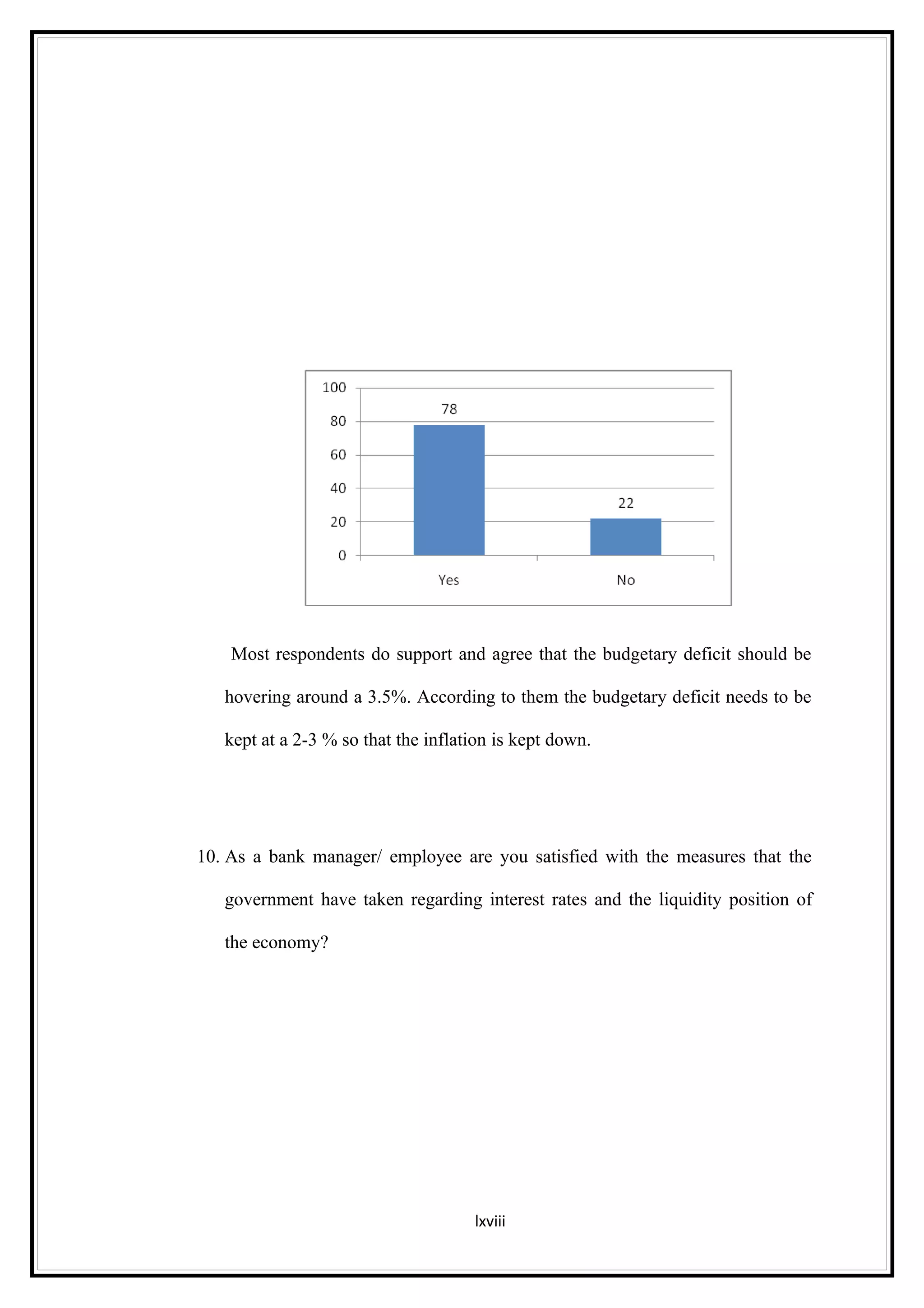
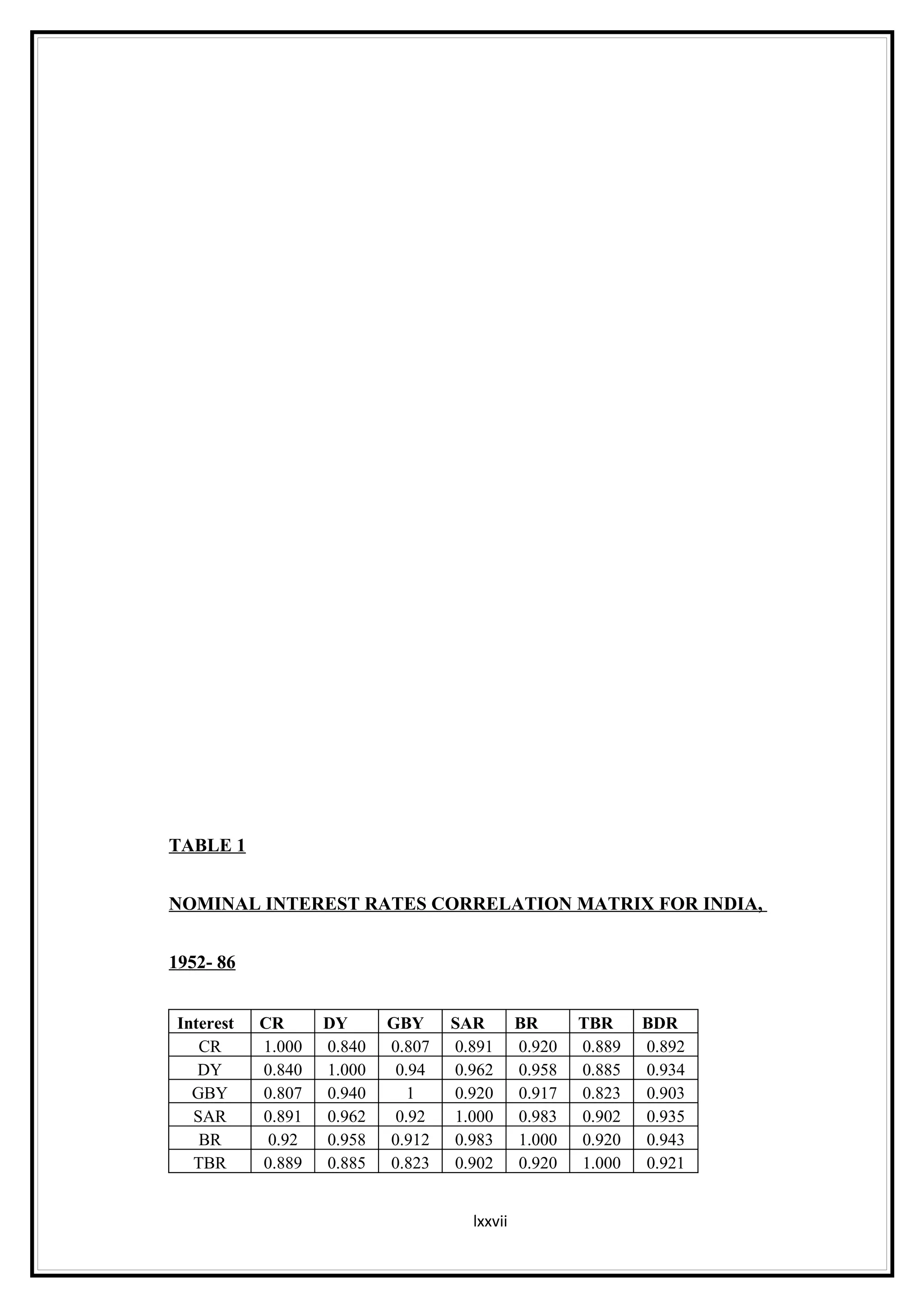
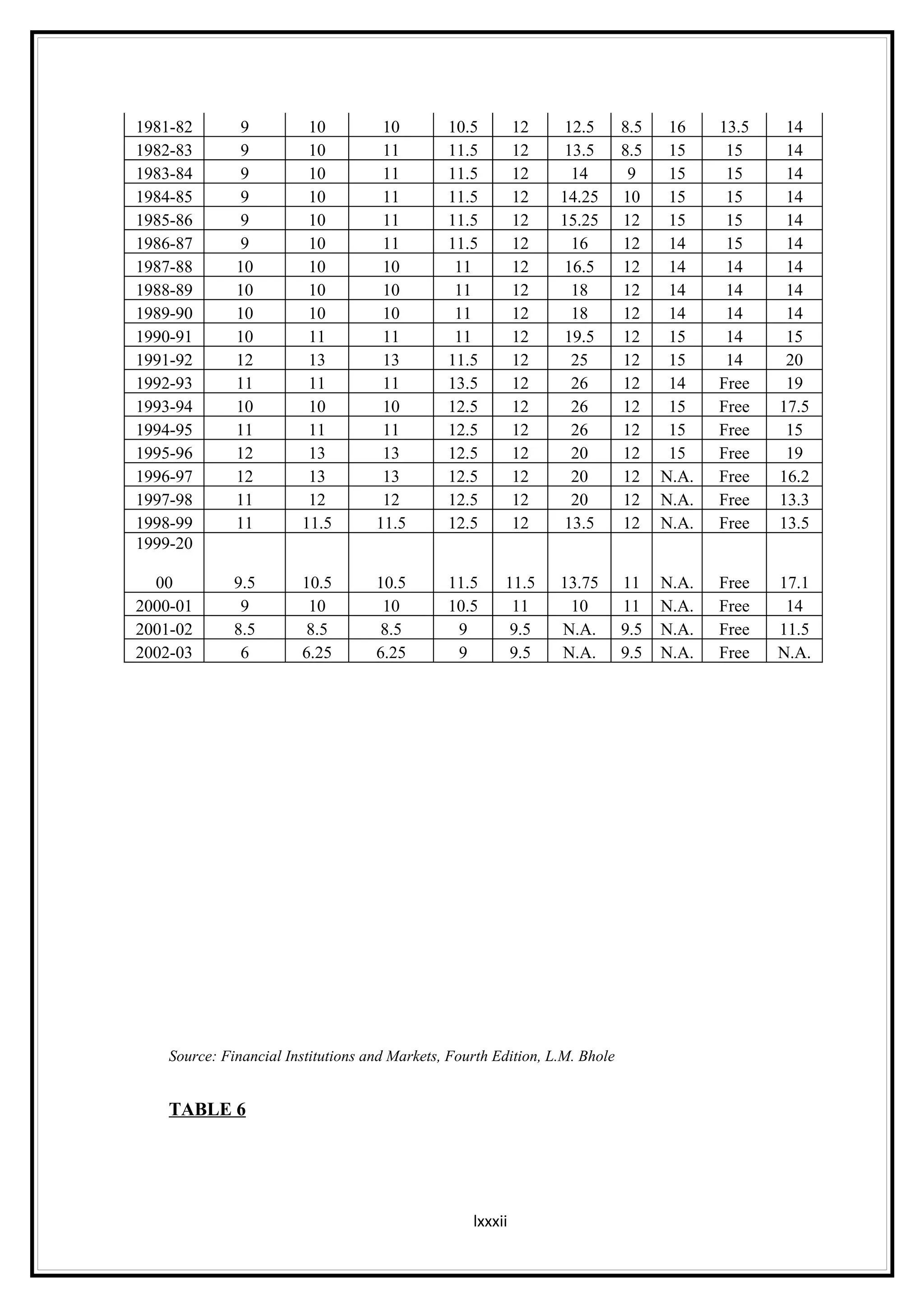
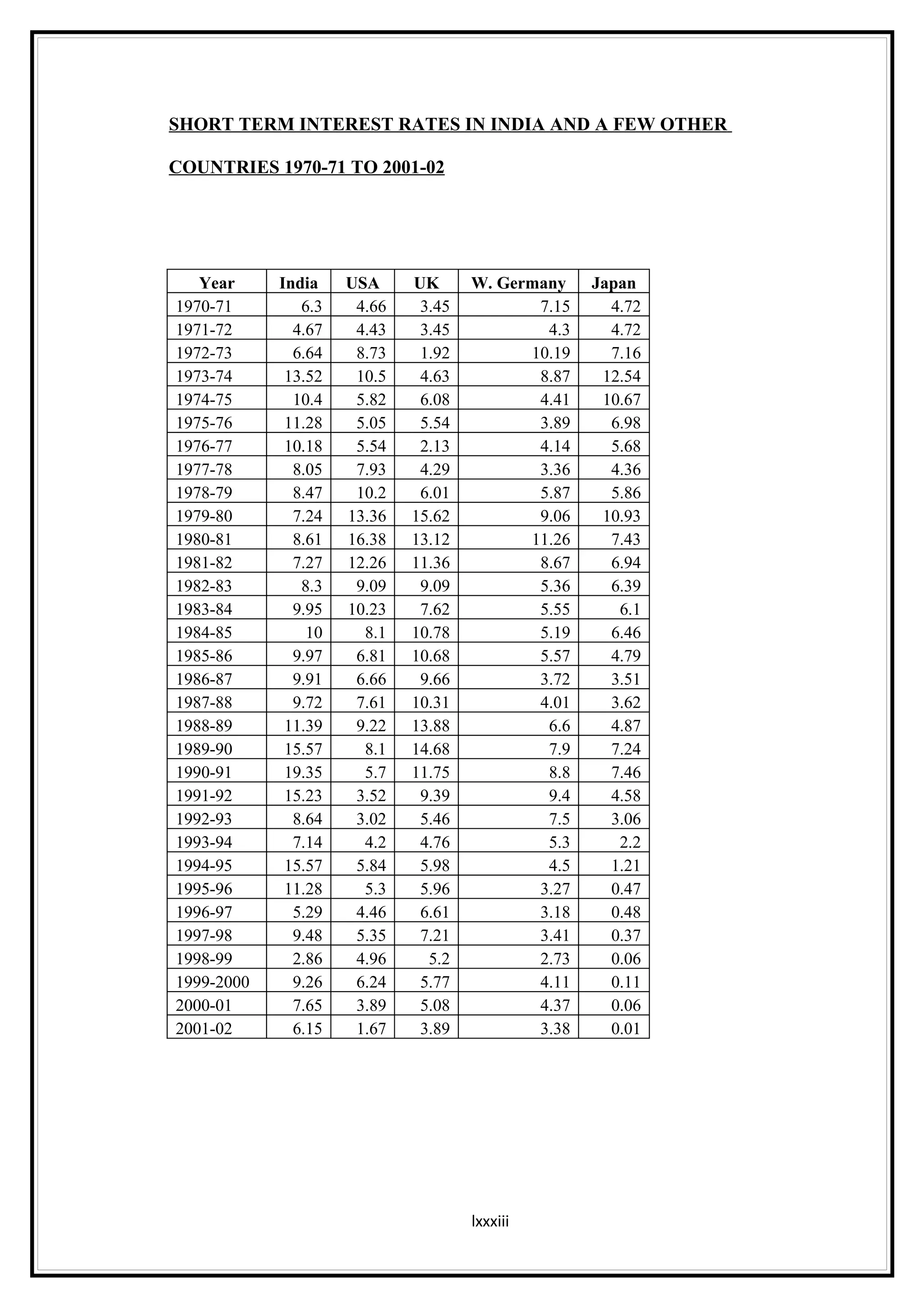
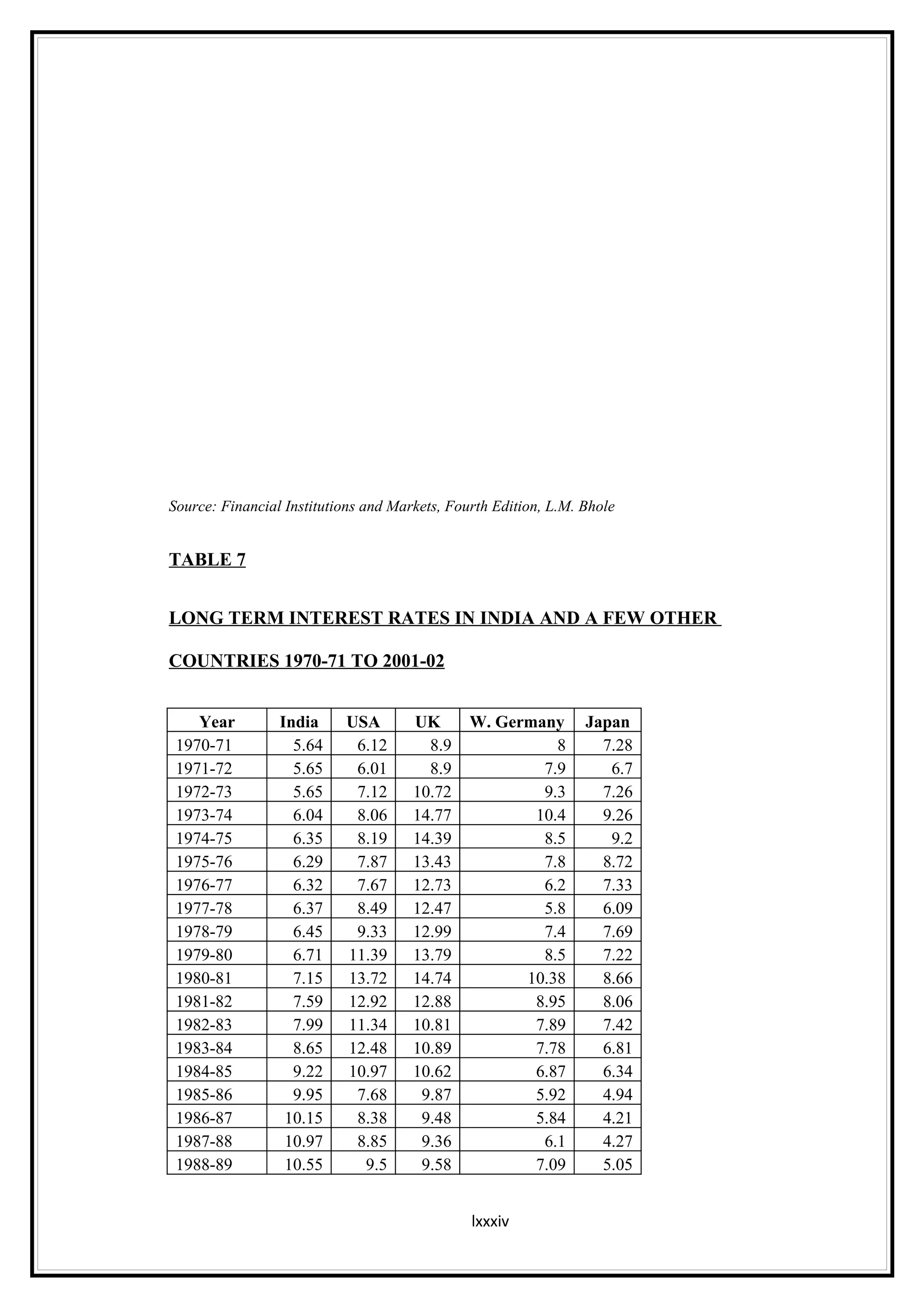
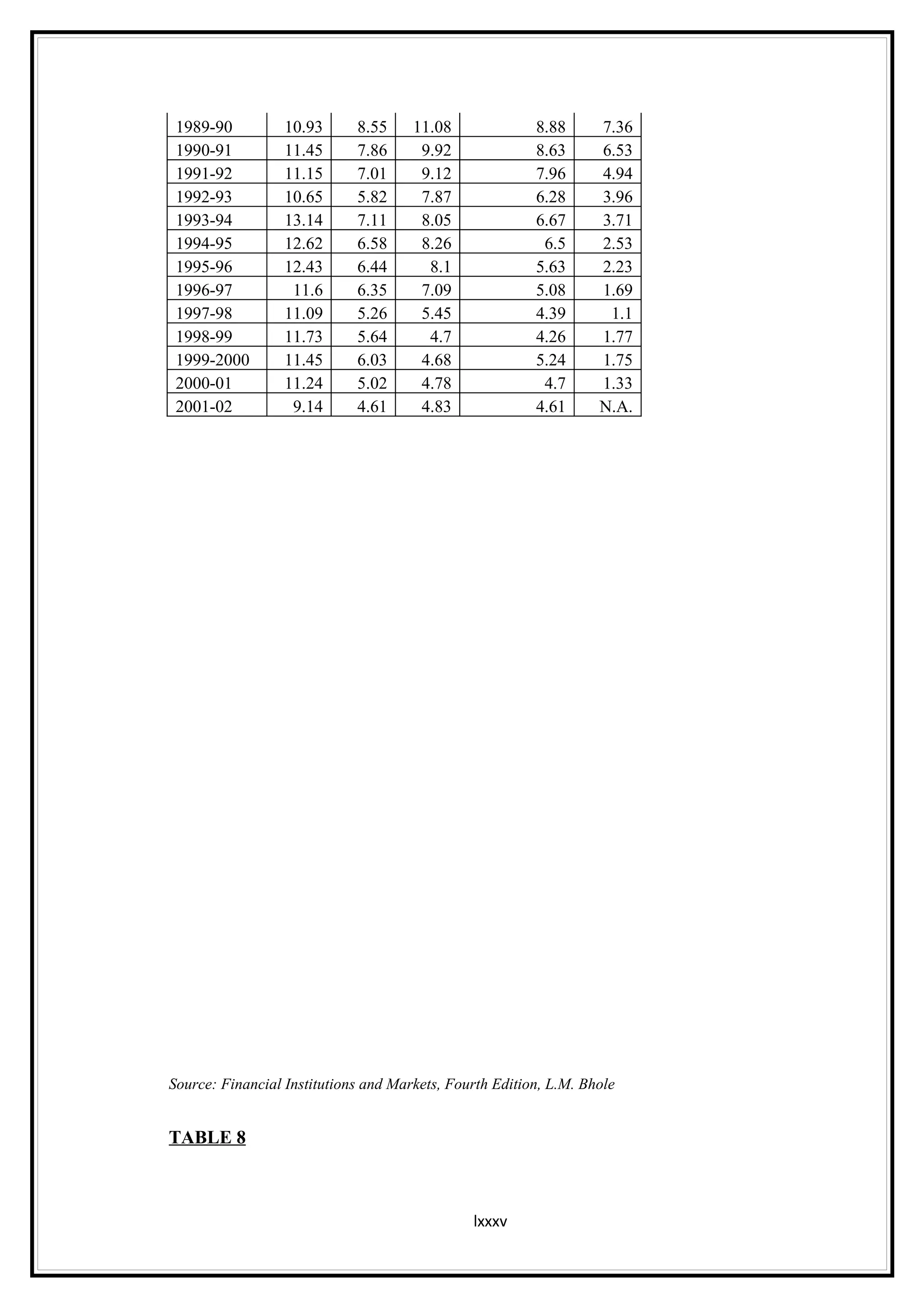
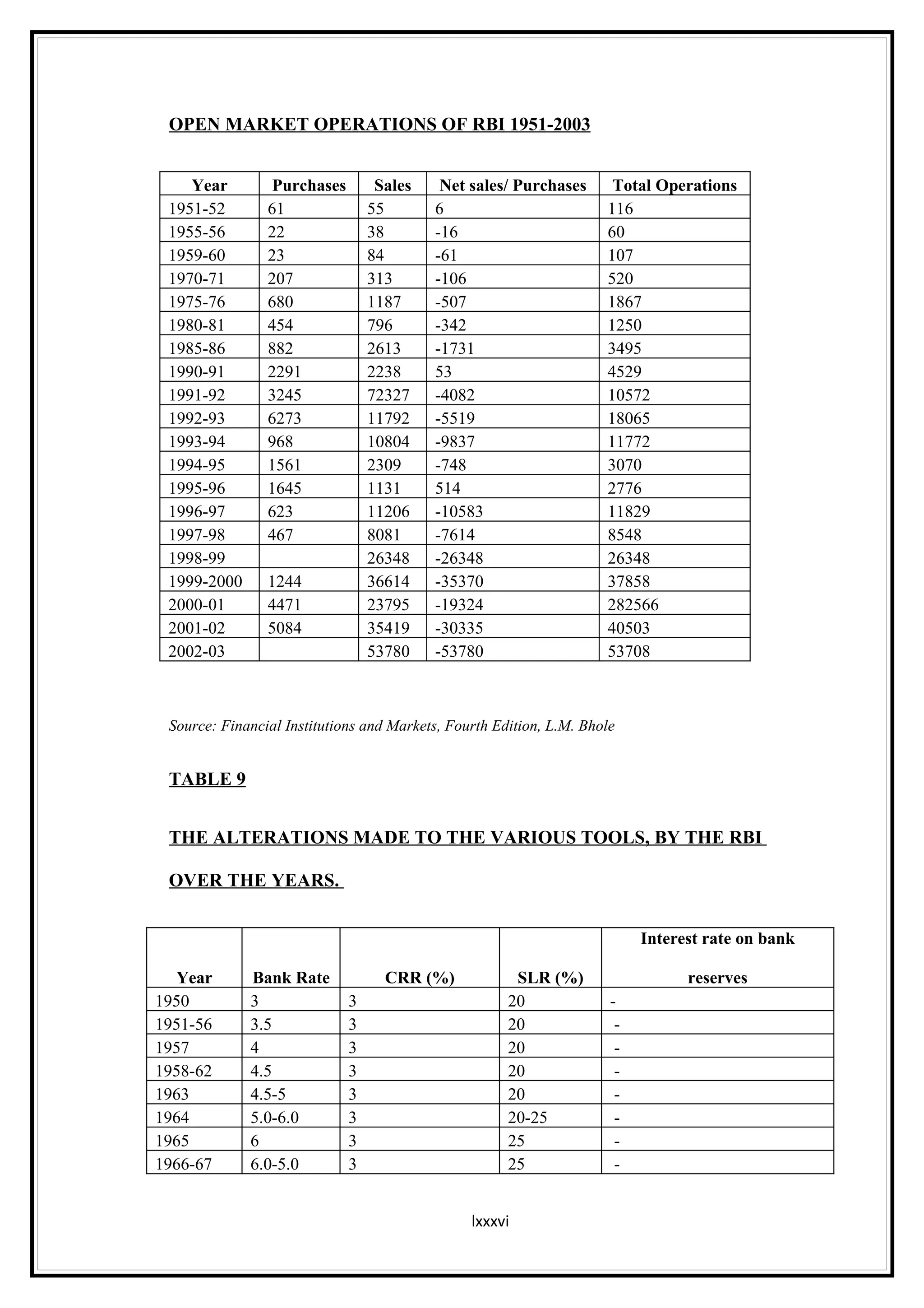
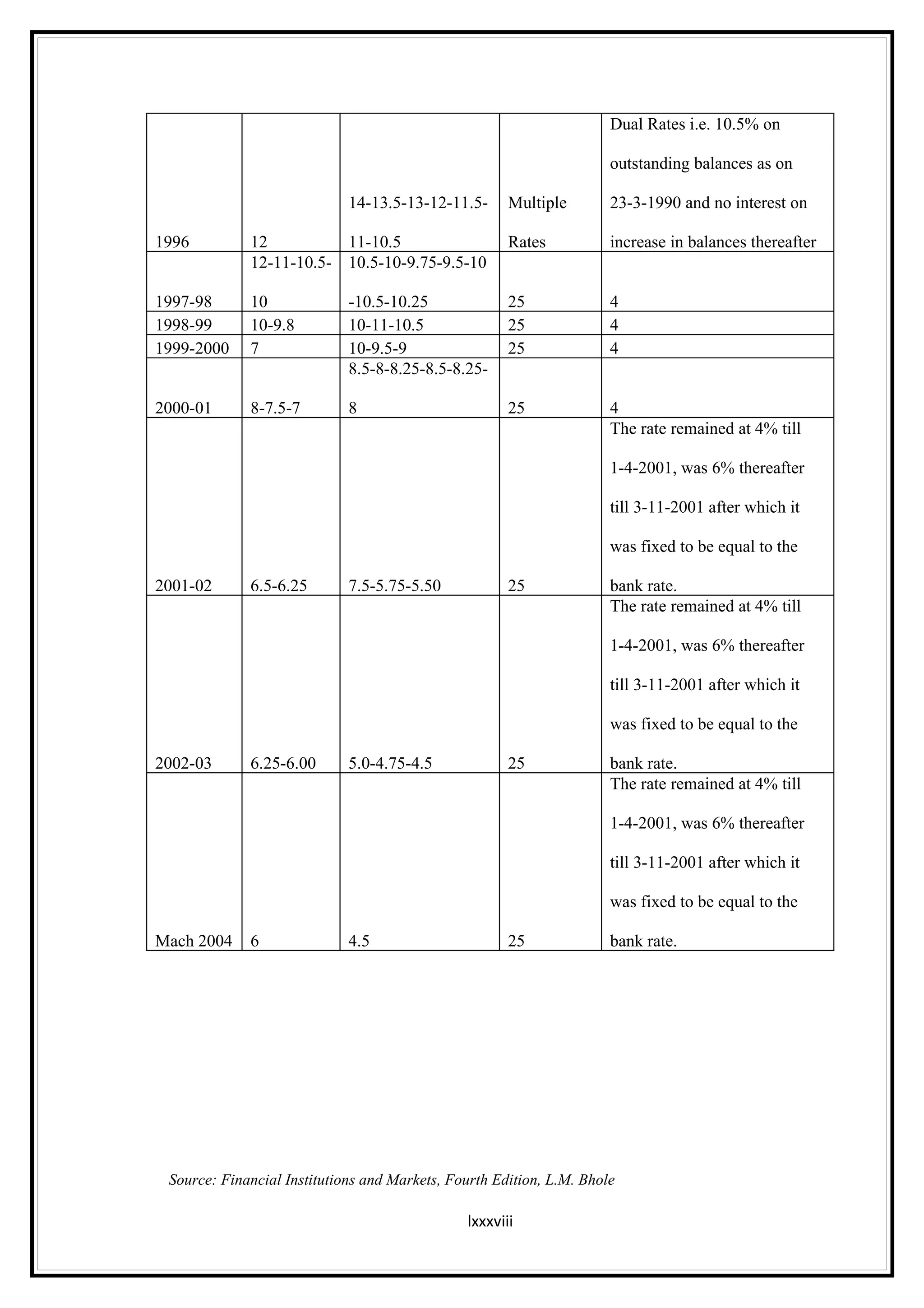
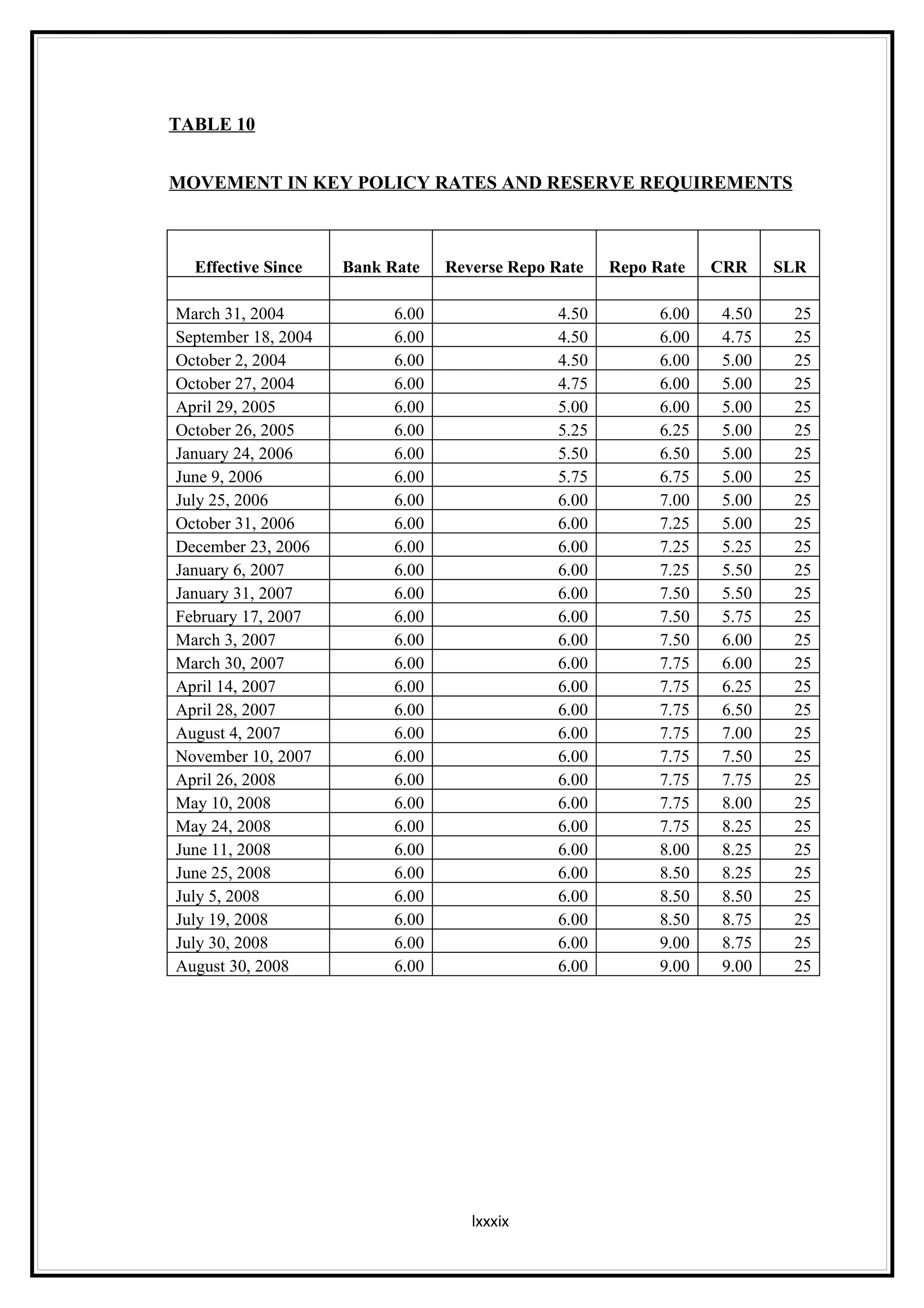
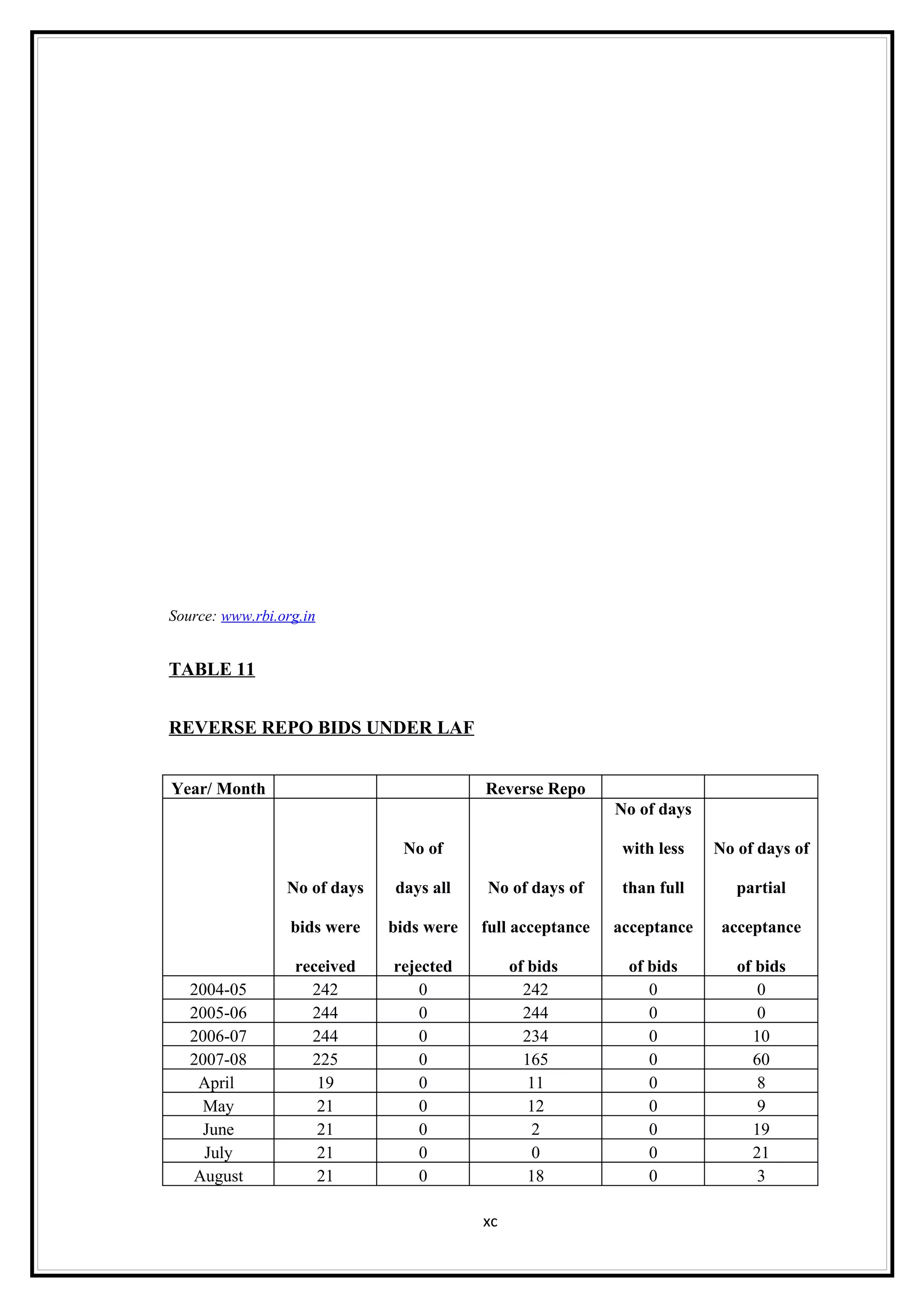
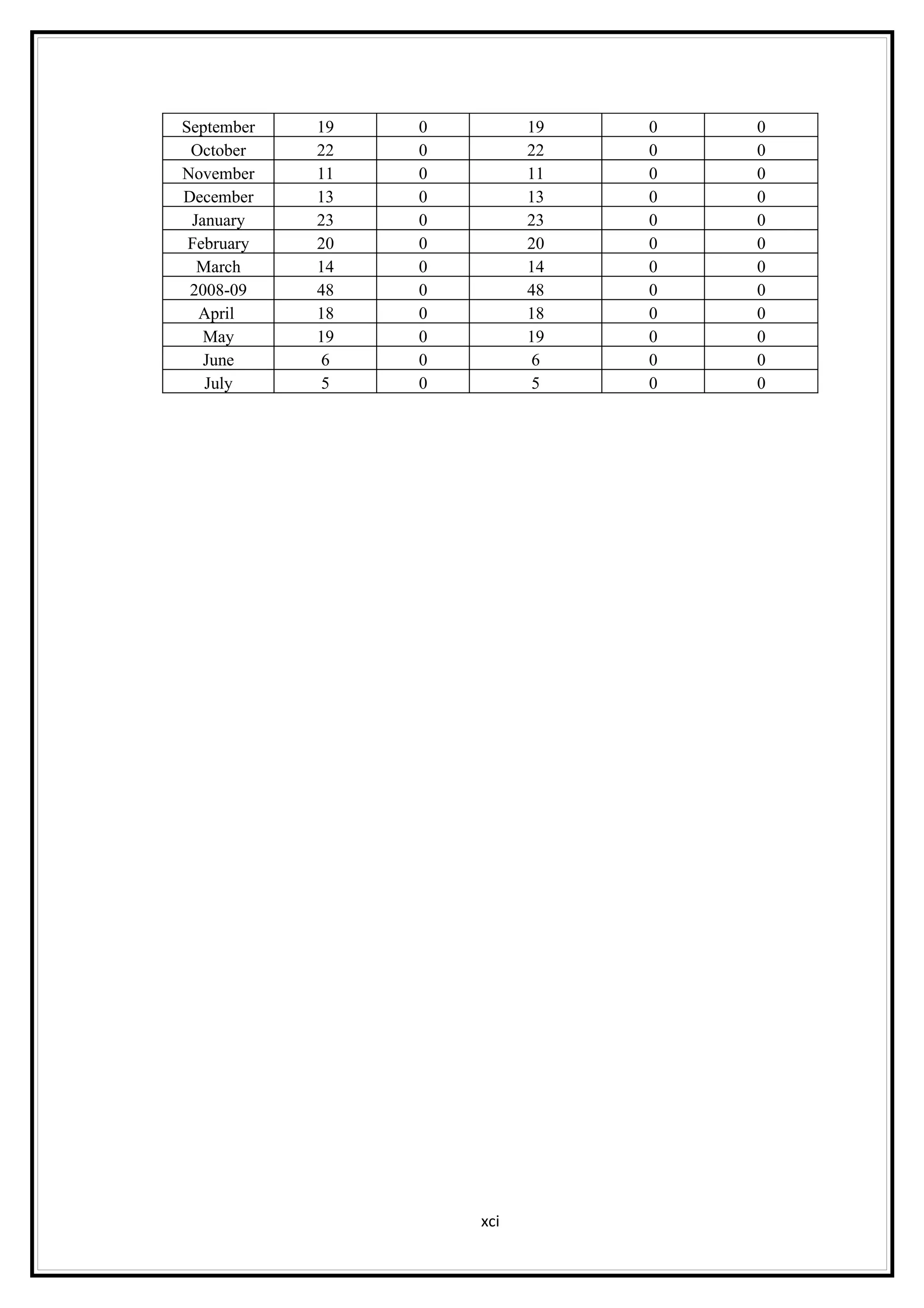
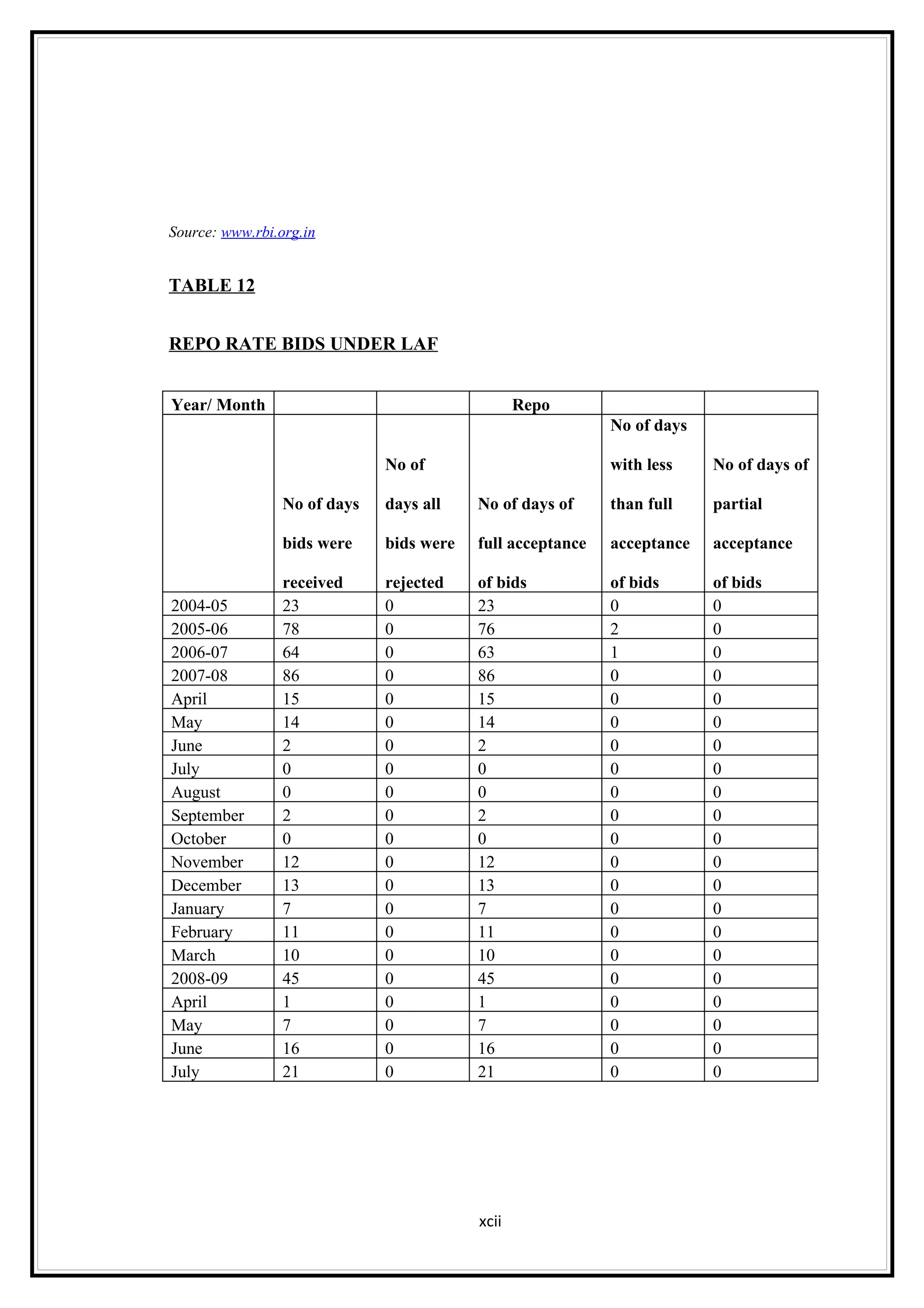
Interest rates play an important role in determining a country's liquidity position. Higher interest rates aim to decrease liquidity in the economy by increasing savings. Lower interest rates increase liquidity by making capital more accessible and encouraging borrowing. Theories of interest rate determination include the classical theory that real factors like savings and investment determine rates, and the Keynesian theory that interest rates are a monetary phenomenon influenced by the money supply. Different interest rates exist based on the maturity of financial instruments.